* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
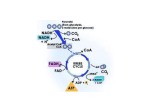
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
2004 BCOR 11 Exam 2 Name:_________________ Section: _______________ Please note that the chapters covered in this exam 2 (2004) are not the same chapters we are covering this year (2005). That means that you won't be getting more questions on cell membranes but will be getting questions on cell communication. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. According to the first law of thermodynamics, A. the universe loses energy because of friction. B. matter can be neither created nor destroyed. C. energy is neither created nor destroyed. D. all processes increase the entropy of the universe. E. systems rich in energy are intrinsically unstable. 2. Whenever energy is transformed, there is always an increase in the A. entropy of the system. B. enthalpy of the universe. C. entropy of the universe. D. free energy of the universe. E. free energy of the system. 3. Which of the following is the most randomized form of energy? A. thermal (heat) energy B. light energy C. electrical energy D. mechanical energy E. chemical potential energy 4. Why is ATP an important molecule in metabolism? A. Its phosphate bonds are easily formed and broken. B. Hydrolysis of its phosphate groups is endergonic. C. It energizes other molecules by transferring phosphate groups. D. Two of the above. E. All of the above. 5. How can one increase the rate of a chemical reaction? A. Increase the entropy of reactants. B. Increase the activation energy needed. C. Add a catalyst. D. Decrease the concentration of reactants. E. Cool the reactants. 6. A solution of starch at room temperature does not decompose rapidly to a sugar solution because A. the activation energy barrier cannot be surmounted in most of the starch molecules. B. the hydrolysis of starch to sugar is endergonic. C. the starch solution has less free energy than the sugar solution. D. starch hydrolysis is nonspontaneous. E. starch cannot be hydrolyzed in the presence of so much water. 7. All of the following are true of enzymes except A. Enzymes are essentially protein in their chemical compound. B. Enzyme function is dependent on the pH and temperature of the reaction environment. C. Enzyme function is dependent on the three-dimensional structure or conformation of the enzyme. D. Enzymes provide activation energy for the reaction they catalyze. E. Enzyme activity can be inhibited if their allosteric site is bound with a noncompetitive inhibitor. 8. How does an enzyme catalyze a reaction? A. by changing the equilibrium of a spontaneous reaction B. by lowering the energy of activation of a reaction C. by supplying the energy to speed up a reaction D. by lowering the G of a reaction E. by increasing the amount of free energy of a reaction 9. Consider the following: Succinic acid dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction of succinic acid to fumaric acid. The reaction is inhibited by malonic acid, which resembles succinic acid but cannot be catalyzed by succinic dehydrogenase. Increasing the ratio of succinic acid to malonic acid reduces the inhibitory effect of malonic acid. Which of the following is correct? A. Malonic acid is the product, and fumaric acid is a competitive inhibitor. B. Succinic acid dehydrogenase is the enzyme, and fumaric acid is the substrate. C. Fumaric acid is the product, and malonic acid is a noncompetitive inhibitor. D. Succinic acid dehydrogenase is the enzyme, and malonic acid is the substrate. E. Succinic acid is the substrate, and fumaric acid is the product. The following question is based on the reaction A + B ¬ C + D shown in Figure1 Figure 1 10. Which of the following best describes the reaction? A. G of zero, chemical equilibrium B. negative G, spontaneous C. positive G, exergonic D. positive G, nonspontaneous E. negative G, endergonic 11. Ions diffuse across membranes down their A. electrochemical gradients. B. concentration gradients. C. electrical gradients. D. chemical gradients. E. Both A and B are correct. 12. The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is directly involved in A. the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. B. glycolysis. C. accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain. D. the citric acid cycle. E. the phosphorylation of ADP. 13. All of the following substances are produced in a muscle cell under anaerobic conditions except A. NADH. B. pyruvate. C. ATP. D. acetyl CoA. E. lactate. 14. In addition to ATP, what are the end products of glycolysis? A. CO2 and ethyl alcohol B. H2O and ethyl alcohol C. NADH and pyruvate D. CO2 and NADH E. CO2 and H2O 15. All of the following are functions of the Krebs cycle except A. production of ATP. B. production of NADH. C. adding electrons and protons to oxygen to form water. D. production of FADH2. E. release of carbon dioxide. 16. The Krebs cycle produces which of the following molecules that then transfer energy to the electron transport system? A. FADH2 and NADH B. ATP and CO2 C. NADH, FADH2, and ATP D. NADH and ATP E. CO2 and FAD 17. A young relative of yours has never had much energy. He goes to a doctor for help and is sent to the hospital for some tests. There they discover his mitochondria can use only fatty acids and amino acids for respiration, and his cells produce more lactate than normal. Of the following, which is the best explanation of his condition? A. His mitochondria lack the transport protein that moves pyruvate across the outer mitochondrial membrane. B. His cells have a defective electron transport chain, so glucose goes to lactate instead of to acetyl CoA. C. His cells contain something that inhibits oxygen use in his mitochondria. D. His cells lack the enzyme in glycolysis that forms pyruvate. E. His cells cannot move NADH from glycolysis into the mitochondria. 18. In chemiosmotic phosphorylation, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP + Pi to ATP? A. energy released as electrons flow through the electron transport system B. No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic. C. energy released from substrate-level phosphorylation D. energy released from ATP synthase pumping hydrogen ions against their concentration gradient E. energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase 19. Which metabolic process is most closely associated with intracellular membranes? A. glycolysis B. ethanolic fermentation C. the Krebs cycle D. oxidative phosphorylation E. substrate-level phosphorylation 20. How many moles of ATP are produced from the complete oxidation of a mole of glucose in cellular respiration? A. 30 B. 15 C. 12 D. 38 E. 20 21. Phosphofructokinase is an important control enzyme. All of the following statements concerning this enzyme are true except: A. It is inhibited by ATP. B. It is a coordinator of the processes of glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. C. It is activated by AMP. D. It is activated by citrate. E. It is an allosteric enzyme. 22. When a red blood cell is placed in an isotonic solution, which of the following will occur? A. The cell will shrivel. B. The cell will swell and burst C. The cell will shrivel and then return to normal D. The cell will swell and then return to normal. E. Nothing 23. Active transport is important because it can move molecules A. from a high concentration to a lower concentration. B. from a low concentration to a high concentration. C. that resist osmosis across the membrane. D. with less ATP than might otherwise be used to move the molecules. E. by increasing their diffusion coefficient. 24. Osmosis moves water from a region of A. high concentration of dissolved dissolved material to a region of low concentration. B. low concentration of dissolved material to a region of high concentration. C. hypertonic solution to a region of hypotonic solution D. negative osmotic potential to a region of positive osmotic potential E. low concentration of water to a region of high concentration of water. 25. How does a competitive inhibitor inhibit binding of a substrate to an enzyme? A. It binds to the substrate. B. It binds to an area of the enzyme different than the active site. C. It lowers the activation energy. D. It increases the delta G of the reaction. E. It competes with the substrate for the active site. 26. When a molecule gains hydrogen atoms (not hydrogen ions), it becomes A. Reduced B. Oxidized C. Redoxed. D. dehydrogenated. E. Hydrolyzed. 27. The formation of ethanol from pyruvate is an example of A. an exergonic reaction B. providing an extra source of energy from glycolysis C. a fermentation process that takes place in the absence of oxygen. D. cellular respiration E. None of the above. 28. In plants, the final electron acceptor in the light reactions is A. NADP+ B. CO2 C. H2O D. O2 E. Rubisco 29. The mechanism by which electron transport is coupled to ATP production by means of a proton gradient is called A. chemiosmosis B. crassulacean acid metabolism C. fluorescence D. the C3 pathway E. the C4 pathway 30. The enzyme directly responsible for almost all carbon fixation on Earth is A. Rubisco B. PEP carboxylase C. ATP synthase D. Phophofructokinase E. Ligase 31. In C4 plants, C4 and C3 pathways occur at different _________, whereas in CAM plants, CAM and C3 pathways occur at different ___________. A. times of day; locations within the leaf B. seasons; locations C. locations; times of day D. locations; seasons E. times of day; seasons 32. What accumulates in the thylakoid space during the light reactions? A. glucose B. RuBP C. Rubisco D. hydrogen ions E. carbon dioxide 33. Within chloroplasts, the semi-liquid medium in which the Calvin cycle occurs is called A. stroma B. thylakoids C. grana D. photosystem E. matrix 34. Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis when A. the carbon is removed from carbon dioxide to form carbohydrates B. hydrogen from water is added to carbon dioxide to make carbohydrates C. water molecules are split to provide electrons for Photosystem II D. water molecules are split to provide electrons for Photosystem I E. when electron in the electron transport chain reach the final acceptor 35. In cyclic electron flow A. oxygen gas is released B. ATP is formed C. water donates electrons and protons D. NADPH and H+ form E. CO2 reacts with RuBP 36. Because bundle-sheath cells are relatively protected from atmospheric oxygen the level of _____________ is held to a minimum in C4 plants. A. glycolysis B. photosynthesis C. oxidative phosphorylation D. photorespiration E. decarboxilation of a four carbon organic acid 37. Some photosynthetic organisms contain chloroplasts that lack Photosystem II, yet are able to survive. The best way to detect the lack of Photosystem II in these organisms would be A. to determine if they have thylakoids in their chloroplasts B. to test for the release of O2 in the light C. to test for CO2 fixation in the dark D. to perform experiments that generate an action spectrum E. to test for the production of starch 38. In a plant cell, where is ATP synthase located? A. thylakoid membrane B. plasma membrane C. inner mitochondrial membrane D. a and c E. a, b, and c 39. In mitochondria, chemiosmosis translocates protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space, whereas in chloroplasts chemiosmosis translocates protons from A. the stroma to the chlorophyll B. the matrix to the stroma C. the stroma into the thylakoid compartment D. the intermembrane space to the matrix E. the light reactions to the Calvin cycle 40. The Calvin cycle requires all of the following molecules EXCEPT A. CO2 B. ATP C. RuBP D. glucose E. NADPH 41. CAM plants can keep stomata closed in daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they A. fix CO2 into organic acids during the night B. fix CO2 into sugars in the bundle-sheath cells C. fix CO2 into pyruvic acid in the mesophyll cells D. use the enzyme phosphofructokinase which out-competes Rubisco for CO2 E. use Photosystems I and II at night 42. In mechanism, photophosphorylation is most similar to A. substrate-level phosphorylation B. oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration C. the Calvin cycle D. carbon fixation E. reduction of NADP+ 43.The three substrates (normal reactants) for the enzyme RuBP carboxylase/oxidase (rubisco) are A.RuBP, ATP, and NADPH. B. CO2, O2, and RuBP. C. RuBP, CO2, and ATP. D.CO2, glucose, and RuBP. E. triose-P, glucose, and CO2. 44. Why are C4 plants able to photosynthesize with no apparent photorespiration? A. They conserve water more efficiently. B. They are adapted to cold, wet climates. C. They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO2. D. They do not participate in the Calvin cycle. E. They exclude oxygen from their tissues. 45. The color of light least effective in driving photosynthesis is A. red. B. orange. C. blue. D. yellow. E. green. 46.Which process in eukaryotic cells will normally proceed whether O2 is present or absent? A. electron transport B. glycolysis C. fermentation D. oxidative phosphorylation E. the Krebs cycle 47. During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence? A. food ¬ glycolysis ¬ Krebs cycle ¬ NADH ¬ ATP B. food ¬ NADH ¬ electron transport chain ¬ oxygen C. food ¬ Krebs cycle ¬ ATP¬ NAD+ D. glucose ¬ ATP¬ oxygen E. glucose ¬ ATP ¬ electron transport chain ¬ NADH 48.You have a friend who lost 15 pounds of fat on a diet. Where did the fat go (how was it lost)? A. Chemical energy was converted to heat and then released. B. It was released as CO2 and H2O. C. It was converted to ATP, which weighs much less than fat. D. It was converted to urine and eliminated from the body. E. It was broken down to amino acids and eliminated from the body. The questions below are based on the stages of glucose oxidation listed below. A. B. C. D. stage I: glycolysis stage II: oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA stage III: Krebs cycle stage IV: oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis) 49.Which one of the stages produces the most ATP when glucose is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water? D 50. Which one of the stages occurs in the cytosol of the cell? A 51. Carbon dioxide is released during which stage(s)? A. stages III and IV B. stage III only C. stages II, III, and IV D. stages II and III E. stages I, II, and III 52. When a plant cell is placed in distilled water it will: A. develop high amounts of internal pressure B. burst C. shrink D. plasmolyse E. stay the same