* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine and Exocrine
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
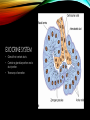
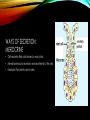
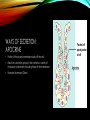
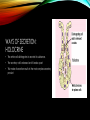
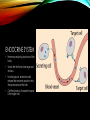
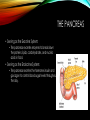
ENDOCRINE AND EXOCRINE A lesson on both of the systems and their functions LESSON PLAN 1. Walkthrough PowerPoint. 2. Show and explain model. 3. Answer any questions. 4. Hand out and work on worksheet. EXOCRINE SYSTEM • Glands that contain ducts. • Contain a glandular portion and a duct portion. • Three ways of secretion. WAYS OF SECRETION: MEROCRINE • Cells excrete their substances by exocytosis. • Membrane-bound secretory vesicles internal to the cell. • Example: Pancreatic acinar cells. WAYS OF SECRETION: APOCRINE • Portion of the plasma membrane buds off the cell • Results in a secretory product that contains a variety of molecular components including those of the membrane. • Example: Mammary Gland WAYS OF SECRETION: HOLOCRINE • The entire cell disintegrates to excrete its substance. • The secretory cell is released and it breaks apart. • This mode of secretion results in the most complex secretory product. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Hormone producing structures of the body. • Some, like the thyroid are large and obvious. • In lacking ducts, endocrine cells release their secretory products into the spaces around the cells. • Cell that product is headed towards is the target cell. THE PANCREAS • Serving as the Exocrine System: • The pancreas excretes enzymes to break down the proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids in food. • Serving as the Endocrine System: • The pancreas secretes the hormones insulin and glucagon to control blood sugar levels throughout the day. DISEASES INCLUDED IN MAJOR GLANDS/ORGANS • Pancreatic Cancer • A malignant neoplasm originating from transformed cells arising in tissues forming the pancreas. • Endocrine gland hyposecretion • Hyposecretion of hormones • Endocrine gland hypersecretion • Over production of hormones • Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) • Caused by a degenerative disease of the pancreas. Does Anyone Have Any Questions? CREATED BY: Brooke Mentel and Nic Peña BIBLIOGRAPHY • "Pancreatic Diseases: MedlinePlus." U.S National Library of Medicine. U.S. National Library of Medicine, n.d. Web. 10 Mar. 2014. • "Endocrine Glands: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia." U.S National Library of Medicine. U.S. National Library of Medicine, n.d. Web. 12 Mar. 2014. • "Exocrine." Exocrine. N.p., n.d. Web. 12 Mar. 2014. • "Endocrinology." UCSF Medical Center. N.p., n.d. Web. 12 Mar. 2014.