* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Unit Test Review
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sympatric speciation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
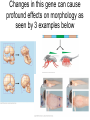
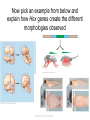
BLAST Lab Discussion • Was your hypothesis of phylogeny tree placement correct? • How were the genes that you blasted useful in determining where on the tree the mystery fossil went? • The fossil is actually called Sinosauropteryx • Sinosauropteryx is a compsognathid (small and carnivorous) dinosaur. Described in 1996, it was the first dinosaur taxon outside of Avialae to be found with evidence of feathers. It was covered with a coat of very simple filament-like feathers. Evolution Unit Test Review AP Bio Hardy-Weinberg • There are 150 deer in a population. 80 are DD, 50 are Dd, 20 are dd. Find p and q and the frequencies of each allele. • 80x2=160 • 50x1=50 • 20x2=40 • 160+50=210, 40+50=90 • 210/150x2=.7 (p), .3 (q) • .72 + 2(.7)(.3) + .32=1 • DD=.49, Dd=.42, dd=.09 Name the hypothesis shown below and answer the questions What kind of cell is this? Prokaryote • Endosymbiosis What evidence do we have that mitochondria and plastids were once their own independent free-living cells? They have their own membranes, DNA, ribosomes, and can replicate What is being engulfed here? Mitochondria What kind of cells do we have now? Eukaryotes What is engulfed here? Plastid Name 2 types of evidence that can be used to create a phylogeny tree • Homologous structures, morphology, DNA/genes, fossil record What caused the sudden rise of eukaryotes from prokaryotes? Hint: banded iron formations • Oxygen Revolution Oxygen released from these rocks in the ocean, and evaporated into the atmosphere causing a huge increase in oxygen Select whether the following are examples of sympatric or allopatric speciation • Polyploidy • Emergence of a mountain range • Population switches to new food source or resource • Evaporation of large lake causes several small lakes to form • Sympatric • Allopatric • Sympatric • Allopatric Georges Cuvier supported this idea based on his observations in the fossil record that major floods, etc. created the boundaries between each strata • Catastrophism • Hutton and Lyell supported uniformitarianism Which of the following correctly describes the evolutionary beliefs of Lamarck? • • • • • • A. Use and disuse B. Inheritance of acquired characteristics C. Natural and artificial selection D. Homologous structures E. Both A and B are correct Answer: E What is an example of an acquired characteristic? • A weightlifter’s son will be born with more muscle mass What is the process by which species are modified by humans? For example, selective breeding for milk or meat. • Artificial selection Name 3 pieces of evidence for evolution • Direct observations, fossil record, homology, biogeography • Also vestigial organs, embryology Give an example for each of the following: homologous structure, embryonic homology, vestigial organ, analogous structure • Homologous- anatomical signs of evolution (forelimbs of bats and whales, both had ancestor that used for walking) (divergent evolution!) • Embryonic- vertebrates have tail and pharyngeal pouches • Vestigial- appendix, tailbone, wisdom teeth • Analogous- similar problem=similar solution, torpedo shape of penguin, dolphin, and shark (convergent evolution!) What are the 5 conditions for Hardy-Weinberg? • • • • • No mutations Random mating No natural selection Population size is large No gene flow (immigration/emigration) Name 2 or 3 things that can alter allele frequencies in a population. • Natural selection, genetic drift (founder effect and bottleneck effect), gene flow, mutations, geographic/reproductive isolation Name 3 examples of reproductive isolation. • Pre and postzygotic factors, habitat/behavioral/temporal/mechanical/ gametic isolation, hybrid breakdown Changes in this gene can cause profound effects on morphology as seen by 3 examples below Now pick an example from below and explain how Hox genes create the different morphologies observed What type of evolution (convergent or divergent) occurs when 2 organisms developed similarities as they adapted to similar environmental challenges • Convergent evolution (streamlined body of tuna and dolphin) Draw a phylogeny tree using the characters below, don’t forget sister taxa if they occur Bacteria Horseshoe Salamander Ape Crab Humans Eukaryotic Cells 0 1 1 1 1 Exoskeleton 0 1 0 0 0 Backbone 0 0 1 1 1 Hair 0 0 0 1 1 Example Tree Ape Salamander Horseshoe crab Backbone Exoskeleton Eukaryotic cells Bacteria Humans Hair To make a phylogeny tree well supported by evidence, what are a few things that should be used to construct them? • Answer: morphology (weak), DNA, amino acids, homology, fossil record, metabolic pathways, chemical content (food/diet), behavioral