* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. dia - immunology.unideb.hu
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
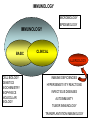
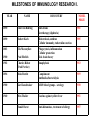
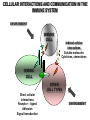
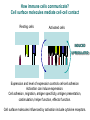
IMMUNOLOGY BASIC IMMUNOLOGY IMMUNE PATHOLOGY Árpád Lányi Department of Immunology LSB 2.201 [email protected] IMMUNOLOGY COURSE 26 LECTURES 11 SZEMINARS/PRACTICALS 2 lectures/week Weeks 1-13 1 class/week Weeks 1-11 BASIC IMMUNOLOGY and IMMUNOPATHOLOGY DEMO 1. BASIC + SEMINARS 2. PATHOLOGY + PRACTICALS BOOKS Peter Parham: The immune system (Garland Science) 3rd Edition 2009 Rosen F., Geha R.: Case Studies in Immunology (Garland Publishing) 5th Edition 2009 Abbas A.K., Lichtman A.H., Pillai S.: Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Elsevier,Saunders Company) 7th Edition 2010 www.immunology.unideb.hu Username: student PASSWORD: download IMMUNOLOGY MICROBIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY IMMUNOLOGY BASIC CLINICAL ALLERGOLOGY CELL BIOLOGY GENETICS BIOCHEMISTRY BIOPHYSICS MOLECULAR BIOLOGY IMMUNE DEFICIENCIES HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INFECTIOUS DISEASES AUTOIMMUNITY TUMOR IMMUNOLOGY TRANSPLANTATION IMMUNOLOGY Immunitas – exemption from service or duty Immunological memory Thucydides, historian, Athen 430 B:C. plague „yet it was with those who recovered from the disease that the sick and the dying found most compassion……. No fear for themselves; as no man was never attacked twice – never at least fatally” FIRST VACCINATION Edward Jenner 1749 – 1823 Immunity (protection) can be induced (cowpox - smallpox) In 1979, after 3 years in which no case of smallpox was recorded, the World Health Organization announced that the virus had been eradicated. Louis Pasteur 1880 rabies, 1887 Pastuer Institute Immunization with attenuated pathogens Emil Adolf von Behring 1890 Antitoxins, serum therapy 1. Many disease occurs only once (natural protection) 2. Some diseases can be prevented by vaccination 3. The blood contains anti-bacterial activity (anti-toxins, serum therapy) 1884 Ilya Mechnikoff Phagocytosis Intestinal bacteria, yoghurt Paul Ehrlich 1900 Side chain theory Cell protoplasm contains special side chains to which the toxin binds. If the organism survives the effects of the toxin, the blocked side-chains are replaced by new ones. If there is a surplus of side chains they can also be released into the blood as antibodies.. MILESTONES OF IMMUNOLOGY RESEARCH I. YEAR NAME DISCOVERY NOBEL PRIZE 1890 Emil von Behring Anti-toxins Serotherapy (diphteria) 1901 1890 Robert Koch Tuberculosis, anthrax Cellular immunity, tuberculin reaction 1905 1883 Elie Mecsnyikov 1908 1900 Paul Ehrlich Phagocytosis, inflammation Cellular protection Side chain theory 1902 Charles Richet (Paul Portier) Anaphylaxis 1913 1894 Jules Bordet Complement Antibodies/bacteriolysis 1919 1900 Karl Landsteiner A/B/0 blood groups - serology 1930 1940 Max Theiler Vaccine against yellow fever 1951 Daniel Bovet Anti-histamines, treatment of allergy 1957 MILE STONES OF IMMUNOLOGY RESEARCH II. 1944 Peter Medawar Macfarlane Burnet Acquired tolerance Clonal selection theory 1960 1959 Rodney Porter Gerald Edelman Antibody structure 1972 Rosalyn Yalow Roger Guillemin Andrew Schally Radioimmunoassay Peptide hormon production in brain 1977 1958 Baruj Benacerraf Jean Dausset, George Snell Histocompatibility antigens 1980 1975 George Köhler Cesar Milstein Niels Jerne Monoclonal antibody 1984 Susumi Tonegawa Gene rearrangement 1987 E. Donnall Thomas Joseph Murray Transplantation immunology 1990 Rolf Zinkernagel, Peter Doherty MHC restriction 1996 1979 1974 Network theory MILE STONES OF IMMUNOLOGY RESEARCH III. Avram Hershko Protein degradation, antigen presentation 2004 Bruce Beutler, Jules Hoffmann, Ralph Steinman Activation of innate immunity 2011 GENERAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM GENERAL FEATURES OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1. STRUCTURE – various cell types, diffuse Cell communication Th Partners Mode macrophage – direct B pathogen – soluble factors extracellular matrix macrophage Cell – to – cell communication 2. ACTION – dynamic Homeostasis – environmental factors Adhesion Homing Migration neutrophil Replacement vs death Activation vs differentiation Endothelial cell 3. FUNCTION Inflammed tissue 4. SPECIAL FEATURES Recognition – self - antigen - danger Defense against pathogens Recognize, prevent spread, clear from the body Signal processing and transduction Signal storage – learning, memory Protection of self SIMILARITIES TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CELLULAR INTERACTIONS AND COMMUNICATION IN THE IMMUNE SYSTEM ENVIRONMENT IMMUNE CELL Indirect cellular interactions Soluble molecules Cytokines, chemokines IMMUNE CELL OTHER CELL TYPES Direct cellular interactions Receptor – ligand Adhesion Signal transduction ENVIRONMENT How immune cells communicate? Soluble mediators Infection CYTOKINES & CHEMOKINES Phagocyte activation INFLAMMATION Diverse collection of soluble proteins made by cells that affect the behaviour of other cells. The balance & level of cytokines and chemokines secreted affects the outcome of the response Early events involve endothelial cells and result in the accumulation of fluid, plasma proteins & leucocytes. Later events involve the activation and maturation of lymphocytes and granulocytes. How immune cells communicate? Cell-cell contact Peripheral lymphoid tissues trap antigen-containing phagocytic cells and concentrate cells together to promote cell-cell contact. Cell-cell contact occurs at many stages of immune responses. Killing CTL Target cell T Y Antigen presentation B T Ab production Accessory cell activation How immune cells communicate? Cell surface molecules mediate cell-cell contact Resting cells Activated cells INDUCED UPREGULATED Expression and level of expression controls cell-cell adhesion Activation can induce expression. Cell adhesion, migration, antigen specificity, antigen presentation, costimulation, helper function, effector function. Cell surface molecules influenced by activation include cytokine receptors.