* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Procedure Notes
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
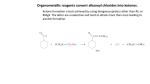
Chemistry 2412L Esterification pre-lab lecture Properties of Esters • The purpose of this lab is to study the chemical properties of esters • Esters are derivatives of carboxylic acids which are found in many natural sources. Esters tend to have a pleasant odor associated with them and can be found as a key component of the odor and taste of many fruits and flowers. Procedure Notes • You will create eight different known esters and two unknown esters. You will identify the unknowns by comparing to the eight known compounds. • The eight esters will be created from the combination of different alcohols and carboxylic acids. • Each ester will be reacted in a test tube and heated to a steady temperature of 40-60 ºC for 15 minutes. Procedure Notes • The alcohols are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Isobutyl alcohol Amyl alcohol 1-Octanol 1-Propanol Methanol Ethanol • The carboxylic acids are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Formic acid Acetic acid Propanoic acid Salicylic acid Cinnamic acid Procedure Notes • Fischer esterification is a reaction that involves refluxing an alcohol and a carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst. • The process is in equilibrium which means that once equilibrium is reached there could be a large amount of the starting materials remaining. This could result in a poor yield of the desired ester. Adding additional products could shift the reaction to the right, or adding additional water could lead to a shift to the left. O O + + C R OH R'OH H + C R OR' H2O Procedure Notes • Esters are more commonly used as flavoring rather than scents that are added to the body due to the fact that the reaction is in equilibrium and esters are not very stable. The addition of water and heat from perspiration can cause the reaction to favor the reactants. Carboxylic acids tend to be associated with a foul smelling odor that one would not want to wear on their body. • Esters also may have biological properties. For example isoamyl acetate, which smells like bananas, is also an alarm pheromone released by bees. This pheromone will attract bees to any person which is wearing this ester on their person. Procedure Notes • A small amount of acid is needed to act as a catalyst for the reaction. • Since a catalyst is never used up in a reaction, only a small amount of catalyst is needed. • Using heat is also a way to accelerate the reaction. Procedure Notes • The esterification process is a slow process that could take hours to complete. • If not given time to finish the reaction it is more likely that the carboxylic acid will still be left in the reaction and would thus have a sour smell. • Producing esters on a small scale in a test tube, such as the experiment in this lab, will not produce a lot of the ester. • The smell of the ester can be masked by the smell of the carboxylic acid. Safety Notes • Concentrated acids such as H2SO4 can cause burns. Wash immediately with water if spilled on the skin. • As always, be careful with the hot plates!!!! • Wear Safety Glasses!!!! • Perform experiment in the hood.