* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHEMISTRY 3
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Acid strength wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
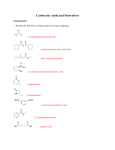
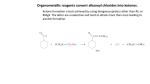
CHEMISTRY 3.5 WORKSHEET NINE Name: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Carboxylic acids and their derivatives #2 1. After making an ester by heating a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, water is added to the mixture and the ester separates out as an oily layer that floats to the top and produces a strong fruity odour. Comment on the physical properties of esters that these observations suggest. 2. Lipids are triglycerides and their structure consists of a molecule of glycerol bonded through three ester linkages to three “fatty” acids. 3. (a) Write the condensed structural formula for glycerol. (b) What is the systematic name for glycerol? (c) Draw the molecular structure of the lipid produced from glycerol and three molecules of stearic acid (C17H35COOH). (d) Explain why an esterification reaction can be also described as a condensation reaction. Because esters are made by forcing the equilibrium reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to the right, it should also be possible to split an ester back into its constituents by forcing the same equilibrium to shift itself in the reverse direction, ie to the left. (a) Write the equilibrium reaction between methanoic acid and ethanol that produces the ester, ethylmethanoate. (b) If the forward reaction is called condensation, explain why the reverse reaction is called hydrolysis. (c) Concentrated sulfuric acid was needed to force the equilibrium to the right and produce the ester. Name the chemical that is commonly used to hydrolyse esters by moving the equilibrium to the left. (d) Explain with the aid of an equation, how the chemical you have named in (c) acts to shift the equilibrium in the desired direction. 4. Amides can be produced from the reaction of esters with ammonia but the reaction is slow. What is the preferred method of production of amides? 5. Name the following substances. (a) CH3CH2CONH2 (b) HCONH2 6. Amides are crystalline solids at room temperature and the lower members are soluble in water. Explain these properties in terms of the bonding involved. 7. Write an equation for the preferred method of production of ethanamide. 8. Like esters and acyl chlorides, amides can also undergo hydrolysis and revert back to the carboxylic acid that they were derived from. (a) Amides can be hydrolysed by heating with HCl. Write an equation for the reaction of propanamide with HCl. (b) Amides can also be hydrolysed by heating with NaOH. Write an equation for the reaction of propanamide with NaOH.