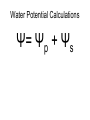* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology Discussion Notes
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
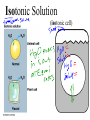
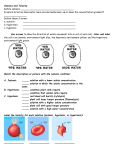
AP Biology Discussion Notes Wednesday 10/12/2016 Goals for the Day 1. Be able to describe how & why things are transported in/out of the cell 2. Be able to identify, describe, and predict the changes to plant & animals cells in different osmotic solutions. 3. Be able to describe and calculate water potential Hand in Assignments! 10/12 Question of the Day Identify the 2 things that set osmosis apart from diffusion and what kind of transport it is considered? The “tonics” Hypotonic Solution (Hypertonic cell) Hypotonic Solution (Hypertonic cell) Animal cell will Lyse or Break due to becoming swollen with water. Hypotonic Solution (Hypertonic cell) Turgor Pressure - the pressure a cell membrane exerts of a cell wall. – the cell is said to be Turgid. Isotonic Solution (isotonic cell) Isotonic Solution (isotonic cell) Animal cells will be normal, while plant cells will become Flaccid. A plant wants Turgid cells – need water for support! Hypertonic Solution (Hypotonic cell) Hypertonic Solution (Hypotonic cell) Animal cells will shrivel in a Hypertonic solution. Hypertonic Solution (Hypotonic cell) Plasmolysis- the cell membrane breaking away from cell wall – cell has been plasmolyzed. Water Potential Calculations Ψ= Ψp + Ψs Water Potential Ψ= Ψp + Ψs Water “potential” – potential refers to water’s potential energy, or water’s ability/capacity to do work. Water Potential Ψ= Ψp + Ψs Water potential – physical property that predicts which direction water will flow. Includes the effects of solute conc. and physical pressure. Water Potential Ψ= Ψp + Ψs Usually measured in MPa. 1MPa = 10x atmospheric pressure, so typical plant cell might have a pressure of .5MPa Pure water in an open container under standard conditions has 0MPa Water Potential Ψ= Ψp + Ψs Solute Potential (Ψs)– directly proportional to molarity(_________) of the solution Ψs of pure water is by definition 0 Water Potential Ψ= Ψp + Ψs Solute Potential (Ψs)– solutes bind to water molecules, which reduces the capacity of water to move and do work (reduces ) As Molarity (amount of solute) increases the Ψs becomes more negative Water Potential Ψ= Ψp + Ψs Pressure Potential (Ψp)– physical pressure of a solution so it can be positive or negative relative to the atmosphere Water in living cells is under positive pressure Calculating Ψ Ψ= Ψp + Ψs 1. Add pressure & solute to find Ψ inside & outside the cell. 2. Determine where Ψ is high and where it is low. 3. Draw an arrow from high Ψ to low Ψ. 4. Determine what type of solution the cell is in and what the cell is relative to the solution. 5. Use the Direction of Water Movement to Identify the type of Solution (and cell). Questions? Reading & Notes Assignment 1. Read pages 58-66 • • • • Take notes on main ideas Define vocab words Draw & Describe the experiment in fig 4.2 Add functional groups pg64-65 to notes • Be able to recognize functional groups • Draw Cholesterol (pg 77), Estrodial & Testosterone (pg 63) Compare the 3 chemicals in terms of differences and similarities in structure/function *Remember cholesterol is a precursor to making steroids, including sex hormones.