* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 26. Mixed cranial nervest
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Craniometry wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
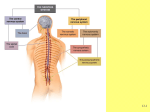
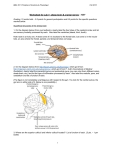
Mixed cranial nerves • Cranial nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. • Carry sensory or motor information or a combination and function in parasympathetic nervous system. • Cranial nerves I, II and VIII are purely sensory. • Cranial nerves III, IV, VI, XI and XII are motor (although also function balance). Cranial Nerves • Indicated by Roman numerals I-XII from anterior to posterior • May have one or more of 3 functions – Sensory (special or general) – Motor (skeletal muscles) – Parasympathetic (regulation of glands, smooth muscles, cardiac muscle) • Balance – Positional information of body Cranial Nerves • • • • • • • Olfactory (I) Optic (II) Oculomotor (III) Trochlear (IV) Trigeminal (V) Abducens (VI) Facial (VII) • Vestibulocochlear (VIII) – Also known as auditory • Glossopharyngeal (IX) • Vagus (X) • Accessory (XI) – Also known as spinal accessory • Hypoglossal (XII) Nervous System II: Cranial Nerves Cranial nerves Cranial Nerves • Trochlear (IV) – Visual tracking of eye • Trigeminal (V) – Sensory (face, nasal cavity, cheeks, lips, skin of mandible) –Motor (muscles of mastication, anterior belly of digastric, mylohyoid) • Abducens (VI) – Motor (1 eye muscle) Cranial Nerve V Trigeminal • Sensory from face, cornea, mouth, nose, temporomandibular joint • Motor to muscles of mastication V Trigeminal Nerve • Sensory information from the face and body is processed by parallel pathways in the central nervous system. Cranial nerves V: Trigeminal (3 nerves in 1!) • V1. Ophthalmic – Exits with eye muscle group (superior orbital fissure, through orbit to superior orbital notch/foramina) – Sensory to forehead, nasal cavity • V2. Maxillary – Exits foramen rotundum through wall of maxillary sinus to inferior orbital foramina) – Sensory to cheek, upper lip, teeth, nasal cavity • V3. Mandibular – – – – Exits foramen ovale to mandibular foramen to mental foramen Motor to jaw muscles--Masseter, temporalis, pterygoids, digastric Sensory to chin Sensory to tongue Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves CN VI: ABDUCENS AND CN VII: FACIAL • Cranial Nerve VI • Function: Eye movements • Clinical test: lateral eye movement • Effects of damage: inability to rotate eye laterally; at rest – eye rotates medially because of action of antagonistic muscles • Cranial Nerve VII • Function: facial expression; sense of taste • Clinical test: motor functions – close eyes, smile, whistle, frown, raise eyebrows; taste • Effects of damage: inability to control facial muscles; distorted sense of taste • Facial (VII) Cranial Nerves – Sensory (taste) – Motor (facial muscles, posterior belly of digastric) – Parasympathetic (salivary glands, glands of nasal cavity) • Vestibulocochlear (VIII) – Sensory (hearing and balance) • Glossopharyngeal (IX) – Sensory (taste, back of mouth, tonsils, middle ear) – Motor (1 muscle of pharynx) – Parasympathetic (salivary gland, glands of tongue) Cranial Nerve VII Facial • Sensory from anterior 2/3 of tongue • Motor to muscles of facial expression • Parasympathetic to salivary and lacrimal glands • Injury causes facial droop, dry eyes, dry mouth VII Facial Nerve • Supplies the muscles of facial expression VII: Facial Nerve (exits cranial cavity with VIII--internal auditory meatus) • Facial muscles (five branches fan out over face from stylomastoid foramen) – – – – – Temporal Zygomatic Buccal Mandibular Cervical • “chorda tympani” (crosses interior ear drum to join V3 ) – Taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue – Submandibular, sublingual salivary glands • Lacrimal glands Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerve IX Glossopharyngeal • Sensory posterior 1/3 of tongue, auditory tube, pharynx • Parasympathetic to parotid gland Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves IX Glossopharyngeal • Innervates the muscle that allows you to swallow CN IX: GLOSSOPHARANGEAL AND CN X: VAGUS • Cranial Nerve IX • Function: swallowing, salivation, gagging; touch, pressure, taste, and pain sensations from tongue, pharynx, and outer ear • Clinical tests: gag reflex, swallowing, and coughing • Effects of damage: difficulty swallowing • Cranial Nerve X • Function: swallowing; taste; speech; respiratory, CV, and GI regulation; sensations of hunger, fullness, and intestinal discomfort • Clinical tests: test with cranial nerve IX • Effects of damage: hoarseness or loss of voice; impaired swallowing and GI motility Cranial Nerve X Vagus • Sensory larynx and pharynx • Motor to larynx and pharynx • Parasympathetic to chest and abdomen • Vagus (X) Cranial Nerves – Sensory (taste, back of mouth, larynx, thoracic and abdominal organs) – Motor (muscles of larynx, 1 muscle of tongue) – Parasympathetic (thoracic and abdominal organs) • Accessory (XI) – Motor (sternocleidomastoid, trapezius) • Hypoglossal (XII) – Motor (tongue and throat muscles) X Vagus • The vagus nerve is the longest of the cranial nerve. Its name is derived from Latin meaning "wandering". • The vagus nerve helps to regulate the heart beat, control muscle movement, keep a person breathing, and to transmit a variety of chemicals through the body Human Anatomy, Frolich, Head/Neck IV: Cranial Nerves