* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Compare and Contrast table for Photosynthesis and Cellular
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
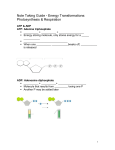
NAME______________________________________________________________DATE________ TEST REVIEW for Unit 3 (Idea 2 and 4, SB1b, SB3a) Chapter 8 Review 1. Define the following terms: metabolism, catabolic, anabolic, entropy, endergonic, exergonic, free energy, enthalpy, reactants, products, hydrolysis, ATP, ADP, phosphorylation, activation energy, enzyme-substrate complex, active site, denature, cofactors, co-enzymes, competitive inhibitors, noncompetitive/allosteric inhibitors 2. What is ΔG? What does it mean if it is negative? What does it mean if it is positive? 3. Compare and contrast exergonic and endergonic. 4. Explain how different environmental conditions effect enzyme productivity? 5. What are characteristics of enzymes? 6. Explain the relationship between ATP synthesis and degradation and endergonic and exergonic reactions. 7. Write the formula for Gibbs free energy and understand how variations in the equation affect the value of ΔG. Fill in the Blanks 1.) The totality of an organism’s chemical processes. ________________________ 2.) Pathways that require energy to combine molecules together. ________________ 3.) The term for the measure of randomness or disorder. _______________________ 4.) Inhibitors that decrease an enzyme’s activity by binding to the active site. _________________. 5.) Organic molecules that bind to enzymes and are necessary for their functioning. __________________ 6.) Inorganic molecules that bind to enzymes and are necessary for their functioning. ____________ 7.) The type of pathway body builders are interested in maximizing. ________________ 8.) The free energy of a non-spontaneous reaction. ____________________ 9.) Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. _______________________________________ 10.) A state of balance within a system. ______________________________ 11.) The ΔG of an exergonic reaction. _______________________. 12.) Adding a phosphate to a molecule. _________________________. Chapter 9 and 10. Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration What kind of organisms preform each process? What is the BALANCED equation? Underline the reactants and circle the products. When will each process occur in a cell/organism? What organelle(s) does each process take place in? Why do organisms use each process? What are the processes or reactions involved? Draw the picture of ADP and ATP. Explain why ATP has more energy than ADP as well as how it is cycled through the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Photosynthesis Review 1. Define the following vocabulary terms: autotroph, heterotroph, producer, chloroplast, grana, chemical equation, reactants, products, ATP, ADP, photosynthesis, chlorophyll, thylakoid, stroma, light dependent reaction, light independent reaction, stomata, mesophyll, photosystem I and photosystem II 2. Write the complete balanced photosynthesis equation. 3. Explain what happens in the light dependent reaction? Where is it located? What are the reactants and the products? 4. Explain what happens in the light independent reaction? Where is it located? What are the reactants and the products? 5. Describe the general steps in photosystem II and photosystem I. 6. What is another name for the light independent reaction? 7. Explain the difference between ADP and ATP? Which energy molecule provides more energy? 8. Name the pigment molecule absorbs the sunlight for the light dependent reaction? 9. Describe how light is absorbed at different wavelengths and why most plants are green. 10.Compare and contrast C3, C4 and CAM plants. 11.Make sure you have an understanding of the photosynthesis lab. Cellular Respiration Review 1. Define the following vocabulary terms: glucose, ATP, glycolysis, citric acid cycle, electron transport chain, anaerobic, aerobic, fermentation, lactic acid fermentation, mitochondria, aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration, FAD+/FADH2, NAD+/NADH, chemiosmosis, acetyl CoA, pyruvate, oxidative phosphorylation, substrate phosphorylation, proton gradient, phosphofructokinase 2. Write the balanced equation for cellular respiration. What reactants are oxidized? What reactants are reduced? 3. What are the reactants and products of glycolysis, citric acid cycle and ETC/chemiosmosis? 4. Why is cellular respiration considered exergonic? 5. Where do glycolysis, citric acid cycle and ETC/chemiosmosis occur in prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 6. Explain the process of aerobic respiration. Be sure you write what is required and produced and where it happens in a cell. 7. Explain the process of anaerobic respiration. Be sure you write what is required and produced and where it happens in a cell. 8. Describe how ATP synthase makes ATP from ADP. 9. What is the evolutionary significance of glycolysis? 10. How do allosteric enzymes inhibit cellular respiration? Give an example. Does it require oxygen? Where does it occur? Reactants Products Fermentation Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle Oxidative phosphorylation ETC and Chemiosmosis Using the following diagrams: describe and add illustrations to show the relationship or cycle between photosynthesis and cellular respiration.