* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Darwin VS Lamarck
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
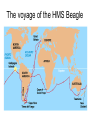
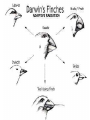
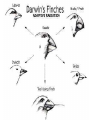
Fri 2/28 • Test-Chp.12 today Pg.65-Title page • Title page for Chp.14,15 and 16. – Title for all 3 chapters – 3 pictures total – 3 key words total – 3 colors Mon 3/3 • Reminder: Chp.12 Test Retakes before or after school until FRIDAY!!! • Describe evidence for the scientific theories of the origins of life. In: pg.66 Where do living things come from? Where do living things come from? • Spontaneous generation= living things come from nonliving things • Biogenesis= living things come from living things Pg.67- Origins of Life Chart Scientists Redi Experiment Picture (Pg.279) Spallanzani (pg. 280) Pasteur (pg. 281) Miller-Urey (pg. 285) Fox (pg.286) Redi 1626-1697 • Wanted to see if flies came from rotting meat or other flies. Spallanzani 1729-1799 • Concluded that boiled broth became contaminated with microorganisms from the air. • Opponents said that air contained a “vital force” that microorganisms needed to live. Pasteur 1822-1895 Paris Academy of Science offered a prize to anyone who could settle the spontaneous generation vs. biogenesis debate. • Used a curved neck flask that allowed air inside the flask but prevented microorganisms from entering. • Broth was clear for a year, when neck was broken off broth became cloudy with microorganisms within a day. • Pasteur disproved spontaneous generation. Miller-Urey 1953 • Created environment similar to ancient Earth (water, methane, ammonia, H2) and simulated a lightning strike. • Found that organic compounds were formed. Fox 1912-1998 Took the simple compounds from Miller-Urey and found that in acidic environments they would form simple, cell-like structures capable of growth, reproduction and simple metabolism. Pg.67 - Analysis Questions 1. How is biogenesis different from spontaneous generation? 2. What did Redi’s experiment prove? 3. What hypothesis was Spallanzani testing? 4. Who disproved the idea of spontaneous generation? 5. How was Pasteur’s experimental setup different from Spallanzani’s? 6. What was Miller-Urey’s experiment modeling? 7. How does Fox’s experiment relate to Miller-Urey’s experiment? 8. Based on these experiments, what conclusions do modern scientist draw about the origins of life? Homework • Finish Diagrams and analysis questions Out - pg.66 1. Do you think there is enough evidence to prove where life came from? 2. Why? Tues 3/4 • CCSD NHPE Testing Day Wed 3/5 • Reminder: Chp.12 Test Retakes before or after school until FRIDAY!!! • Provide examples of geological and biological evidence supporting evolution. In: pg.68 1. What forms of life have existed in the past but no longer exist today? Give at least 2 examples. 2. What happened to these organisms? Pg. 69 – Relative Dating Fossil Lab Glue in as flip Geologic history movie clip (50s-2:56) Use movie clip to answer #1 complete relative dating activity & data table Complete analysis questions on the back Out – pg. 68 1. In your daily life, are there events that tell you approximate times, even when you cannot see a clock? 2. What are they? Thur 3/6 • Reminder: Chp.12 Test Retakes before or after school until FRIDAY!!! • Provide examples of geological and biological evidence supporting evolution. In: Pg. 70 Anticipation Guide 1. T or F All traits have variation because they all have at least 2 alleles. 2. T or F Helpful variations become more common in a population because individuals that have them survive and reproduce. 3. T or F Traits an organisms gets during its lifetime (like big muscles on a weightlifter) can be passed on to offspring. Pg.71 Cornell notes Chp.15: Theory of Evolution What is Evolution? • Populations, not individuals, evolve. • Evolution occurs as a population’s genes and their frequencies change over time. What is Evolution? • Theory of Evolution= Development of new species from preexisting species over time. • Modern definition: – Evolution= heritable change in the characteristics of a population from generation to generation. Lamarck’s Ideas • Use and Disuse= The more an organism uses a part of its body, the more that body part develops. • Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics= Physical traits an organism gets during its lifetime can be passed on to its offspring. Who was Charles Darwin? • 19th century British scientist. • Traveled as a naturalist and collected various species, noticing their variations. • Published a book “The Origins of Species” that proposed a mechanism of how evolution happens (called the theory of natural selection) The voyage of the HMS Beagle Darwin’s Theories • Common Descent –All living things are descended from a common ancestor. • Descent with Modification –Change happens as a series of small steps over long periods of time. Theory of Natural Selection – a mechanism for change in populations. – It occurs when organisms with certain beneficial traits survive, reproduce, and pass their traits to the next generation= (Fitness) – Over time, beneficial traits become more common in a population. 4 Requirements for natural selection 1. Overproduction of offspring: More offspring are born than are needed to continue the species 2. Genetic variation: Within a population, individuals have different traits determined by differences in DNA. 3. Struggle to survive: Some traits (adaptations) improve an individuals chance to survive. 4. Differential reproduction: Organisms with the best adaptations are most likely to survive and reproduce. Evidence of Evolution • Fossils – Show that species change over time. – Some species go extinct – Transitional fossils • Biogeography – Closely related species adapt to different environments. • Divergent evolution – Species that are not related may look alike if they live in similar environments • Convergent evolution • Embryology-embryos of different species look very similar. – Gill slits and tail • Molecular (Biological Molecules) -All organisms have the same DNA code. • Anatomy – Homologous structures • Same structure, different function – Analogous structures • Same function, different structure – Vestigial structures • Used to have a function but no longer do. Artificial Selection • Humans choose what individuals will breed. – We act as a selective force all the time!! Coevolution • When 2 or more species have evolved adaptations together. Finish Cornell Notes • 3 questions in the left column • 3-sentence summary at bottom Pg. 72-73 3 Column Vocab-Chp.14 and 15 1. Evolution 2. Natural selection 3. Adaptation 4. Fitness 5. Homologous structure 6. Analogous structure 7. Vestigial structure 8. Convergent evolution 9. Divergent evolution 10.Adaptive radiation 11.Artificial selection 12.Coevolution Homework • Finish vocab Out – Pg.70 Tent Paragraph-highlight the words as you use them in the paragraph. • Evolution • Darwin • Natural selection Fri 3/7 • Provide examples of geological and biological evidence supporting evolution. In: pg.74 Requirements for Natural Selection Requirements for natural selection 1. Overproduction of offspring: More offspring are born than are needed to continue the species 2. Genetic variation: Within a population, individuals have different traits determined by differences in DNA. 3. Struggle to survive: Some traits (adaptations) improve an individuals chance to survive. 4. Differential reproduction: Organisms with the best adaptations are most likely to survive and reproduce. Pg. 75 - Natural Selection Activity • Rotate through the stations. • At each station you will complete the task the judge describes. The judge will then initial either “live” or “die” on your chart. The judges’ decisions are final!!! • When you have rotated through all 6 stations, answer the questions & hi-lite answers. STATION LIVE DIE 1 2 3 Questions 4 1. What does it mean to be “fit” when you are talking about 5 natural selection? 6 2. Which stations were you “fit” at? What traits helped you survive these stations? 3. What was being selected for at station 2? If this were the environment in which a group of organisms lived, what traits would you expect them to have? Why? 4. What did this activity demonstrate about fitness in different types of environments? Homework • Finish Natural Selection questions. Out – pg.74 Explain why some biologists say “fitness is measured in grandchildren”. Mon 3/10 • Provide examples of geological and biological evidence supporting evolution. In: pg.76 Watch the “Making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation” 1. What trait was studied in this investigation? 2. How does this trait affect the survival of mice in different environments? 3. What caused the initial change in fur color? Pg.77 Blending Butterflies • Design a butterfly that can be camouflaged in the classroom. • Cut out your butterfly and write your name on the back. • Place your butterfly on a visible surface in the classroom (you can’t hide them behind objects). Make the butterfly as invisible as possible. • Return to your seat and copy down the table below: Total # of butterflies # of butterflies seen Questions: 1. What types of camouflage were used to disguise the butterflies in the classroom? 2. Which type of camouflage was best at disguising butterflies in the classroom? Why do you think this worked the best? 3. How do you think camouflaged animals evolved their camouflage? Homework • Finish your analysis questions. Out – Pg.76 Explain how this insect may have evolved its unique appearance?…use what you know about the process of natural selection. 3+ sentences Tues 3/11 • INB Quiz today get out ½ sheet, #1-10 • Next Wednesday (3/19) is the last day for any missing/absent work for Qtr.3!!!!! In: pg. 78 Tape in the diagram and answer the questions. 1.Which represents analogous structures, the forelimbs or the wings? 2.Why? 3.Which represents homologous structures, the forelimbs or the wings? 4.Why? Pg. 79 - Concept Map-Evidence of Evolution • Read section 15.2 (pg.302-307) in the textbook and create a concept map about the evidence for evolution. • Must have 3 levels: main idea, subtopics, details • Must include definitions for: – fossil, transitional species, biogeography, anatomy, embryology, homologous structures, analogous structures and vestigial structures. Pg.79 - Concept Map-Evidence of Evolution Relative age determined by superposition. Absolute age determined by radiometric dating. use book pg.302-306 Fossil Record Biogeography Evidence of Evolution Biological Molecules Anatomy Homework • Finish concept map. Out-pg.78 1. What evidence provides information on horse evolution? 2. What aspects of a horse’s environment do you think changed to cause it to evolve the way it did? Wed 3/12 • Wednesday (3/19) is the last day to make up “mi” and “ab” work for Quarter 3!!!!!!. In: pg.80 Read Section 15-3 (pg.308-309) Evolution in Action 1.What happens in convergent evolution? 2.What happens in divergent evolution? 3.What is adaptive radiation? Pg. 81 • Bird and Beak Lab – complete activity, data table, and analysis questions – Glue as flip up • Under lab on notebook pg.81 Create a multiple bar graph representing your groups lab data Homework • Finish lab analysis questions & graph. Out – Pg.80 1. What is another example of convergent evolution? 2. What is another example of divergent evolution? (you may not use the examples discussed in class today)