* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Which Cell Parts Can You See With the Microscope?
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
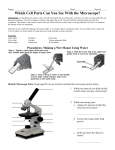
Name: _________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: ____ Which Cell Parts Can You See With the Microscope? Specimen #1: Prepare a wet mount of onion cells. 1. Obtain a clean slide & place a drop of iodine in the middle of the slide. If needed, rinse your slide with water & wipe dry to clean. 2. Peel a thin layer of cells from the inside of an onion as seen in the picture to the right. If the onion layer is not thin, peel another layer. 3. Place the onion peel in the drop of iodine. 4. Add a cover slip over your onion. 5. Examine the onion under medium and high power and using a pencil, draw your observations below. Be sure to find and label the Cell wall, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Nucleolus (optional). Introduction: Living things are made of cells. All cells have parts that do certain jobs. Cells have an outer covering called the cell (plasma) membrane. The cell membrane controls what can enter/exit a cell. The clear jellylike material inside the cell is the cytoplasm. The nucleus is the control center of the cell. Plant cells have a thick outer covering called the cell wall. It is found on the outside of the cell membrane. Cell parts can be studied by making wet mounts slides. A wet mount slide is a temporary slide. It is not made to last a long time. You can make wet mount slides of living and once living materials to study cell parts. Materials: • Glass slides • Cover slips • Microscopes • Droppers • Forceps • Elodea leaf • Onion skin • Various prepared slides • 50 ml beaker Procedures: Making a Wet Mount Using Water 1. Place the specimen in the center of a CLEAN slide. 2. Place a drop of water on the specimen. 3. Place a cover slip on the slide. Put one edge of the cover slip into the drop of water, and slowly dower the cover slip over the specimen. 4. Remove any air bubbles from under the cover slip by gently tapping the cover slip Procedures: Staining a Specimen 1. Place a drop of stain at one end of the cover slip. Identify Microscope Parts: Read page R8 of your textbook and label the microscope picture below. 1. Which two parts do you think should be held when carrying a microscope? ____________________________________________________ 2. Which microscope part: a. Adjusts the amount of light that enters the microscope? _______________________________________ b. Focuses the image under high power? _______________________________________ c. Holds and turns the objective lenses? ___________________________________ 5. Dry any excess water before placing the slide on the microscope stage for viewing. Filter paper 2. Hold a piece of filter paper with forceps at the other end of the cover slip. The stain will flow underneath the cover slip and stain the specimen. Onion Analysis: Best Writing Skills (complete sentences) 1. Onion cells (and skin cells) are flat and seem to overlap. Explain why this arrangement is beneficial. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Specimen #2: Prepare a wet mount of Elodea cells. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Obtain a clean slide & place a drop of water in the middle of the slide. If needed, rinse your slide with water & wipe dry to clean Pick a leaf from the Elodea plant and place the leaf in the drop of water. Make sure the leaf is flat. Add a cover slip over your elodea cell. Examine the elodea under medium and high power and using a pencil, draw your observations below. Be sure to find and label the Cell wall, Chloroplast, and the Cytoplasm. Elodea Analysis: Best Writing Skills (complete sentences) 1. In what particular process do the chloroplasts function? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Specimens 4 and 5: Examine prepared slides of cork and blood. 1. Obtain a prepared slide of cork and blood from your teacher. 2. Place the slides under the microscope and observe. Draw the power that best shows the cells. 3. Draw and label the parts you can see on the next page. 2. Using the fine adjustment with high power, focus up and down on one particular cell. As you focus, some of the chloroplasts go out of view and others come into view. How can you explain this? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Specimen #3: Prepare a wet mount of your cheek cells. 1) Obtain a clean slide and add a drop of methylene blue in the middle of the slide. If needed, rinse your slide with water and wipe dry to clean. 2) GENTLY rub the flat end of the toothpick against the inside of your cheek. 3) Rub the used toothpick in the drop of methylene blue to transfer your cheek cells. 4) Add a coverslip and observe under medium and high power of your microscope. 5) Draw a picture of your cheek cells and label the parts you can see. Cork Analysis: Best Writing Skills (complete sentences) 1. Knowing that cork is the remains of dead plant cells, which part (or parts) were you able to see? What is the function of this (these) part(s)? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Blood Analysis: Best Writing Skills (complete sentences) 1. What is the function of red blood cells? How does their shape allow them to do their job? Cheek Analysis: Best Writing Skills (complete sentences) 1. Review your drawing of an elodea cell. What differences do you notice between an animal cell and a plant cell that can carry on photosynthesis? ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ General Analysis: Best Writing Skills (complete sentences) 1. When first viewing an object under the microscope, explain why you should always find it under the lowest power available. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Why do cells have different shapes? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________