* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
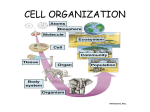
Name: KEY Date: Science Section 3.2 – STUDY GUIDE Specialized cell organ prokaryote nucleus organ system bone marrow eukaryote embryo organism unicellular organism meristem zygote stem cell tissues Vocab words: UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS (Don’t forget to highlight key words!) Unicellular Organisms Stem Cell Organisms that are made up of only one cell, which have to carry out ALL life functions. A cell that can become many different types of cells Prokaryote A unicellular organism made of one prokaryotic cell, without a nucleus. Example: bacteria The locations for adult stem cells Bone Marrow Eukaryote nucleus A unicellular organism made of one eukaryotic cell, with a nucleus. Examples: algae and fungus that causes athletes foot A specialized structure located inside eukaryotic cells. zygote The name given to a fertilized egg embryo The location where many stem cells are found Vocab words: MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS (Don’t forget to highlight key words! Be able to match these with appropriate pictures! (Levels of Organization Mini-Lab) Specialized cell A cell in a multicellular organism that performs one function (has one job) Tissues Groups of similar types of cells that work together to carry out specific tasks. Examples: vascular (plants), connective (animals) Groups of different tissues working together to perform a particular job. Examples: roots, stem, leaves (plants), heart, brain, lungs (animals) Groups of different organs that work together to complete a series of tasks. Examples: shoot/root system (plants), digestive/immune system (animals) Group of organ systems that work together to carry out all the jobs needed for survival. The highest level of organization. Examples: sunflower, dog Stem cells in animals are similar to this in plants. Found on the tip of plant roots. organ Organ system Organism meristem Vascular dermal ground Epithelial connective muscle nervous Types of Tissue: PLANTS (Don’t forget to highlight key words!) Dermal Protection and prevention of water loss Ground Photosynthesis, food storage, regeneration, support, and protection Vascular Transport of water and mineral, transport of food Types of Tissue: ANIMALS (Don’t forget to highlight key words!) Connective Epithelial Helps support our body Examples: bone, cartilage, blood Skin and other important organs are lined with this Nervous Sends signals to the brain Muscle Three types of this tissue. Voluntary or skeletal (contain long fibers that help us move), cardiac (help our heart beat), and smooth (food digestion) Fiber Differentiation Complex Other Vocab: (Don’t forget to highlight key words!) Complex Made of two or more cell parts Differentiation Process in which cells become specialized Cell Basic unit of life Fibers A long muscle cell, thread like Cycle A series of repeat events or activities Cycle Cell Fill in the blank. ALL ABOUT UNICELLULAR AND MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 1.) Unicellular organisms carry out all the activities necessary to survive, like responding to their environment, getting rid of waste, growing, reproduction, etc. 2.) Unicellular organisms can be prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 3.) Each type of cell in a multicellular organism has one specific job that is important to the survival of the organism. 4.) All cells in a multicellular organism comes from a single cell, a fertilized egg. 5.) Multicellular organisms have stem cells (adults and embryos). 6.) Multicellular organisms are always eukaryotes, Multiple Choice: What is the correct sequence of the levels of organization from smallest to largest? A. Cell, organ, tissue, organ system, organism B. Organism, organ, organ system, tissue, cell C. Cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism D. Tissue, organ, organism, organ systems, cell Using this study guide, compare unicellular organisms to multicellular organisms. Prokaryotic organisms Eukaryotic organisms -Unicellular -Unicellular -Unicellular or -no membrane -Contain Multicellular bound organelles genetic -membrane -no nucleus material bound organelles -simple -Go through -nucleus cell division -more complex