* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOT 3 Lecture 4 Gel Electrophoresis
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
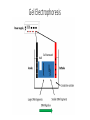
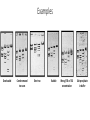
Lecture 4 January 7, 2016 Biotech 3 Gel Electrophoresis Factors Influencing DNA Migration • • • • • • • Size (length) – Reported as bp or Kb Net charge Shape (linear, circular, supercoiled, tertiary) ssDNA or dsDNA Bound protein or stain Buffer system Electrical field strength Agarose Gels • Large pore size - larger samples >200 bp • 0.3 – 0.6 % depending on DNA sizes (0.8% for our plasmids) • 3-4 mm thick - thinner: better resolution - thicker: more volume Concentration of Agarose to Use More fragile Less fragile What are the expected band sizes of the digested pET3a? Which gel percentage would you choose? Buffer Depth • 3 – 5 mm over gel - too little: may dry during run - too much: band slowing, distortion, heating • Buffer depletion (chamber design, run times) Agarose Gel Buffers (Continuous buffer system) Continuous vs. Discontinuous Buffer Systems Continuous buffer system • composition of the buffer in the gels, wells and chambers are similar • Gel pore size and molecular charge density are the only factors that have any effect on stacking • Limited in separating smaller molecules, smaller molecules have less of a difference between their mobility Discontinuous buffer system: • Different buffer ions and pH in the gel and in the electrode reservoirs. • Samples are loaded onto a non-restrictive large pore gel, called the “stacking” gel, which overlays a smaller pore resolving gel • Resolution is much greater • Resolution is a direct result in the way samples concentrate into narrow zones during migration through the gel) • More on this topic when we discuss SDS-PAGE and protein separation Sample Size • Depends on fragments length, sizedistribution, well volume, detection method, etc. • Too small – not detected (10 ng DNA w/Ethidium bromide, 10 ng protein w/ Coomassie) Sample Loading Buffers • Increases density (sucrose, glycerol) • Adds color to the sample • Adds mobility dye - Bromophenol blue (front dye runs ~300 bp) - Xylene cyanol (rear dye runs ~4 – 5 Kbp) • May contain SDS, reducing agents, special loading buffer Examples Overloaded Comb removed too soon Short run Bubble Wrong TBE or TAE concentration Salt precipitate in buffer O'GeneRuler™ DNA Ladder 1kb