* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 51 p1081-1096
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
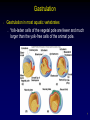
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
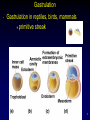
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
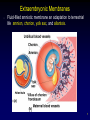
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
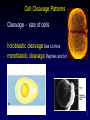
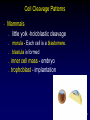
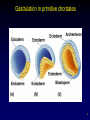
Vertebrate Development Chapter 51 1 Fertilization • • • Penetration – hydrolytic enzymes in acrosome of sperm head Activation – events initiated by sperm penetration egg nucleus complete second meiotic division metabolic activity Nuclei fusion Syngamy - fusion of sperm nucleus with egg nucleus to form the diploid nucleus. 2 Cell Cleavage Patterns • • • Cleavage - size of cells holoblastic cleavage Sea Urchins meroblastic cleavage Reptiles and birds 3 Cell Cleavage Patterns • Mammals – little yolk -holoblastic cleavage – – – – morula - Each cell is a blastomere. blastula is formed inner cell mass - embryo trophoblast - implantation 4 Blastula & Gastrulation • Certain groups of cells invaginate and involute from the surface of the blastula during gastrulation. – By the end of gastrulation - 3 germ layers ectoderm mesoderm endoderm 5 Gastrulation in primitive chordates 6 Gastrulation • Gastrulation in most aquatic vertebrates – Yolk-laden cells of the vegetal pole are fewer and much larger than the yolk-free cells of the animal pole. 7 Gastrulation • Gastrulation in reptiles, birds, mammals primitive streak 8 Extraembryonic Membranes • Fluid-filled amniotic membrane an adaptation to terrestrial life amnion, chorion, yolk sac, and allantois. 9 Vertebrate Embryonic Development Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny Embryological development (ontogeny) involves the same progression of changes that have occurred during evolution (phylogeny 10