* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ch7_1 v2
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
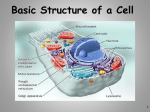
Chapter 7 Section 1 Cells The Cell Theory • . The Cell Theory states that all organisms are composed of similar units of organization called cells. Beginning of the Cell Theory • In 1838, a German botanist named Matthias Schleiden concluded that all plants were made of cells • Schleiden is a cofounder of the cell theory copyright cmassengale 3 Beginning of the Cell Theory • In 1839, a German zoologist named Theodore Schwann concluded that all animals were made of cells • Schwann also cofounded the cell theory copyright cmassengale 4 . Schleiden and Schwann • Matthias Schleiden observed plants and Theodor Schwann observed animals. Both of them concluded separately that all organisms are made of cells. Beginning of the Cell Theory • In 1855, a German medical doctor named Rudolph Virchow observed, under the microscope, cells dividing • He reasoned that all cells come from other pre-existing cells by cell division copyright cmassengale 6 The Cell Theory 1. All known living things are made up of cells. 2. The cell is the unit of structure & function of all living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. (No spontaneous generation ). Microscopes • The Cell Theory would not exist if it wasn’t for the development of the microscope and the work of others. Microscopes • Until scientists began using microscopes they believed diseases were caused by curses and supernatural spirits. They didn’t know about bacteria and other microscopic organisms. . Robert Hooke • In 1663 Robert Hooke discovered cells in a piece of cork, and coined the word CELL. • What he saw looked like small boxes First to View Cells • Hooke is responsible for naming cells • Hooke called them “CELLS” because they looked like the small rooms that monks lived in called Cells copyright cmassengale 11 Cells Van Leeuwenhoek Anton van Leeuwenhoek used his single lens microscopes and was the first person to observe 3. bacteria and protozoa. Leeuwenhoek’s microscope Types of Microscopes • Compound light microscope • Electron Microscope –SEM –TEM –STM Compound Light Microscope • Can magnify object up to 1500X • This is an onion cell at 1000x magnification. Electron Microscope • Uses electron beams to magnify structures up to 500 000 times. • Structures inside of the cell can be seen with electron microscope. • SEM, TEM and STM Compound Light Microscope • Ocular lens • . (eyepiece) times objective lens give total magnification • EX: 10 x 40 1.Two Basic Cell Types • Prokaryotic Cells • Eukaryotic Cells Mainly single Mainly celled organisms multicellular organisms, although some are single celled (amoeba,algae, yeast) 2. Prokaryotic Cell • Prokaryotes have no membrane bound organelles. • Example – • bacteria cell 3 and 4. Eukaryotic Cells • Eukaryotes – contain membrane bound organelles • Example – plants, animals, fungi, and protists Organelles • 5. An organelle is a small specialized structure inside of a cell. • An example of an organelle is the nucleus which controls cell functions. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) • Can see inside a cell and the organelles Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) • Scan the surface of cell to see its 3 D shape. . Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) • Can image atoms on the surface of a molecule.