* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Replication
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
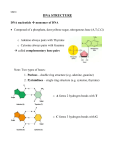
DNA Structure and Replication DNA Rap Song http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d1UPf7lXeO8 Student Expectations B 6.A1 Identify components of DNA. DNA Structure DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid Shape: Double helix Monomers: Nucleotides (has 3 parts) Sugar, (deoxyribose), phosphate nitrogenous base Bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. Four Nitrogenous Bases Adenine (A) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Thymine (T) Purines (double ring) Adenine and Guanine Pyrimidines (single ring) – Cytosine and Thymine Chargaff’s rule: Adenine pairs with thymine. A –T T – A Guanine pairs with cytosine. G – C C – G Nucleotides: Purines Adenine Pyrimidines Guanine Phosphate group Thymine Cytosine Cytosine Thymine Sugar: Deoxyribose Build a DNA molecule http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna /builddna/ A Closer Look at DNA: Page 294 Nucleotide Hydrogen bonds Sugar-phosphate backbone Key Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) A closer look at DNA: How DNA condenses Chromosome Centromere Supercoils DNA Histones Chromatin double helix Student Expectation B 5.A1 Describe the stages of the cell cycle, including deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication. What is Replication? The process of copying DNA during S phase of interphase in the nucleus Makes sure that a daughter cell will have a complete set of chromosomes Original strand of DNA serves as a template for 2 new strands Template: a pattern; an original model Each new strand will be identical to the original strand because of Chargaff’s rule. How does replication work? 1) Helicase unwinds the double helix, forming a “replication fork,” where replication takes place 2) DNA polymerase bonds the necessary nucleotides to the original DNA strand to complete 2 new DNA molecules 3) DNA polymerase also “proofreads” the new DNA strand to make sure it is an exact copy of the original DNA DNA Replication Facts: DNA polymerase can only work in one direction so: 2 new strands of DNA are made in opposite directions One strand is made in sequence of nucleotides The other strand is what we call the “lagging strand” because nucleotides are added in fragments DNA Replication: Page 298 Original DNA New strand strand polymerase DNA polymerase Growth Growth Replication fork Replication Nitrogenous fork bases New strand Original strand Videos http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&featur e=fvwp&v=bW5JnYZImJA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5VefaI0Lrg E&feature=related