* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.2 Probability Student pages
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
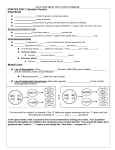
Lesson Review Questions On separate paper. Recall 1. Write a short paragraph in which you correctly use the concepts chromosome, gene, allele, locus, and trait. Apply Concepts 2. Use a Punnett square to determine the possible offspring genotypes of parents with the genotypes Bb and bb. Assume that B is the dominant allele for violet flower color in peas and b is the recessive allele for white flower color. What is the expected ratio of violet-flowered to white-flowered offspring based on your Punnett square? Think Critically 3. Compare and contrast genotype and phenotype. Points to Consider Mendel choose wisely when he decided to study garden peas. Today we know that not all organisms follow the basic patterns that he observed. 4. Can you think of a trait that has more than two phenotypes? Dragon Genetics 1. In dragons, the allele for fire breathing is dominant. Dragons can be fire breathers, or non-fire breathers. Show the genotypes and phenotypes of all possible dragons. 2.If a heterozygous fire-breathing dragon is crossed with one that does not breathe fire, how many offspring will be fire breathers? 3.If two heterozygous dragons are crossed, how many offspring would you expect to NOT be fire-breathers? 4.Also in dragons, wings are a dominant trait. If you crossed two wingless dragons, how many of their offspring would you expect to have wings? 5.If a purebred winged dragon is crossed with a purebred wingless dragon, how many of their offspring will be winged and what is their genotype? 6. A dragon with wings (Dd) is crossed with ones that does not have wings. What percentage of their offspring will be wingless? Student Notes 3.2 Answers 1. A gene is a section of DNA, with many bases that code for a protein. This results in a trait. 2. Traits are controlled by genes. Genes are found on chromosomes and have a genetic code for a protein. The position of the gene on the chromosome is called the locus. 3. Different versions of a gene for a given trait are called alleles. See Diagram: purple flower and white flower. These alleles are how variations of traits occur within a species. 4. In sexually reproducing organisms, chromosomes come in pairs. They will have the same gene located Allele for at the same loci. The alleles may be the same or they maybe white color different for that trait. 5. When gametes unite in fertilization, the zygote inherits 2 alleles for every gene. a. One from the __mom Locus for Flower color Allele for purple color b. One from the __dad These 2 alleles = the individuals genotype. If they are the same= homozygous and if they are different = heterozygous for that gene. Example Genotypes alleles B and b, with B dominant to b Genotypes BB (homozygote) Bb (heterozygote) bb (homozygote) 6. The expression of the genotype is called the phenotype. Phenotype refers to the individuals traits. Example Phenotype with Alleles B and b, with B dominant to b Phenotypes BB= purple flowers Bb=purple flowers bb= white flowers 7. Different genotypes can produce the same phenotype. How? a. One allele is DOMINANT (B) to the other allele which is RECESSIVE (b) Dominant and recessive are terms from Mendel’s factors. 8. What happens when you cross Bb x Bb? Give the genotype ratios and phenotype ratios Student Notes 3.2 1. A _______is a section of DNA, with many bases that code for a __________.This results in a _________. 2. Traits are controlled by ___________. Genes are found on _____________and have a __________code for a protein. The position of the gene on the chromosome is called the _____________ Locus for Flower color 3. Different ________________ of a gene for a given trait are called _______________. See Diagram: purple flower and white flower. These alleles are how _________________of traits occur within a species. 4. In ____________________reproducing organisms, chromosomes come in pairs. They will have the same ___________located Allele for Allele for purple color at the same __________. The alleles may be the __________ or white color they may be ________________for that trait. 5. When the______________unite in fertilization, the _____________inherits 2 alleles for every gene. a. One from the ________ b. One from the ________ These 2 _____________= the individuals ______________. If they are the same= ________________ and if they are different = _______________for that gene. Example Genotypes for the alleles B and b, with B dominant to b Genotypes _______ (homozygote) _______ (heterozygote) _______ (homozygote) 6. The _______________of the genotype is called the _________________. Phenotype refers to the individuals traits. Example Phenotype for the alleles B and b, with B dominant to b Phenotypes BB=______________ flowers Bb=______________ flowers bb= ______________flowers 7. Different genotypes can produce the same ____________________. How? One allele is __________________(B) to the other allele which is ____________________ (b) Dominant and recessive are terms from Mendel’s factors. 8. What happens when you cross Bb x Bb? Give the genotype ratios and phenotype ratios