* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning your WBC`s
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
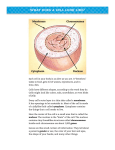
Cell Type Nucleus Content Function Neutrophil (60%) 3-5 lobes; interconnected OR Banded (newly produced) Specific: anti-bacterial (smaller/less dense) Nonspecific: antimicrobial (larger/more dense) Glycogen First to confront bacterial invasion Eosinophil (3%) 2-3 lobbed nucleus Specific granules: large, anti-parasitic (football shaped) Non specific: lysosomal enzymes Anti-parasitic and secondarily recruited to site of basophilic activity to counteract inflammation by basophil Basophil (1%) Poorly lobated or Sshaped, basophil nucleus Basophilic granules spread throughout entire cell Respond to antigenic stimulation; create inflammation Lymphocyte (30%) Heterochromatin rich nucleus; thin rim of basophilic cytoplasm Few organelles; many free ribosomes Monocyte (6%) Deeply indented or folded nucleus; lacey chromatin pattern; substantial cytoplasm Abundant organelles; many lysosomes Long lived; cellular immunity (T cells) and humoral immunity (B cells) Precursors for macrophages Platelet Anucleate; biconvex shaped; derived from cytoplasm of megakaryocyte in bone marrow Granulomere: central region with vesicles, glycogen, lysosomes, canaliculi, and tubular elements Hyalomere: peripheral region with ring of microtubules *Plasma membrane has dense glycocalyx Respond to tears in blood vessels and secrete factors that promote platelet aggregation; catalyze fibrinogen to fibrin for blood clotting; PDGF released and actin and myosin contract clot; clot is dissolved using lysosomal granules (more details pg. 179)