* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download living organisms - Ciencias SEK
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
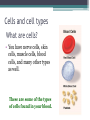
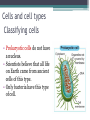
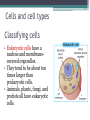
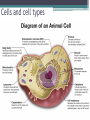
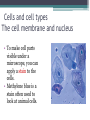
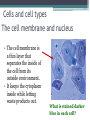
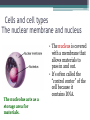
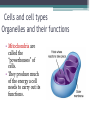
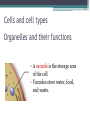
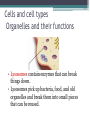
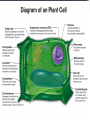
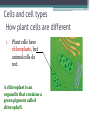
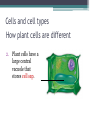
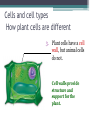
LIVING ORGANISMS Natural Science 2º ESO / III PAI INDEX 1. What are living things? 2. Cells and cell types 3. The discovery of cells What are living things? Classification of Living Things Kingdom Moneran Everything that is living can be sorted into these 5 kingdoms Protist Kingdom Animal Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Plant Kingdom What are living things? Kingdom Moneran Tiny, single-celled organisms Do not have a nucleus E.g. bacteria What are living things? Protist Kingdom Single-celled organisms with a nucleus Live in damp places of water E.g. amoeba What are living things? Fungi Kingdom Body is made up of a network of threads called hyphae E.g moulds, mushrooms What are living things? Plant Kingdom Multicellular – made up of lots of cells Make their own food by photosynthesis Lots of examples: flowering plants / non-flowering plants What are living things? Animal Kingdom Multicellular – made up of may specialised cells Cannot make own food Can be further classified into vertebrates and nonvertebrates then into classes such as amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals What are living things? What are living things? CHEMICAL COMPOSITION Inorganic Compounds Organic Compounds What are living things? HOW MANY VITAL FUNCTIONS HAS A LIVING THINGS? What are living things? THE THREE VITAL FUNCTIONS NUTRITION INTERACTION REPRODUCTION Stimuli Descendents Energy Reacting Appropiate way What are living things? CELLS All living things are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that can perform the three vital functions What are living things? Unicellular (one cell) - ex. Bacteria Multicellular (many cells) - ex. Animals, plants Tissues Organs ystems Cells and cell types What are cells? • A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in a living thing. • Your body is composed of billions of cells. Cells and cell types What are cells? • You have nerve cells, skin cells, muscle cells, blood cells, and many other types as well. These are some of the types of cells found in your blood. Cells and cell types What are cells? • Each cell in your body shares the characteristics of all living things. Cells and cell types Similarities among cells • In many-celled organisms like you, there are many different specialized cells. • All cells share certain common characteristics. Cells and cell types Similarities among cells 1. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. 2. All cells contain organelles. 3. All cells contain cytoplasm. 4. All cells contain DNA. Cells and cell types Classifying cells • Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. • Scientists believe that all life on Earth came from ancient cells of this type. • Only bacteria have this type of cell. Cells and cell types Classifying cells • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membranecovered organelles. • They tend to be about ten times larger than prokaryotic cells. • Animals, plants, fungi, and protists all have eukaryotic cells. Cells and cell types Comparing cell types Cells and cell types Cells: A Look Inside • A cookie factory is like a cell. • An analogy is a way of explaining something complicated using an easier example. • A cookie factory is a good analogy for understanding all the cell parts and their functions. Cells and cell types Comparing cells to a factory • Every cell part has a job or function. • This chart shows how a cell is like a cookie factory Cells and cell types Cells and cell types The cell membrane and nucleus • To make cell parts visible under a microscope, you can apply a stain to the cells. • Methylene blue is a stain often used to look at animal cells. Cells and cell types The cell membrane and nucleus • The cell membrane is a thin layer that separates the inside of the cell from its outside environment. • It keeps the cytoplasm inside while letting waste products out. What is stained darker blue in each cell? Cells and cell types The nuclear membrane and nucleus The nucleolus acts as a storage area for materials. • The nucleus is covered with a membrane that allows materials to pass in and out. • It’s often called the “control center” of the cell because it contains DNA. Cells and cell types Organelles and their functions • Mitochondria are called the “powerhouses” of cells. • They produce much of the energy a cell needs to carry out its functions. Cells and cell types Organelles and their functions • A vacuole is the storage area of the cell. • Vacuoles store water, food, and waste. Cells and cell types Organelles and their functions • The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of tunnels throughout the cytoplasm. • They transport proteins from one part of the cell to another. Cells and cell types Organelles and their functions • Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cell. • When ribosomes make proteins, they release them into the ER. Cells and cell types Organelles and their functions • Golgi bodies receive proteins and other compounds from the ER. • They package these materials and distribute them to other parts of the cell. Cells and cell types Organelles and their functions • Lysosomes contain enzymes that can break things down. • Lysosomes pick up bacteria, food, and old organelles and break them into small pieces that can be reused. Cells and cell types Organelles and their functions • The cytoskeleton is a series of fibers made from proteins. • It provides structure to the cell and gives it its shape. Cells and cell types How plant cells are different 1. Plant cells have chloroplasts, but animal cells do not. A chloroplast is an organelle that contains a green pigment called chlorophyll. Cells and cell types How plant cells are different 2. Plant cells have a large central vacuole that stores cell sap. Cells and cell types How plant cells are different 3. Plant cells have a cell wall, but animal cells do not. Cell walls provide structure and support for the plant. The discovery cells BIBLIOGRAPHY • Natural Science (2 Secondary Education). C. Echevarría, M.J. Benito, B. Cano, M. Hutchings. Anaya English. 2011. • http://www.cposcience.com/home/ForEducator s/MiddleSchoolLifeScience/tabid/276/Default.a spx