* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of immunity :- 1- innate immunity 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
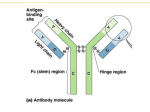
docdroid cod.ال م ناعه Report Share o o o o o Twitter Facebook Embed Download o DOC o o o o PDF ODT TXT Types of immunity :1- innate immunity 2- adaptive ( acquired ) immunity . * Innate immunity :-antigen independent ( No require antigen ) - invariant ( generalized ) - early , limited specifity . - the first line of defense . - not have memory . *Cells of innate immunity :1- Neutrophil 2- eosinophil 3- basophil 4- NK cells ( natural killer ) 5- macrophage 6- mast cells . *Adaptive immunity :- antigen dependent ( require antigen ) - variable - later , highly specifity - have memory . - mediated by lymphocytes . - may give lifelong immunity . * Cells of adaptive immunity :1- T-lymphocyte ( CD4 - CD8 ) 2- B-lymphocyte . 3- dendritic cells . * antigen :- substance capable of inducing specific immune response . White Blood Cells ( WBCs ) :-directional movement of WBCs by :- Chemotaxis There are two main types of WBC involved in the adaptive immune response :1- antigen - presenting cells (APCs ) :- it is activate T-cell , example : macrophage 2- Lymphocytes :- consist of two types :- 1- T-cell 2- B-cell *Cells of innate immunity :1- Neutrophil :-Function :- Phagocytosis . -Antigen Receptor :- No . -short life span . 2- eosinophil :-Function:- Parasites killer . e.g ( schistosoma , helminthes ) - Antigen Receptor :- No . 3- Basophil :-Function:- Important in allergic disorders - Antigen receptor :- No - Found in IgE . 4- NK cell :Function : kill tumors and viruses infected cells . Antigen receptor :- No 5- macrophage :Function : phagocytosis and antigen presentation to T-cell . Antigen Receptor :- No 6- Mast cell :Function : Kill parasites . Antigen receptor :- No -Found in IgE. - Found in connective Tissue . * Cells of adaptive immunity :1- T-lymphocyte :-Function :- the main regulators of immune system -Antigen Receptor :- Yes . - maturation in thymus . 2- B-lymphocyte :- Function :- Production of antibodies . - Antigen Receptor :- Yes . - Maturation in Bone Marrow . - Regulated By T-cells . 3- dendritic cells :- Function :- transport antigen and activate T-cell *Monocytes :- Function :- to become macrophage . - Both monocyte and macrophage act as phagocytosis . *Lymphocytes :- Responsible for the adaptive immune response. - there are 2 classes :1- T-lymphocytes . ( Low and high Zone tolerance ) ( for cellular immunity ) 2- B-lymphocytes. ( high zone tolerance ) ( for humoral immunity ) * T-lymphocytes may differentiate into several classes of effector cells :1- Helper T lymphocytes ( CD4 ) :- Secrete Cytokinase . and help other cell to mount immune response . 2- Cytotoxic T lymphocyte ( CD8 ) :- kill virus infected or allogenic . 3- Regulatory T lymphocytes :- Help to mediate Immuno Tolerance . * Lymphoid Organs :1- Primary lymphoid organs :- consist of Bone marrow and Thymus 2- Secondary Lymphoid organs :- consist of lymph nodes , spleen , mucosa – associated lymphoid tissue ( MALT ) e.g :- tonsils , peyer patches,appendix, bronchial, mammary tissues. General Information of Immunology :* Antibodies ( immunoglobulin ) :- it is proteins secreted from B-Lymphocytes ( plasma cell ) -there are 5 classes of immunoglobulin :1- IgM :- the most Ig secreted in primary immune responses . and represent the cell surface receptor of B-lymphocytes . 2- IgG :- the major Ig found in the blood 3- IgD :- the minor Ig . 4- IgE :- stimulate mast cells and cause them release histamine . 5- IgA:- Found in secretion , Such as Saliva & breast Milk . * Role of antibodies :1- Precipitation 2- Agglutination 3- Virus Neutralization . 4- Toxin Neutralization . 5-Complement Fixation . 6- Opsonezation :- antibody molcules can coat cellular antigen making it easier for phagocyte . - Complements :- series of proteins in the blood , that can mediate lysis red cells . - lymphocytes can be detected by using :- Immunoflurescence technique . - the part of antigen recognized by the antigen combining sites of receptors called antigenic determinant or epitope . - Affinity :- Binding in homogenous system . - Avidity :- Binding in hetrogenous system Immunoglobulin in Body :- 1- IgG :- IgG is The smallest antibody in the human. - IgG Found in large amount in blood . - IgG can cross placenta . - IgG antibodies are involved in the secondary immune response - IgG is The most common antibody involved in warm antibody -IgG is monomeric immunoglobulin 2- IgM :- IgM is largest antibody in the human ( highest in electrophoresis ) - IgM have five molecule (pentamer immunoglobulin ) - IgM can not cross placenta - IgM is the main antibody involved in primary immune response - IgM are efficient activator of the complement fixation - IgM Increased of IgM cause cold agglutination syndrome - IgM represent the cell surface receptor of B-lymphocytes . - IgM is blood grouping antibody . 3- IgE :- It is found in small amounts in serum tissue. - IgE only been found in mammals - IgE plays an important role in allergy , parasitic worms. - IgE is monomeric immunoglobulin . -IgE found in mast cells and basophil IgE are un flexible 4- IgA :- IgA is the main immunoglobulin found in mucous secretions, including tears, saliva. - IgA prevent attachment of viruses and bacteria to epithelial surfaces. -IgA dimmer imunogloblin 5- IgD :- IgD function is not known, -IgD is monomeric imunoglobulin