* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
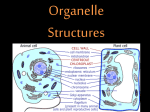
Name: _____________________________ Concept 5.3: Lipids What makes something a lipid? Fats: Constructed from 2 molecules: What is a triglycerol? How are saturated fats different from unsaturated fats? What is the purpose of fats? Sketch and explain the regions of a phospholipid: Why are they important to cells? What makes something a steroid? Why are human sex hormones considered to be lipids? Concept 5.4: Proteins What are proteins used for? Explain the role of enzymes in living systems: What is a polypeptide? Why is it called that? What are amino acids? Sketch a generic one and label all the parts: Explain a peptide bond and show how one is formed: What makes one protein different from another? A protein’s function is determined by There are 4 basic levels of protein structure. Explain each, make a sketch to clarify each step, and be sure to include the forces at work on each of the levels of structure: (1) (2) (3) (4) What is denaturation, and what does it have to do with protein shape? Why does a denatured protein no longer function normally? A genetic mutation can change a protein’s primary structure. How can this destroy the protein’s function? Egg white is made of protein. Explain why the appearance of an egg changes when you fry it: Explain the protein-folding problem: