* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra 2 - Miss Stanley`s Algebra Wiki
Survey
Document related concepts
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli number wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
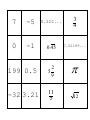
Algebra 2 Unit 1, Lesson 2: The Real Number System Objectives - Unit Skills Students are able to place any real number in its correct location on a Venn Diagram of the real number system. Students can determine if logical statements about real numbers are true or false, and explain why with reference to the Venn Diagram. 1-1 Materials and Handouts Homework - Answer transparency for hw #1-1 #1-2 - Classification warm-up Mastering the real - Sets of cards with numbers number system - Transparencies for number system activity (worksheet) - Classifying real numbers / understanding real numbers & answer transparencies - Homework: Mastering the real number system Time Activity Homework Check / Warm-up Activity 15 min - Put the answers to hw #1-1 on the overhead, with 10 questions circled to grade. Students get one point for each correct, and write their total at the top of the page. - When finished checking, they should begin the warm-up: Classification Warm-Up - As they are working, circulate to record grades and stamp homework checkers. Developing understanding of the number system 40 min - Give each group a set of cards that each have a single number on them. - On the overhead, show the text: “Whole Numbers”. Ask students to find all their cards that have this kind of number, and to put them in the middle. - On the overhead, show the text: “Integers: positive and negative whole numbers”. Students should identify the cards that are integers, and put them in the center. - Now we will begin to develop the number system diagram on the board. Tell students that we want to organize whole numbers and integers with a Venn Diagram. As a reminder, show an overlapping and a subset style Venn Diagram on the overhead. Ask groups to talk for a minute and decide which one makes more sense to use in this situation. Clarify why the subset option is preferable, and draw the first two circles of the number system on the whiteboard. - On the overhead, show the text: “Rational Numbers: numbers that can be expressed as a fraction in the form - p where p and q q are both integers, and q ≠ 0.” Clarify what this means. Ask students to identify their rational number cards and place them in the middle. Refer back to the numeracy skill builder if students forget to include whole numbers and decimals. Based on this, call on a student to add the rational numbers circle to the diagram on the board. - On the overhead, show the words “Irrational Numbers: numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction in the form 20 min 5 min p where p q and q are both integers, and q ≠ 0.” Ask students to identify these numbers on their cards. They should realize that it is all the numbers that they have not already put in the center. - Based on this, call on a student to put the irrational number circle on the board. With discussion, the class should understand that this circle must be mutually exclusive. - Explain that these numbers together are considered real numbers; draw in a final circle to complete the diagram. - Write all the numbers from the cards in the correct location on the completed Venn Diagram. - Hand out the Classifying Real Numbers practice sheet. Give students a few minutes to complete it and then review answers on the overhead. Individual Practice - Students should complete the Understanding Real Numbers worksheet. Review on the overhead if time permits. Closure - Students: o Write down homework in their logs/planners o Self-assess on College Habits, filling in their logs o Report their grades out loud, one by one. Algebra 2 Unit 1, Lesson 2: Warm-up Period: Name: Classification Warm-Up Directions: Use the Venn Diagram to determine if each statement is true or false. If it is false, explain why. Venn Diagram #1: Overlapping Circles 1) It is possible to be both Alpha and Omega at the same time. Omegas 2) All Omegas are Alphas. B Alphas C 3) If you’re not an Alpha, you must be an Omega. A D Venn Diagram #2: 4) Some Alphas are not Omegas. Subsets Clydes 1) All Clydes are Inkies. Blinkies 2) All Inkies are Clydes. Inkies 3) No Blinkies are Inkies. A D B C 4) If you’re not a Blinky, you’re a Clyde. Numeracy Skill Builder: Write each number as a fraction. 1) 0.5 2) 3.871 3) 6 4) -2 5) 0.333333... 6) 5¾ Bonus neat-o numeracy trick! You can write any repeating decimal as a fraction by putting 9’s in the denominator. Count the number of digits that repeat, and use that many 9’s in the denominator. For example: 0.323232... 0.530530... 32 . 99 530 Three digits repeat, so this decimal equals . 999 Two digits repeat, so this decimal equals Don’t believe me? Grab a calculator and try it! If you want to know why it works, come during lunch and ask! Algebra 2 Unit 1, Lesson 2: Classwork Period: Name: Classifying Real Numbers Directions: Write each number in the correct location on the Venn Diagram of the real number system. Each number should be written only once. 3 6, 2.73, , 7 2, 1 9, 100, 0, , 1, , 3.8, 5.42, 8.293017... 2 Real Numbers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Integers Whole Numbers True or false? If false, explain why. 1) All whole numbers are integers. are integers. 3) Some rational numbers 2) All integers are whole numbers. irrational numbers. 4) Some whole numbers are Understanding Real Numbers 1) List the numbers in the set 4 5 , 18, 0, 5, 1 , 2.01, 5, 2 , 2.513, 5.1823159... that are: Whole numbers Integers Rational numbers Irrational numbers Real numbers 2) Put a check mark for each set that the number is a part of: Whole Number s Intege rs Ration al Number s Irrati onal Number s Real Number s -7 ¾ 2 5 0.398 3) True or false? If false, explain why. a. All integers are rational. b. If a number is rational, then it must be a whole number. c. Some irrational numbers are integers. d. All irrational numbers are real numbers. e. No whole numbers are integers. Algebra 2 Homework #1-2 Period: Name: Mastering the Real Number System 1) Write each number in the correct location on the Venn Diagram of the real number system. Each number should be written only once. 3, 2.09824..., 24, 25, 2 , 5 2 2 100, 7, , , 6.5, 3.01, 3 5 7 Real Numbers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Integers Whole Numbers 2) List the numbers in the set are: Whole numbers Integers Rational numbers 17, 0, 1 5 3, , , 7.99, 8, 6 7 , 0.03986..., 0.53 that Irrational numbers Real numbers 3) True or false? If false, explain why. a. Some irrational numbers are integers. b. All rational numbers are whole numbers. c. If a number is not an integer, then it is not a whole number. d. If a number is not an integer, then it is not a rational number. e. Some irrational numbers are not real numbers. f. No rational numbers are integers. 4) Put a check mark for each set that the number is a part of: Whole Number s Intege rs Ration al Number s 0 2.07 -35 7 7 3 5) Write each number in fraction form. Irrati onal Number s Real Number s -25 3 5 7 7 0.25 0.002 8 1 9 2.913 0.5555... 0, 1, 2, 3... Whole Numbers Positive and negative whole numbers Integers Numbers that can be p written in the form q where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0 Rationals Numbers that cannot be written in the form where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0 p q Irrationa ls 7 -5 0.222... 0 -1 0.45 3 4 7.02189... 199 0.5 2 5 9 -32 3.21 11 5 12