* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download genetics vocabulary - Mrs. Stolting
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
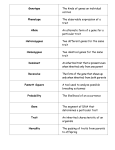
GENETICS VOCABULARY 1. Genetics - The science that studies the laws of heredity 2. Heredity - The passing of traits from parent to offspring 3. Gregor Mendel - Austrian monk, known as the Father of Genetics, who did experiments on pea plants and determined the basic laws of heredity 4. Chromosome - Rod shaped structure containing genes -Humans have 46 or 23 pairs where one chromosome of each pair comes from the mother and the other in the pair comes from the father 5. Gene - Location on a chromosome that controls a particular trait 6. Pure Trait - When the pair of genes for a trait is identical 7. Homozygous Trait - Same as the pure trait 8. Hybrid Trait - When the pair of genes for a trait are different 9. Heterozygous Trait - Same as the hybrid trait 10. Dominant Gene/Trait - One in the pair for a trait that can mask the other one in the pair 11. Recessive Gene/Trait - One in the pair that can be masked or hidden by the other one in the pair 12. Phenotype - The physical trait that you see 13. Genotype - The words describing the make up of the gene pair ex. - pure dominant - hybrid dominant - pure recessive 14. Punnett Square - Method used to predict the possible outcomes of the offspring 15. Incomplete Dominance - When unlike genes for a trait are expressed as a mix or blend 16. Codominance - When unlike genes for a trait are both expressed 17. Pedigree Chart - A record of marriages and births in a family from generation to generation following a single trait through those generations 18. Sex-linked Trait - A trait caused by genes found only on the X chromosome 19. DNA - Deoxyribonucleic Acid, large molecule that contains the hereditary information 20. Mutation - any change in the genetic material (DNA) 21. Allele – The different form of a gene