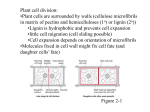
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Zoo/Bot 3333
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Zoo/Bot 3333 Spring 2007 Genetics Quiz 3 3/16/07 For answers to the quiz, click here: Questions 1-2 pertain to the following. The father of Mr. Spock, first officer of the Starship Enterprise, came from the planet Vulcan; his mother came from Earth. A Vulcan has pointed ears (P), adrenals absent (A) and a right-sided heart (R). All of these alleles are dominant over Earth alleles. These genes are autosomal, and they are linked as shown in this linkage map: P/p----------------15 m.u.------------------A/a----------------20 m.u.--------------------------R/r If Mr. Spock marries an earth woman and there is no interference, what proportion of their offspring: 1) Will have Vulcan ears, but earth heart and adrenals? a) 35%; b) 17%; c) 8.5%; d) 6%; e) 1.5%. 2) Will show Vulcan appearance for all three characters? a) 100%; b) 75%; c) 67%; d) 34%; e) 17%. Questions 3-4 pertain to the following: The following are four Drosophila recessive mutations: Allele Symbol Gene Name Mutant Phenotype dwp dwarp small body, warped wings rmp rumpled deranged bristles pld pallid pale wings rv raven dark eyes and bodies Two crosses are performed with the indicated results: 1) dwarp, rumpled females x pallid, raven males dwarp, rumpled males and wild-type females 2) pallid, raven females x dwarp rumpled males pallid raven males and wild-type females Finally, F1 females from cross number 1 were crossed to males homozygous for all four mutant genes (dwarp, rumpled, pallid, raven). The 1000 progeny obtained from this third cross were as follows: pallid 3 pallid, raven 428 pallid, raven, rumpled 48 pallid, rumpled 23 dwarp, raven 22 dwarp, raven, rumpled 2 dwarp, rumpled 427 dwarp 47 3. In the above problem, the gene loci that are closest to one another in the linkage map are: a) rumpled and raven; b) pallid and dwarp; c) dwarp and raven; d) rumpled and pallid; e) rumpled and stilskin. 4. The map distance from rumpled to raven is: a) 2.5 map units; b) 5 map units; c) 10 map units; d) 15 map units; e) can't be calculated from this data set, since the genes are farther than 50 map units apart or are on separate chromosomes. 5. In humans, the genome size is estimated to be 3 billion bases. The human genome is estimated to contain approximately 25,000 genes. Approximately how many kb of DNA (1000 base pairs = 1 kilobase = 1 kb) is occupied by an average gene plus intergenic sequence? a) 0.12 kb; b) 8.3 kb; c) 10 kb; d) 25 kb; e) 100 kb. Canada: Questions 6-8 pertain to the following. A geneticist studying gene a b c d e f linkage in different strains of Drosophila collect two pure-breeding a 0 12 14 23 3 29 strains in Canada and in Spain. He performs linkage studies of flies b 0 2 35 15 17 within each strain for six traits, associated with loci a through f. He c 0 37 17 15 notes the following recombinant frequencies in test crosses, and graphs d 0 20 50 them into the tables on the right, where recombination frequencies are e 0 32 expressed as percentages: f 0 6. True or false. For both strains, c is between f and a. Spain: 7. True or false. Theoretically, the location of gene b relative to a and c can be mapped by crossing heterozygotes for the a, b and c loci to a b c d e f individuals homozygous recessive for the a, b and c loci. a 0 12 7 30 3 22 b 0 19 18 15 34 8. In a Canadian-Spanish hybrid, approximately what recombination c 0 37 4 15 frequency would be expected between the a and c loci? d a) zero; b) 7%; c) 14%; d) 21%; e) 50%. 0 33 50 e 0 19 f 0 9. Deletions can be used to determine the orientation of genes on a chromosome. A series of 5 deletions "uncovered" the following recessive mutations in deletion heterozygotes, allowing them to show pseudodominance (see text 448 2e/496 3e): deletion 1: deletion 2: deletion 3: deletion 4: deletion 5: o, n m, h, r o, m, n o, t h, m The order of the genes can be represented: a) mhrotn; b) tonrhm; c) tonmhr; d) monrth; e) ontrmh. 10. The old world cotton species G. herbaceum has a 2n chromosome number of 26, while the new world species G. hirsutum has a 2n chromosome number of 52. Crosses between G. thurberi and G. herbaceum produce 13 large univalents and 13 small univalents during meiosis. Crosses between G. thurberi and G. hirsutum produce 13 small bivalents and 13 large univalents during meiosis. These results imply: a) G. thurberi chromosomes are smaller than G. herbaceum’s; b) G. hirsutum is a tetraploid; c) G. hirsutum is an allopolyploid; d) G. hirsutum is an amphidiploid; e) all of the above.