* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transport worksheet
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
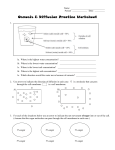
SBI 4U TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES 1. In the animal cell below, what change do you expect to occur? Why? Water molecule Sugar molecule Cell membrane (impermeable to sugars, permeable to water) 2. Why does a paramecium (a freshwater unicellular organism) have to continually pump water out of itself? 3. Compare the following pairs of processes: a) facilitated diffusion and active transport b) passive transport and active transport c) phagocytosis and pinocytosis d) exocytosis and endocytosis 4. In the diagram of the plant cell shown below, the dots represent water molecules and the circles represent sugar molecules. a) Explain the movement of sugar molecules into or out of the cell. b) Explain the movement of water into or out of the cell. Cell wall Cell membrane (permeable to both sugar and water) 5. A red blood cell is placed in distilled water. Describe and explain the changes in the shape of the red blood cell. 6. If you took a fresh water amoeba (unicellular organism) and placed it in sea water, what changes would occur to the organism? 7. Two cells are attached by a common membrane. In cell A, there is a sugar concentration of 0.5% and a starch concentration of 0.4%. In cell B, there is a sugar concentration of 0.6% and no starch. Sugar can pass through the membrane, but starch cannot (starch molecules are too large). Assume that all other solutes are found in equal concentrations within the two cells. a) In what direction will the sugar move? Why? b) In what direction will osmosis occur? Why? 8. The disease chlolera is caused by a bacterium which enters the body through drinking water. Once inside the body, it adheres to the intestinal lining and secretes a toxic product. In response, the lining secretes chloride ions. Sodium ions follow the chloride ions out of the cells. How do these events explain the fluid loss associated with cholera?