* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9.3 student Fill in notes
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
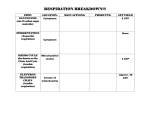
Class Starter Answer the following questions: How are the products of photosynthesis and respiration related? What kinds of organisms undergo cellular respiration? Objectives •How does glycolysis produce ATP? •How is ATP produced in aerobic respiration? •Why is fermentation important? Section 9.3: Cellular Respiration Introduction • The cells of most organisms transfer energy found in __________________ compounds, such as those in foods, to __________. • The primary fuel for cellular respiration is _____________. ____________ can be broken down to make ATP. • ________________ and ___________________ can also be used to make ATP, but they are usually used for building important cell parts. Glycolysis - enzymes break down one ________-carbon molecule of glucose into two _________-carbon ___________________ molecules. • The breaking of a sugar molecule by glycolysis results in a net gain of ______ ATP molecules. • This process of glycolysis is __________, or takes place without _____________. • Glycolysis is the only source of energy for some prokaryotes. • Other organisms use oxygen to release even more energy from a glucose molecule. Metabolic processes that require oxygen are ______________. • In aerobic respiration, the ______________ product of glycolysis undergoes another series of reactions to produce more _______________ molecules. Fermentation • To make ATP during glycolysis, NAD+ is converted to ____________. • Organisms must recycle NAD+ to continue making ________through glycolysis. • The process in which carbohydrates are broken down in the absence of oxygen is called ____________________. • Fermentation enables glycolysis to continue supplying a cell with ATP in ______________ conditions. • lactic acid fermentation – pyruvate is converted to _______________. – • During vigorous exercise, lactic acid fermentation also occurs in the ________________ of animals, including humans. alcoholic fermentation – one enzyme removes _________________ from pyruvate. A second enzyme converts the remaining compound to ______________, recycling NAD+ in the process. Aerobic Respiration • Organisms such as humans can use ______________ to produce _______ efficiently through aerobic respiration. • The first stage of aerobic respiration is the ___________________, a series of reactions that produce electron carriers. • The electron carriers enter an electron transport chain, which powers ______________ ___________________. • Up to ________ATP molecules can be produced from one _____________ molecule in aerobic respiration. Krebs Cycle • Pyruvate (from ____________________) is broken down and combined with other carbon compounds. • Each time the carbon-carbon bonds are rearranged during the Krebs cycle, ______________ is released. • The total yield of energy-storing products from one time through the Krebs cycle is ______________, _________________, and _________________. Electron Transport Chain • The second stage of aerobic respiration takes place in the inner membranes of ____________________, where ATP synthase enzymes are located. • Electron carriers, produced during the _____________________, transfer energy through the electron transport chain. • Energy from the electrons is used to ___________________ transport __________________ ions out of the inner mitochondrial compartment. • Hydrogen ions ____________________ through ____________________, providing energy to produce several ATP molecules from __________. • At the end of the electron transport chain, the electrons combine with an ____________________atom and two hydrogen ions to form two __________ molecules. • If oxygen is not present, the electron transport chain _________. The electron carriers are not recycled, so the _________________ also stops. Efficiency of Cellular Respiration • In the first stage of cellular respiration, ________________ is broken down to ________________ during ________________, an ________________ process. • Glycolysis results in a net gain of ______ATP molecules for each glucose molecule that is broken down. • In the second stage, pyruvate either passes through the _________________ or undergoes ___________________ – Fermentation recycles __________ but does not produce _____________. • Cells release energy most efficiently when ________________ is present because they make most of their ATP during ______________ respiration. • For each glucose molecule that is broken down, as many as ______ ATP molecules are made during the Krebs cycle. • The Krebs cycle feeds _____________ and __________________ to the electron transport chain, which can produce up to ____________ ATP molecules. Summary • The breaking of a sugar molecule by glycolysis results in a net gain of two ATP molecules. • The total yield of energy-storing products from one time through the Krebs cycle is one ATP, three NADH, and one FADH2. Electron carriers transfer energy through the electron transport chain, which ultimately powers ATP synthase. • • Fermentation enables glycolysis to continue supplying a cell with ATP in anaerobic conditions.