Explain the steps in protein synthesis.
... Location: Eukaryotes-nucleus Prokaryotes-cytoplasm • 1. RNA polymerase binds to the gene’s promoter • 2. The two DNA strands unwind and separate. • 3. Complementary nucleotides are added using the base pairing rules EXCEPT: • A=U • The rest are the same C=G, T=A, G=C ...
... Location: Eukaryotes-nucleus Prokaryotes-cytoplasm • 1. RNA polymerase binds to the gene’s promoter • 2. The two DNA strands unwind and separate. • 3. Complementary nucleotides are added using the base pairing rules EXCEPT: • A=U • The rest are the same C=G, T=A, G=C ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... The Sugar is a ______Carbon Sugar called ___________________________ To each Deoxyribose, there is a _____________________________________ connected. The Rungs are connected by weak ___________________________________ ...
... The Sugar is a ______Carbon Sugar called ___________________________ To each Deoxyribose, there is a _____________________________________ connected. The Rungs are connected by weak ___________________________________ ...
Slide 1
... • One of the two strands is then transferred to a matching sequence on a messenger RNA, and an enzyme called "slicer" then cleaves the mRNA at the position of the duplex. • The cleaved mRNA is rapidly degraded. • In other cellular systems, instead of the mRNA being degraded it stays intact, but the ...
... • One of the two strands is then transferred to a matching sequence on a messenger RNA, and an enzyme called "slicer" then cleaves the mRNA at the position of the duplex. • The cleaved mRNA is rapidly degraded. • In other cellular systems, instead of the mRNA being degraded it stays intact, but the ...
DNA NOTES
... Section 8.1 From Genotype to Phenotype 8. Define Protein Synthesis: (pg. 182) 9. Use Figure 8.1 and complete the table. RNA and DNA: Structural Differences RNA DNA ...
... Section 8.1 From Genotype to Phenotype 8. Define Protein Synthesis: (pg. 182) 9. Use Figure 8.1 and complete the table. RNA and DNA: Structural Differences RNA DNA ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... • Transcription factors are a set of proteins needed to RNA polymerase to bind to promoter – Activators bind to transcription factors, RNA polymerase, enhancers ...
... • Transcription factors are a set of proteins needed to RNA polymerase to bind to promoter – Activators bind to transcription factors, RNA polymerase, enhancers ...
DNA Replication, RNA Molecules and Transcription
... A transcription reaction requires a DNA molecule to serve as template for transcription with a promoter (and, in vivo, transcription factors) to indicate where to begin transcribing and which strand to transcribe. Transcription reactions also require an RNA polymerase that recognizes the promoter on ...
... A transcription reaction requires a DNA molecule to serve as template for transcription with a promoter (and, in vivo, transcription factors) to indicate where to begin transcribing and which strand to transcribe. Transcription reactions also require an RNA polymerase that recognizes the promoter on ...
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
... a cluster of genes working together a region of the chromosome near the cluster: operator a region of the chromosome next to the operator: promotor products that initiates the production of enzymes are inducers ...
... a cluster of genes working together a region of the chromosome near the cluster: operator a region of the chromosome next to the operator: promotor products that initiates the production of enzymes are inducers ...
What is a protein? - Hicksville Public Schools
... • Brings code to ribosome *** remember, when it copies the code from DNA, A will pair up with U there will not by any T in RNA. ...
... • Brings code to ribosome *** remember, when it copies the code from DNA, A will pair up with U there will not by any T in RNA. ...
Protein Synthesis Review Concepts • Protein synthesis occurs in two
... Protein Synthesis Review Concepts • Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation • Transcription is the process in which information is copied from DNA to RNA • Translation is the process in which information from RNA codes for amino acids • Cells with the same DNA can speci ...
... Protein Synthesis Review Concepts • Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation • Transcription is the process in which information is copied from DNA to RNA • Translation is the process in which information from RNA codes for amino acids • Cells with the same DNA can speci ...
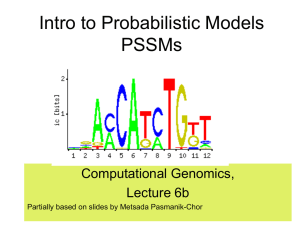
CG7b-PSSM
... Computational Genomics, Lecture 6b Partially based on slides by Metsada Pasmanik-Chor ...
... Computational Genomics, Lecture 6b Partially based on slides by Metsada Pasmanik-Chor ...
Design and Operation of Large Scale RNA production v2
... Problems of RNA synthesis • Reagents and their waste are a major problem. • If we could recycle and reuse these organic wastes, it would significantly reduce cost of waste reagents bought and waste removal costs. ...
... Problems of RNA synthesis • Reagents and their waste are a major problem. • If we could recycle and reuse these organic wastes, it would significantly reduce cost of waste reagents bought and waste removal costs. ...
Distinguish between mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. What molecule does
... information carried by a gene. mRNA is transcribed from a DNA template, and carries information to the sites of protein synthesis: the ribosome. ...
... information carried by a gene. mRNA is transcribed from a DNA template, and carries information to the sites of protein synthesis: the ribosome. ...
1 Biology 20 Protein Synthesis DNA: How is this linear information
... The proteins produced are in the 1˚ level of protein structure, which the genes determine Some proteins are modified further before they do their specific jobs What are some of the possible roles for these proteins? The following tRNA has the anticodon UAC. What is the DNA base code for this tRNA? W ...
... The proteins produced are in the 1˚ level of protein structure, which the genes determine Some proteins are modified further before they do their specific jobs What are some of the possible roles for these proteins? The following tRNA has the anticodon UAC. What is the DNA base code for this tRNA? W ...
Extraction of RNA File
... 5) The second step include activation or loading the amino acid by some enzyme and contact the active amino acid with the tRNA that special with it, after that the 6) t RNA transport to ribosomes and contact with m RNA the anti codon that found on the tRNA. 7) The m RNA contain the nucleotides calle ...
... 5) The second step include activation or loading the amino acid by some enzyme and contact the active amino acid with the tRNA that special with it, after that the 6) t RNA transport to ribosomes and contact with m RNA the anti codon that found on the tRNA. 7) The m RNA contain the nucleotides calle ...
SI Worksheet 12
... a. operators....promoters b. exons....introns c. silencers....enhancers d. introns....exons e. promoters....operators 4. Which of the following mechanisms of gene regulation operates after mRnA transcription but before translation of mRNA into protein? a. mRNA splicing b. DNA packing c. repressors a ...
... a. operators....promoters b. exons....introns c. silencers....enhancers d. introns....exons e. promoters....operators 4. Which of the following mechanisms of gene regulation operates after mRnA transcription but before translation of mRNA into protein? a. mRNA splicing b. DNA packing c. repressors a ...
protein synthesis
... amino acid methionine but also indicates the start of translation. • Three codons do not indicate amino acids but signal the termination of translation. • Multiple codons for some amino acids ...
... amino acid methionine but also indicates the start of translation. • Three codons do not indicate amino acids but signal the termination of translation. • Multiple codons for some amino acids ...
Central dogma: from genome to proteins
... DNA transcription produces a single-stranded RNA molecule, complementary to one strand of DNA ...
... DNA transcription produces a single-stranded RNA molecule, complementary to one strand of DNA ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Transcription=part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence of RNA. 1. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to and unzips the DNA. It uses 1 strand as a template. 2. A single strand of mRNA is made. (U) replaces (T). 3. mRNA breaks off from the DNA, leaves the nucleus an ...
... Transcription=part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence of RNA. 1. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to and unzips the DNA. It uses 1 strand as a template. 2. A single strand of mRNA is made. (U) replaces (T). 3. mRNA breaks off from the DNA, leaves the nucleus an ...
Biology 105: Biology Science for Life with Physiology, 3rd Ed., Belk
... recognized as safe (GRAS); 20 genetically modified organism (GMO); 21 genetic code; 22 genome;23 helicase; 24 in vitro; 25 messenger RNA (mRNA); 26 model organisms; 27 mutations; 28 nitrogenous base; 29 nucleases; 30 nucleotide; 31neutral mutation; #s in bold are from Holt’s Modern Biology text. 1 e ...
... recognized as safe (GRAS); 20 genetically modified organism (GMO); 21 genetic code; 22 genome;23 helicase; 24 in vitro; 25 messenger RNA (mRNA); 26 model organisms; 27 mutations; 28 nitrogenous base; 29 nucleases; 30 nucleotide; 31neutral mutation; #s in bold are from Holt’s Modern Biology text. 1 e ...