Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... D. alteration in chromatin structure to facilitate loading and translation by ribosomes and, thus, enhance gene expression. 25. The phenomenon known as “RNAi” (RNA interference) can be used experimentally to A. reduce expression of a specific target gene. B. reduce translation rate from a specific g ...
... D. alteration in chromatin structure to facilitate loading and translation by ribosomes and, thus, enhance gene expression. 25. The phenomenon known as “RNAi” (RNA interference) can be used experimentally to A. reduce expression of a specific target gene. B. reduce translation rate from a specific g ...
worksheet 12-3
... b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase binds only to DNA promoters, which have specific base sequences. d. Promoters are signals in RNA that indicate to RNA polymerase when to begin transcription. ...
... b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase binds only to DNA promoters, which have specific base sequences. d. Promoters are signals in RNA that indicate to RNA polymerase when to begin transcription. ...
Gene Regulation - Two Rivers High School
... O Ex. Unicellular organisms must be able to adapt genetic material quickly to adjust to changing circumstances and new environments, since the failure to do so will cause not only death of the cell, but death of the organism itself. O Gene regulation allows such organisms to do things that will allo ...
... O Ex. Unicellular organisms must be able to adapt genetic material quickly to adjust to changing circumstances and new environments, since the failure to do so will cause not only death of the cell, but death of the organism itself. O Gene regulation allows such organisms to do things that will allo ...
Chapter 13.1 and 13.2 RNA, Ribosomes, and Protein Synthesis
... – Each codon attracts an anticodon aka tRNA – tRNA carries an amino acid. – Amino acids bond and move along the mRNA – Continues until reaches STOP codon and forms polypeptide and mRNA is released. ...
... – Each codon attracts an anticodon aka tRNA – tRNA carries an amino acid. – Amino acids bond and move along the mRNA – Continues until reaches STOP codon and forms polypeptide and mRNA is released. ...
Our laboratory studies the regulation of gene expression in
... expression in a position-dependent, promoter-independent (silencing) manner. More recently, we have identified histone methyltransferases that also affect silencing. We are especially interested to know how these and other covalent histone modifications affect accessibility of chromatin to the trans ...
... expression in a position-dependent, promoter-independent (silencing) manner. More recently, we have identified histone methyltransferases that also affect silencing. We are especially interested to know how these and other covalent histone modifications affect accessibility of chromatin to the trans ...
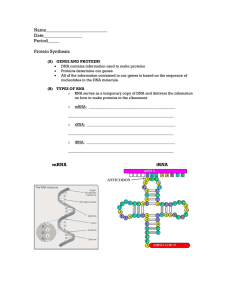
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
Transcription Protein Synthesis So what does it mean? Transcription
... cells, and they act as enzymes • Geneticists accept that the basic mechanism of reading and expressing genes is DNA RNA protein. • This chain of events occurs in all living things, from bacteria to humans. • Scientists refer to this mechanism as the central dogma of biology: DNA codes for RNA, w ...
... cells, and they act as enzymes • Geneticists accept that the basic mechanism of reading and expressing genes is DNA RNA protein. • This chain of events occurs in all living things, from bacteria to humans. • Scientists refer to this mechanism as the central dogma of biology: DNA codes for RNA, w ...
NUCLEIC ACID
... SIMPLE FACTS ABOUT DNA AND GENES • The information for development and specific function is stored in genes. • A gene is portion of genetic information definable according to the structure and functions. • Genes lie on chromosomes in the nuclei of the cells. • Chromosomes are made up of long chains ...
... SIMPLE FACTS ABOUT DNA AND GENES • The information for development and specific function is stored in genes. • A gene is portion of genetic information definable according to the structure and functions. • Genes lie on chromosomes in the nuclei of the cells. • Chromosomes are made up of long chains ...
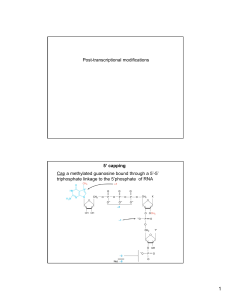
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... base-pairing between antisense transcripts and mRNAs become targets for ribonucleases, which degrade dsRNAs into small fragments of about 21-25bp. This process appears to be part of the natural defense against viral dsRNAs. Small dsRNAs may serve to target nuclear copies of the gene for methylation, ...
... base-pairing between antisense transcripts and mRNAs become targets for ribonucleases, which degrade dsRNAs into small fragments of about 21-25bp. This process appears to be part of the natural defense against viral dsRNAs. Small dsRNAs may serve to target nuclear copies of the gene for methylation, ...
Honors Biology
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
Central Dogma WebQuest - Life Science
... 1. What is the first step in decoding a cell's genetic information? _______________________ 2. List one way that RNA is different from DNA. ____________________________________________ 3. What is the function of mRNA? ________________________________________________________ 4. What is the function o ...
... 1. What is the first step in decoding a cell's genetic information? _______________________ 2. List one way that RNA is different from DNA. ____________________________________________ 3. What is the function of mRNA? ________________________________________________________ 4. What is the function o ...
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... The process of removing the intron is called splicing The intron is looped out and cut away from the exons by snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoprotein) (snurps) The exons are spliced together to produce the translatable mRNA The mRNA is now ready to leave the nucleus and be translated into protein ...
... The process of removing the intron is called splicing The intron is looped out and cut away from the exons by snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoprotein) (snurps) The exons are spliced together to produce the translatable mRNA The mRNA is now ready to leave the nucleus and be translated into protein ...
Slide 1 - Piscataway High School
... Each strand acts as a template to make a new one. Both strands are copied at the same time, but in the opposite direction. ...
... Each strand acts as a template to make a new one. Both strands are copied at the same time, but in the opposite direction. ...
RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 12-3
... Enzyme binds to places with specific DNA PROMOTERS sequences called _______________. RNA POLYMERASE PROMOTERS tell _________________ where to start. Signals at the end of the gene code cause transcription to _____ stop . http://images2.clinicaltools.com/images/gene/dna_versus_rna_reversed.jpg ...
... Enzyme binds to places with specific DNA PROMOTERS sequences called _______________. RNA POLYMERASE PROMOTERS tell _________________ where to start. Signals at the end of the gene code cause transcription to _____ stop . http://images2.clinicaltools.com/images/gene/dna_versus_rna_reversed.jpg ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Changes in the DNA sequence that affect genetic information Gene mutations – result from changes in a single gene. A gene carries the “recipe” for a single protein. Chromosomal mutations – involve changes in whole chromosomes ...
... Changes in the DNA sequence that affect genetic information Gene mutations – result from changes in a single gene. A gene carries the “recipe” for a single protein. Chromosomal mutations – involve changes in whole chromosomes ...
Section 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it relea ...
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it relea ...
Chapter 17: Transcription, RNA Processing, and Translation
... Where does the component bind and how is this assisting the RNA Pol core enzyme? 5.) Once the holoenzyme is bound to the DNA, what change must occur in the DNA helix in order for RNA Pol to transcribe a single RNA strand? What enzyme causes this change? 6.) Is the reaction catalyzed by RNA Polymeras ...
... Where does the component bind and how is this assisting the RNA Pol core enzyme? 5.) Once the holoenzyme is bound to the DNA, what change must occur in the DNA helix in order for RNA Pol to transcribe a single RNA strand? What enzyme causes this change? 6.) Is the reaction catalyzed by RNA Polymeras ...