Biochemistry 2000 Sample Questions 5 Transport, Carbohydrates, Metabolism
... (a) The Ca2+-ATPase pumps Ca2+ out of the cytosol as ATP is hydrolysed. (b) The (H+-K+)-ATPase of the gastric pumps protons out of the cell. Each proton is accompanied by the transport of a K+ into the cell. (c) Subsequently to the action of the describe (H+-K+)-ATPase, the K+ is again transported o ...
... (a) The Ca2+-ATPase pumps Ca2+ out of the cytosol as ATP is hydrolysed. (b) The (H+-K+)-ATPase of the gastric pumps protons out of the cell. Each proton is accompanied by the transport of a K+ into the cell. (c) Subsequently to the action of the describe (H+-K+)-ATPase, the K+ is again transported o ...
Respiration: Occurs in two places in the cell Cytoplasm and
... What do I need to know about glycolysis? Take place in cytoplasm 6C sugar (glucose) ...
... What do I need to know about glycolysis? Take place in cytoplasm 6C sugar (glucose) ...
Exam 3: Biochem 2 Fill in the Blank
... i. Fats have ____more_________ (more/less) kcal per gram than carbohydrate and proteins ii. Locations were fats are made________Liver_________ and _______adipocytes________ 1. Due to the increased NADPH made in these cells during the shunt iii. Location in the cell of synthesis:___cytosol___________ ...
... i. Fats have ____more_________ (more/less) kcal per gram than carbohydrate and proteins ii. Locations were fats are made________Liver_________ and _______adipocytes________ 1. Due to the increased NADPH made in these cells during the shunt iii. Location in the cell of synthesis:___cytosol___________ ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis Chapter 28, Stryer Short Course
... membrane • Prostaglandins as signal molecules • Cholesterol and derivatives ...
... membrane • Prostaglandins as signal molecules • Cholesterol and derivatives ...
L7c RESPIRATION Ch9 etc regulation
... glycerol & fatty acids glycerol (3C) PGAL glycolysis fatty acids 2C acetyl acetyl Krebs ...
... glycerol & fatty acids glycerol (3C) PGAL glycolysis fatty acids 2C acetyl acetyl Krebs ...
Chapter 23 - Evangel University
... Essential Amino Acids • The biosynthesis of proteins requires the presence of all the constituent amino acids • Some species, including humans, cannot produce all of the amino acids and they must come from ____________ and are called essential amino acids ...
... Essential Amino Acids • The biosynthesis of proteins requires the presence of all the constituent amino acids • Some species, including humans, cannot produce all of the amino acids and they must come from ____________ and are called essential amino acids ...
Contents - Garland Science
... Further evidence of the functions of glutamine synthetase isoenzymes has come from studies of mutants and transgenic plants ...
... Further evidence of the functions of glutamine synthetase isoenzymes has come from studies of mutants and transgenic plants ...
Type WBLT Name Here Audience and Learning Goals
... chemical compound formed with the energy released from food and stored in all cells, particularly muscles. Only from the energy released by the breakdown of this compound can the cells perform work. The breakdown of ATP produces energy and ADP. ...
... chemical compound formed with the energy released from food and stored in all cells, particularly muscles. Only from the energy released by the breakdown of this compound can the cells perform work. The breakdown of ATP produces energy and ADP. ...
General Chemistry 110 Quiz 1
... a. A metabolic branch point of glycolysis (prior to pyruvate). Discuss the metabolic choices and how the cell decides which path to follow. b. The hormonal regulation of blood glucose and the effect it has on glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and glycogen metabolism. Mention any organs involved in this p ...
... a. A metabolic branch point of glycolysis (prior to pyruvate). Discuss the metabolic choices and how the cell decides which path to follow. b. The hormonal regulation of blood glucose and the effect it has on glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and glycogen metabolism. Mention any organs involved in this p ...
7 CellRespiration
... 1. What is the ultimate purpose of catabolic reactions like cellular respiration? What is the delta G of cell respiration --- is it exergonic or endergonic overall? Is it an oxidative or reductive process? 2. What does it mean to say that glucose is oxidized? What are the products of oxidation? How ...
... 1. What is the ultimate purpose of catabolic reactions like cellular respiration? What is the delta G of cell respiration --- is it exergonic or endergonic overall? Is it an oxidative or reductive process? 2. What does it mean to say that glucose is oxidized? What are the products of oxidation? How ...
File
... b. glycolysis occurs only in photosynthesis, while oxidative respiration is part of cellular respiration. c. glycolysis occurs in the absence of oxygen, while oxidative respiration requires oxygen. d. Both of these terms are different names for the same process. 15. Which of the following is not for ...
... b. glycolysis occurs only in photosynthesis, while oxidative respiration is part of cellular respiration. c. glycolysis occurs in the absence of oxygen, while oxidative respiration requires oxygen. d. Both of these terms are different names for the same process. 15. Which of the following is not for ...
Fig. 5-1
... some must use oxygen to survive. Microbes that can use oxygen if it is available but do not need it are facultative anaerobes. Aerobes do produce some energy during glycolysis, however, aerobes use glycolysis as a prelude to aerobic respiration – a much more productive process which requires oxygen. ...
... some must use oxygen to survive. Microbes that can use oxygen if it is available but do not need it are facultative anaerobes. Aerobes do produce some energy during glycolysis, however, aerobes use glycolysis as a prelude to aerobic respiration – a much more productive process which requires oxygen. ...
Fermentation
... sugars. Small amounts of ethanol and isopropanol may also be formed. • Butanol and acetone were discovered as the main end products of fermentation by Clostridium ...
... sugars. Small amounts of ethanol and isopropanol may also be formed. • Butanol and acetone were discovered as the main end products of fermentation by Clostridium ...
The following two questions relate to a cell that has an electrical
... a. are attached to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane b. are attached to the outer surface of the mitochondria c. are attached to the outer (cytosolic) surface of the endoplasmic reticulum d. are attached to the interior (nuclear) surface of the nuclear envelope e. are attached to the in ...
... a. are attached to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane b. are attached to the outer surface of the mitochondria c. are attached to the outer (cytosolic) surface of the endoplasmic reticulum d. are attached to the interior (nuclear) surface of the nuclear envelope e. are attached to the in ...
Cell Respiration RG
... 4. In cellular respiration, what is being oxidized and what is being reduced? ...
... 4. In cellular respiration, what is being oxidized and what is being reduced? ...
MCB207_2 - MB207Jan2010
... macromolecules that are require for cells growth and function. - cells are 70% water (life depends almost exclusively on chemical reactions that take place in aqueous solution) - cell chemistry is enormously complex: even the simplest cell is vastly more complicated in its chemistry than any other c ...
... macromolecules that are require for cells growth and function. - cells are 70% water (life depends almost exclusively on chemical reactions that take place in aqueous solution) - cell chemistry is enormously complex: even the simplest cell is vastly more complicated in its chemistry than any other c ...
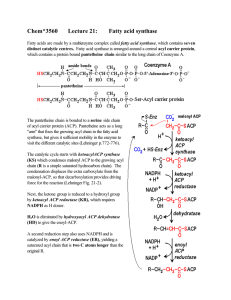
Chem*3560 Lecture 21: Fatty acid synthase
... Overall cost of synthesis in bacteria includes 7 ATP as the energy cost of making 7 malonyl-CoA: acetyl CoA carboxylase 7 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP + 7 CO2 + 7 H2 O → 7 malonyl-CoA + 7 H+ + 7 ADP + 7 Pi Overall cost of synthesis in mammalian cells includes an additional 8 ATP required for citrate lyase cit ...
... Overall cost of synthesis in bacteria includes 7 ATP as the energy cost of making 7 malonyl-CoA: acetyl CoA carboxylase 7 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP + 7 CO2 + 7 H2 O → 7 malonyl-CoA + 7 H+ + 7 ADP + 7 Pi Overall cost of synthesis in mammalian cells includes an additional 8 ATP required for citrate lyase cit ...
2nd Phase of Glycolysis
... NADH produced from one molecule of glucose during glycolysis have three possible metabolic fates. Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is oxidized, with the loss of CO2 to produce acetyl-CoA and NADH. AcetylCoA then enters the citric acid cycle where it is completely oxidized into CO2 and H2O. Under a ...
... NADH produced from one molecule of glucose during glycolysis have three possible metabolic fates. Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is oxidized, with the loss of CO2 to produce acetyl-CoA and NADH. AcetylCoA then enters the citric acid cycle where it is completely oxidized into CO2 and H2O. Under a ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.