Purified Mouse Anti-ATP Synthase α — 612516
... ATP synthase is a large enzyme complex that uses an electrochemical H+ or Na+ gradient to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi, providing the organism with the ATP needed for energy. The complex consists of two major units, F0 and F1. F0 is embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria and, due to it ...
... ATP synthase is a large enzyme complex that uses an electrochemical H+ or Na+ gradient to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi, providing the organism with the ATP needed for energy. The complex consists of two major units, F0 and F1. F0 is embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria and, due to it ...
File
... 1) Glycolysis and Fermentation a) Harvesting Chemical Energy Cellular respiration is the complex precess in which cells make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by breaking down organic compounds. Both autotrophs and heterotrophy undergo cellular respiration to breakdown organic compounds into simpler ...
... 1) Glycolysis and Fermentation a) Harvesting Chemical Energy Cellular respiration is the complex precess in which cells make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by breaking down organic compounds. Both autotrophs and heterotrophy undergo cellular respiration to breakdown organic compounds into simpler ...
Chapter 9 Modified
... glucose NADH electron transport chain proton-motive force ATP • About 34% of the energy in a glucose molecule is transferred to ATP during cellular respiration, making about 32 ATP • There are several reasons why the number of ATP is not known exactly © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... glucose NADH electron transport chain proton-motive force ATP • About 34% of the energy in a glucose molecule is transferred to ATP during cellular respiration, making about 32 ATP • There are several reasons why the number of ATP is not known exactly © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
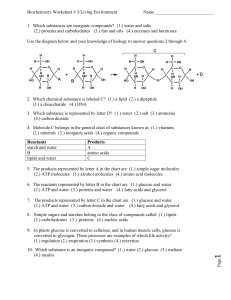
1. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
... 13. The reverse reaction indicated by arrow E illustrates (1.) chemical digestion (2.) synthesis (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration ...
... 13. The reverse reaction indicated by arrow E illustrates (1.) chemical digestion (2.) synthesis (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration ...
doc
... a stepwise cascade much like going down a staircase. The path that electrons take on their way down from glucose to oxygen involves many steps. The first step is an electron acceptor called NAD+. ...
... a stepwise cascade much like going down a staircase. The path that electrons take on their way down from glucose to oxygen involves many steps. The first step is an electron acceptor called NAD+. ...
enviro bio cellular respiration powerpoint 2013
... Alcoholic Fermentation: the process performed by yeast and some bacteria to convert sugar into ATP when there is no oxygen present. This is a TYPE of anaerobic respiration. The products are alcohol, CO2, and ATP. ...
... Alcoholic Fermentation: the process performed by yeast and some bacteria to convert sugar into ATP when there is no oxygen present. This is a TYPE of anaerobic respiration. The products are alcohol, CO2, and ATP. ...
Unit_1_the_living_world part C
... because it is an essential part of biological molecules such as proteins, and nucleic acids (RNA/DNA) The atmosphere is composed of 78% nitrogen, N2, a two-atom molecule However atmospheric nitrogen, N2, is unstable and needs to be “fixed” in order for it to be “used” by organisms ...
... because it is an essential part of biological molecules such as proteins, and nucleic acids (RNA/DNA) The atmosphere is composed of 78% nitrogen, N2, a two-atom molecule However atmospheric nitrogen, N2, is unstable and needs to be “fixed” in order for it to be “used” by organisms ...
Communication
... impermeable to reduced NAD. For this reason a shunt mechanism moves hydrogen ions from reduced NAD made during glycolysis, to the matrix side of the inner mitochondrial membrane. The hydrogens are carried in by another chemical than then becomes reoxidised, reducing NAD that is already in the mitoch ...
... impermeable to reduced NAD. For this reason a shunt mechanism moves hydrogen ions from reduced NAD made during glycolysis, to the matrix side of the inner mitochondrial membrane. The hydrogens are carried in by another chemical than then becomes reoxidised, reducing NAD that is already in the mitoch ...
The simplest enzyme revisited: The chicken and
... network. The distributions and flows with the overlay will be vastly different from the uncatalyzed network. The distribution is an emergent feature of the catalytic property of small molecules. Because both amino acids and nucleotides have molecules of catalytic potential, the chicken and egg argume ...
... network. The distributions and flows with the overlay will be vastly different from the uncatalyzed network. The distribution is an emergent feature of the catalytic property of small molecules. Because both amino acids and nucleotides have molecules of catalytic potential, the chicken and egg argume ...
Consortium for Educational Communication
... separate from each other as both follow different pathways. In anaerobic respiration, the process involves the transfer of electrons through a system of chain system in the membrane of the cell. Fermentation takes place when a co-enzyme, NADH reduces the pyruvate to form the organic compound. It is ...
... separate from each other as both follow different pathways. In anaerobic respiration, the process involves the transfer of electrons through a system of chain system in the membrane of the cell. Fermentation takes place when a co-enzyme, NADH reduces the pyruvate to form the organic compound. It is ...
BHS 150.1 – Biochemistry II Date: 2/8/2013, 2sndhalf Notetaker: Kim
... 9. What is the function of connexins in the lens? cell-cell communication ...
... 9. What is the function of connexins in the lens? cell-cell communication ...
Cellular Respiration
... –Probably evolved in ancient prokaryotes before there was oxygen in the atmosphere ...
... –Probably evolved in ancient prokaryotes before there was oxygen in the atmosphere ...
Overview
... Unit Vocabulary: Chapter 8 Metabolism, metabolic pathway, catabolic pathway, anabolic pathway, bioenergetics, energy, kinetic energy, heat (thermal energy), potential energy, chemical energy, first law of thermodynamics, entropy, second law of thermodynamics, free energy, exergonic reaction, endergo ...
... Unit Vocabulary: Chapter 8 Metabolism, metabolic pathway, catabolic pathway, anabolic pathway, bioenergetics, energy, kinetic energy, heat (thermal energy), potential energy, chemical energy, first law of thermodynamics, entropy, second law of thermodynamics, free energy, exergonic reaction, endergo ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... carbon. 2. The enzymes unique to omega oxidation are located the ER of liver and kidney 3. The preferred substrate are fatty acid of 10 to 12 carbon. 4. The first step introduces a hydroxyl group on to omega carbon by mixed function oxidase involved in cytochrome p450 and NADPH 5. Produce a carboxyl ...
... carbon. 2. The enzymes unique to omega oxidation are located the ER of liver and kidney 3. The preferred substrate are fatty acid of 10 to 12 carbon. 4. The first step introduces a hydroxyl group on to omega carbon by mixed function oxidase involved in cytochrome p450 and NADPH 5. Produce a carboxyl ...
2008b(12): Detail the protective and regulatory roles of the liver
... - catabolic functions: o CHO: glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o fats: ↑lipolysis ketone body formation bile acid formation (for fat absorption) o proteins: ammonium formation (via glutathione synthesis for transport to PCT in ...
... - catabolic functions: o CHO: glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o fats: ↑lipolysis ketone body formation bile acid formation (for fat absorption) o proteins: ammonium formation (via glutathione synthesis for transport to PCT in ...
univERsity oF copEnhAGEn
... are partly used as substrates for energy production when there is reduced pyruvate availability due to hypercapnia. It is proposed that amino acid carbon is made available for oxidation via transamination (aspartate aminotransferase reaction) and deamination (glutamate dehydrogenase reaction) and th ...
... are partly used as substrates for energy production when there is reduced pyruvate availability due to hypercapnia. It is proposed that amino acid carbon is made available for oxidation via transamination (aspartate aminotransferase reaction) and deamination (glutamate dehydrogenase reaction) and th ...
PPT Nts Cellular Respiration
... Cellular respiration: breaks down 2 pyruvate molecules into 6CO2 & 6 H2O and produces 32 ATP in the mitochondria https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pOfyuoa0Ywc – Mitochondria structure ...
... Cellular respiration: breaks down 2 pyruvate molecules into 6CO2 & 6 H2O and produces 32 ATP in the mitochondria https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pOfyuoa0Ywc – Mitochondria structure ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... Fermentation is the breakdown of pyruvic acid in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic) to make ATP. ...
... Fermentation is the breakdown of pyruvic acid in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic) to make ATP. ...
Chapter6summaryHO
... The reducing power generated is used to move electrons through an electron transport chain, generate a PMF and make ATP. Respiration: Electrons from Glucose are fed into electron transport chain to generate PMF. Aerobic respiration: Oxygen is terminal electron acceptor. Anaerobic respiration: simila ...
... The reducing power generated is used to move electrons through an electron transport chain, generate a PMF and make ATP. Respiration: Electrons from Glucose are fed into electron transport chain to generate PMF. Aerobic respiration: Oxygen is terminal electron acceptor. Anaerobic respiration: simila ...
Bell work
... and Krebs to create ATP • Electron Transport - NAPH and FADH pass from carrier to carrier to power hydrogen pumps and create a hydrogen gradient in inter-membrane space! • ATP Production ATP synthase allows H to flow through like turbine (into matix) and produce ATP ...
... and Krebs to create ATP • Electron Transport - NAPH and FADH pass from carrier to carrier to power hydrogen pumps and create a hydrogen gradient in inter-membrane space! • ATP Production ATP synthase allows H to flow through like turbine (into matix) and produce ATP ...
Chapter 29 The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
... Sugars and fat components are broken down in steps ...
... Sugars and fat components are broken down in steps ...
Learning Guide: Origins of Life
... 3. Identify the source of the electrons that travel down the electron transport chain. Explain why oxygen is the final electron acceptor in aerobic cellular respiration. 4. Create a graphic organizer that illustrates the reactants and products for each of the major stages of cellular respiration: (a ...
... 3. Identify the source of the electrons that travel down the electron transport chain. Explain why oxygen is the final electron acceptor in aerobic cellular respiration. 4. Create a graphic organizer that illustrates the reactants and products for each of the major stages of cellular respiration: (a ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.