File
... (including insects, spiders, and crustaceans). Chitin also forms the structural support for the cell walls of many fungi. ...
... (including insects, spiders, and crustaceans). Chitin also forms the structural support for the cell walls of many fungi. ...
Vitamin A - Denton ISD
... 2. The building block of protein are amino acids. 3. 1gram = 4 Calories 4. Enzymes 5. Regulatory & transport functions 1. Insulin 2. hemoglobin 6. Body only makes 12 AA 1. Must include the other 8 AA from your diet ...
... 2. The building block of protein are amino acids. 3. 1gram = 4 Calories 4. Enzymes 5. Regulatory & transport functions 1. Insulin 2. hemoglobin 6. Body only makes 12 AA 1. Must include the other 8 AA from your diet ...
Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry and Applications
... Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry and Applications 3. Chemical Reactivity: Important reactant in metabolic processes such as digestion. 4. Cushioning: Important with CSF (cerebral-spinal fluid) for cushioning brain and with amniotic fluid to protect fetus. B. Salts & Acids and Bases: Electrolytes (dissoci ...
... Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry and Applications 3. Chemical Reactivity: Important reactant in metabolic processes such as digestion. 4. Cushioning: Important with CSF (cerebral-spinal fluid) for cushioning brain and with amniotic fluid to protect fetus. B. Salts & Acids and Bases: Electrolytes (dissoci ...
Course Syllabus AG 408 – Nutritional Biochemistry Spring Semester, 2013 MWF 12:00-12:50
... the energetics of metabolism; the structure and metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids; and the integration of metabolic systems. Included also will be the chemistry of nitrogenous bases and how transcription and translation is accomplished on the cellular level. Student Learning Outcomes ...
... the energetics of metabolism; the structure and metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids; and the integration of metabolic systems. Included also will be the chemistry of nitrogenous bases and how transcription and translation is accomplished on the cellular level. Student Learning Outcomes ...
Fatigue and the Recovery Process
... of the exercise Oxygen is needed to break down the lactic acid back to Pyruvate. (LA +O2 = Pyruvate) Pyruvate can then enter the aerobic system and leave as CO2 and water Lactic acid can also be converted back into glycogen and stored in the liver or muscle What can an active recovery do? ...
... of the exercise Oxygen is needed to break down the lactic acid back to Pyruvate. (LA +O2 = Pyruvate) Pyruvate can then enter the aerobic system and leave as CO2 and water Lactic acid can also be converted back into glycogen and stored in the liver or muscle What can an active recovery do? ...
Biomolecules
... Protein: the work horse of the biomolecules. These molecules carry out most of the functions of the cell, act as building blocks, and allow organisms to move and do many ...
... Protein: the work horse of the biomolecules. These molecules carry out most of the functions of the cell, act as building blocks, and allow organisms to move and do many ...
Carbohydrate: Carbohydrates are a vital component of energy for
... converted into energy very quickly. Complex carbohydrates like spaghetti, and pasta, take longer to absorb into the body. Consumed at appropriate times maximises athletic performance. Be cautious if overloading with carbohydrates and not exercising, glycogen remains in the body and is then converted ...
... converted into energy very quickly. Complex carbohydrates like spaghetti, and pasta, take longer to absorb into the body. Consumed at appropriate times maximises athletic performance. Be cautious if overloading with carbohydrates and not exercising, glycogen remains in the body and is then converted ...
Chapter 7 Review Name: Date: Question Answer Process that
... 24. The Krebs cycle occurs in the __ 25. Oxygen, electrons and protons form ___ 26. Aerobic respiration produces a total of ___ ATP. Fermentation produces a total of ___ ATP 27. The enzyme that forms ATP is called __ 28. Cellular respiration is ___% efficient in the conversion of the energy in gluco ...
... 24. The Krebs cycle occurs in the __ 25. Oxygen, electrons and protons form ___ 26. Aerobic respiration produces a total of ___ ATP. Fermentation produces a total of ___ ATP 27. The enzyme that forms ATP is called __ 28. Cellular respiration is ___% efficient in the conversion of the energy in gluco ...
Chapter 26 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • Fats contain about 9 kcal/g • Carbohydrates and proteins, about 4 kcal/g – sugar and alcohol are “empty” calories -- few nutrients ...
... • Fats contain about 9 kcal/g • Carbohydrates and proteins, about 4 kcal/g – sugar and alcohol are “empty” calories -- few nutrients ...
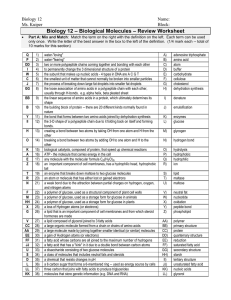
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... a lipid composed of glycerol joined to 3 fatty acids a large organic molecule formed from a chain or chains of amino acids a large molecule made by joining together smaller identical (or similar) molecules a gain of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a fatty acid whose carbons are all joined to the maxim ...
... a lipid composed of glycerol joined to 3 fatty acids a large organic molecule formed from a chain or chains of amino acids a large molecule made by joining together smaller identical (or similar) molecules a gain of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a fatty acid whose carbons are all joined to the maxim ...
Medical Biology Cellular Metabolism
... organisms in order to maintain life. Cellular metabolism involves complex sequences of controlled biochemical reactions. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to environmental changes. Metabolic pathway is divided to: Catabolism: chemical react ...
... organisms in order to maintain life. Cellular metabolism involves complex sequences of controlled biochemical reactions. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to environmental changes. Metabolic pathway is divided to: Catabolism: chemical react ...
Summer 2010 - Wake Forest University
... and Vicky Minderhout (ISBN: 978-1-60263-524-1) for POGIL (Process oriented guided-inquiry learning). Additional required reading is “The Double Helix” by James Watson. The library has several copies, and it is typically available at used bookstores. Attendance/ Academic integrity: Attendance is requ ...
... and Vicky Minderhout (ISBN: 978-1-60263-524-1) for POGIL (Process oriented guided-inquiry learning). Additional required reading is “The Double Helix” by James Watson. The library has several copies, and it is typically available at used bookstores. Attendance/ Academic integrity: Attendance is requ ...
syllabus - Wofford
... We didn’t have much time to consider lipid metabolism in B214, but we will be able to concentrate on them in this course. You will need to know the structures of several major lipid compounds. We will emphasize the effects of fat and cholesterol metabolism on health. Week of ...
... We didn’t have much time to consider lipid metabolism in B214, but we will be able to concentrate on them in this course. You will need to know the structures of several major lipid compounds. We will emphasize the effects of fat and cholesterol metabolism on health. Week of ...
Macromolecules - Nolte Science
... Starches =common storage form of glucose (many glucose molecules) ...
... Starches =common storage form of glucose (many glucose molecules) ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) an ...
... Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) an ...
Aerobic Energy Systems
... This occurs in the mitochondria and produces CO2, H2O, and energy. The advantages of aerobic energy production is that there are no fatiguing by-products, the energy sources are usually abundant and lots of ATP can be produced. The breakdown of glucose into energy (ATP) involves 3 stages: glycolysis ...
... This occurs in the mitochondria and produces CO2, H2O, and energy. The advantages of aerobic energy production is that there are no fatiguing by-products, the energy sources are usually abundant and lots of ATP can be produced. The breakdown of glucose into energy (ATP) involves 3 stages: glycolysis ...
PTHR18866 CARBOXYLASE:PYRUVATE/ACETYL
... • After pruning, the alignment is good • “Biotin carboxylase activity” can be propagated to all • Could also propagate “biotin binding” and “ATP binding” ...
... • After pruning, the alignment is good • “Biotin carboxylase activity” can be propagated to all • Could also propagate “biotin binding” and “ATP binding” ...
Carbon Compounds
... This is a single nucleotide that carries energy in cells. – This is the “currency” of cells. – When food molecules (glucose) are broken down inside of cells (cell respiration), some of the energy in the molecules is stored temporarily in ATP. – Some of this energy is used by cell. All cells need a s ...
... This is a single nucleotide that carries energy in cells. – This is the “currency” of cells. – When food molecules (glucose) are broken down inside of cells (cell respiration), some of the energy in the molecules is stored temporarily in ATP. – Some of this energy is used by cell. All cells need a s ...
Chapter 2: Chemistry of Life
... Muscles – contractile proteins actin & myosin Enzymes – organic catalysts Amino acids are monomers and are joined together by peptide bonds Polymers are polypeptides with 3 levels of structures (fig 2.13 page 28) – heat, low pH can cause unraveling ...
... Muscles – contractile proteins actin & myosin Enzymes – organic catalysts Amino acids are monomers and are joined together by peptide bonds Polymers are polypeptides with 3 levels of structures (fig 2.13 page 28) – heat, low pH can cause unraveling ...
Review 3
... (deoxy)ribonucleotides • Carbamoyl phosphate and urea • Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • PRPP ...
... (deoxy)ribonucleotides • Carbamoyl phosphate and urea • Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • PRPP ...
question Examination questions: Digestion and intermediary
... (glc, gal, fru, pentoses; mtb in eneterocytes) (general formula, properties – oils, fat → types of fatty acids) (general structure, properties, functions in a human body) (structure formula; transport in blood – ...
... (glc, gal, fru, pentoses; mtb in eneterocytes) (general formula, properties – oils, fat → types of fatty acids) (general structure, properties, functions in a human body) (structure formula; transport in blood – ...
cellular-respiration-notes-2016
... compressing a spring. The tightly coiled spring has potential energy. When the compressed spring relaxes, its potential energy is released. The spring's kinetic energy can be used to perform work such as pushing a block attached to one end of the spring. The phosphate bonds are symbolized by springs ...
... compressing a spring. The tightly coiled spring has potential energy. When the compressed spring relaxes, its potential energy is released. The spring's kinetic energy can be used to perform work such as pushing a block attached to one end of the spring. The phosphate bonds are symbolized by springs ...
Network Reconstruction Slides
... Lysine Biosynthesis: Gap analysis Example of Integrated Reconstruction Process : Non-Gene • Genome annotation reveals incomplete pathway for lysine biosynthesis Associated • Gap analysis indicates no other routes for lysine production Reactions • Growth physiology data indicates no auxotrophic requ ...
... Lysine Biosynthesis: Gap analysis Example of Integrated Reconstruction Process : Non-Gene • Genome annotation reveals incomplete pathway for lysine biosynthesis Associated • Gap analysis indicates no other routes for lysine production Reactions • Growth physiology data indicates no auxotrophic requ ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.