Activity 3: Mechanisms for Evolution
... to be variation in a population’s gene pool. Variation means that there are multiple alleles in a population. Some changes in the environment will result in individuals with alleles that code for traits that suit the new environment and therefore be more fit to survive. The survivors will pass on th ...
... to be variation in a population’s gene pool. Variation means that there are multiple alleles in a population. Some changes in the environment will result in individuals with alleles that code for traits that suit the new environment and therefore be more fit to survive. The survivors will pass on th ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... DNA — (deoxyribonucleic acid) A specialized molecule that contains the genetic information that allows characteristics to be passed from parents to offspring. The information contained in the DNA molecule provides a “blueprint,” or a set of codes, for building other molecules used by the cell. ...
... DNA — (deoxyribonucleic acid) A specialized molecule that contains the genetic information that allows characteristics to be passed from parents to offspring. The information contained in the DNA molecule provides a “blueprint,” or a set of codes, for building other molecules used by the cell. ...
CH16 PowerPoint - Deer Creek Middle School
... Darwin’s Theory = Evolution by means of natural selection ...
... Darwin’s Theory = Evolution by means of natural selection ...
Microevolution Evolution within a population
... If p = allele frequency of dominant allele (R), then p2 = frequency of homozygous genotype (RR) If q = allele frequency of recessive allele (r), then q2 = frequency of homozygous genotype (rr) If you complete the square, then the frequency of ...
... If p = allele frequency of dominant allele (R), then p2 = frequency of homozygous genotype (RR) If q = allele frequency of recessive allele (r), then q2 = frequency of homozygous genotype (rr) If you complete the square, then the frequency of ...
RAFT: Genetics - Catawba County Schools
... school-level genetics unit. They are listed in order of difficulty, with the first being the most difficult. Students may complete them individually or with partners. Standards: Investigate and understand that organisms reproduce and transmit genetic information to new generations Utilize approp ...
... school-level genetics unit. They are listed in order of difficulty, with the first being the most difficult. Students may complete them individually or with partners. Standards: Investigate and understand that organisms reproduce and transmit genetic information to new generations Utilize approp ...
Development Through the Lifespan
... Development Through the Lifespan Chapter 2 Biological and Environmental Foundations ...
... Development Through the Lifespan Chapter 2 Biological and Environmental Foundations ...
Mutation - Biology1
... In a population of birds, intermediate Beak size is selected against, and both Very small and very large beak sizes are Favored. What type of selection is this An example of? ...
... In a population of birds, intermediate Beak size is selected against, and both Very small and very large beak sizes are Favored. What type of selection is this An example of? ...
Frost Resistant Crops
... During the genetic manipulation process, the location where a gene is inserted into an organism's genetic code is uncontrollable. Also a stable expression of the gene into the new genetically engineered organism is not guaranteed. This is why when scientists tried to clone an animal; they ended up w ...
... During the genetic manipulation process, the location where a gene is inserted into an organism's genetic code is uncontrollable. Also a stable expression of the gene into the new genetically engineered organism is not guaranteed. This is why when scientists tried to clone an animal; they ended up w ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
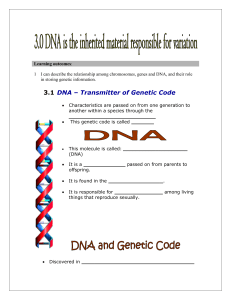
... 1 I can describe the relationship among chromosomes, genes and DNA, and their role in storing genetic information. ...
... 1 I can describe the relationship among chromosomes, genes and DNA, and their role in storing genetic information. ...
Genetics - Bill Nye ANSWERS
... Hemophilia is a ‘sex-linked’ disease, because it is caused by a defective gene on an X chromosome. What organism did Barbara McClintock study? corn Transposons are jumping genes. Viruses are made up of 2 things. What are they? Protein shell (caspid) and DNA Hershey and Chase studied bacteriophage vi ...
... Hemophilia is a ‘sex-linked’ disease, because it is caused by a defective gene on an X chromosome. What organism did Barbara McClintock study? corn Transposons are jumping genes. Viruses are made up of 2 things. What are they? Protein shell (caspid) and DNA Hershey and Chase studied bacteriophage vi ...
B1: You and Your Genes
... the phenotype is the feature or features that result from this combination and interaction with the environment Part 2: how genetic information is inherited I know that....... that the two versions of each gene in a pair of chromosomes are called alleles alleles can be the same (homozygous) alleles ...
... the phenotype is the feature or features that result from this combination and interaction with the environment Part 2: how genetic information is inherited I know that....... that the two versions of each gene in a pair of chromosomes are called alleles alleles can be the same (homozygous) alleles ...
Lecture 13
... 9 to 1 ratio of men to women with violent crimes In this sense the Y chromosome has a VERY high association with violent crimes, it is a genetic marker in this sense But, does the Y chromosome cause crime????? This is just a statistical association HOW do genes and environment interact? Y is a predi ...
... 9 to 1 ratio of men to women with violent crimes In this sense the Y chromosome has a VERY high association with violent crimes, it is a genetic marker in this sense But, does the Y chromosome cause crime????? This is just a statistical association HOW do genes and environment interact? Y is a predi ...
Speciation Practice Free Response Scoring Guidelines
... Hereditary variations are essential to the evolution of populations. A. Describe the different types of hereditary variability. B. Explain how this variability can lead to the origin and maintenance of species. PART (A) SCORING GUIDE (6PTS MAX) MUTATIONS changes in the DNA A single mutation can ...
... Hereditary variations are essential to the evolution of populations. A. Describe the different types of hereditary variability. B. Explain how this variability can lead to the origin and maintenance of species. PART (A) SCORING GUIDE (6PTS MAX) MUTATIONS changes in the DNA A single mutation can ...
Section 16-1 Genes and Variation (pages 393-396)
... c. They always affect an organism’s phenotype. d. They always affect an organism’s fitness. 11. Is the following sentence true or false? Most heritable differences are due to gene shuffling that occurs during the production of gametes. 12. Circle the letter of each choice that is true about sexual r ...
... c. They always affect an organism’s phenotype. d. They always affect an organism’s fitness. 11. Is the following sentence true or false? Most heritable differences are due to gene shuffling that occurs during the production of gametes. 12. Circle the letter of each choice that is true about sexual r ...
Diapositiva 1 - Liceo Statale Cagnazzi
... characteristics) will have more possibilities to survive and so to transmit their descendants the favorable characteristics. From generation to generation the advantageous characteristcs will become dominant among populations. This is the natural selection that can produce some changes in a populati ...
... characteristics) will have more possibilities to survive and so to transmit their descendants the favorable characteristics. From generation to generation the advantageous characteristcs will become dominant among populations. This is the natural selection that can produce some changes in a populati ...
variation
... The differences between individuals in a population is called variation Each way that individuals in a population vary is called a characteristic. The particular version of a characteristic seen in an individual is described as their phenotype. Characteristics can show discrete variation or ...
... The differences between individuals in a population is called variation Each way that individuals in a population vary is called a characteristic. The particular version of a characteristic seen in an individual is described as their phenotype. Characteristics can show discrete variation or ...
Definitions
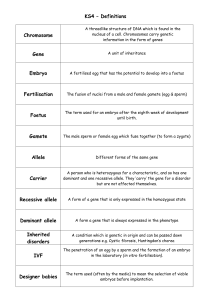
... A threadlike structure of DNA which is found in the nucleus of a cell. Chromosomes carry genetic information in the form of genes ...
... A threadlike structure of DNA which is found in the nucleus of a cell. Chromosomes carry genetic information in the form of genes ...
Charles Darwin
... • Change in inherited characteristics over successive generations • Theory explains the history of life • 2 types: • Microevolution • Macroevolution ...
... • Change in inherited characteristics over successive generations • Theory explains the history of life • 2 types: • Microevolution • Macroevolution ...
AACR and other questions to be used as extra credit at end of 2150
... 2. A child is born with two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome. One way this can occur is due to a mistake in separation of chromosomes in the production of the egg in either meiosis I or II. Explain another way this could occur. ...
... 2. A child is born with two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome. One way this can occur is due to a mistake in separation of chromosomes in the production of the egg in either meiosis I or II. Explain another way this could occur. ...
Ch. 16 Genetic Equilibrium and Selection
... into a population. – Emigration- the movement of individuals out of a population. ...
... into a population. – Emigration- the movement of individuals out of a population. ...