Notes 4-4
... 2. Describe how a cell produces proteins. 3. Identify how mutations can affect an organism. 4-4 The DNA Connection A. The Genetic Code 1. The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits. 2. G ...
... 2. Describe how a cell produces proteins. 3. Identify how mutations can affect an organism. 4-4 The DNA Connection A. The Genetic Code 1. The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits. 2. G ...
Agents of Evolutionary Change
... Least common, mutation leads to trait which serves beneficial to organism. Driving force of evolution ...
... Least common, mutation leads to trait which serves beneficial to organism. Driving force of evolution ...
Unit 8: Chapter 11 PowerPoint Lecture
... lifestyle and marry other members of their community. By chance, at least one of the original 30 Amish settlers in this community carried a recessive allele that results in short arms and legs and extra fingers and toes in offspring. Because of small gene pool, many individuals inherited the recessi ...
... lifestyle and marry other members of their community. By chance, at least one of the original 30 Amish settlers in this community carried a recessive allele that results in short arms and legs and extra fingers and toes in offspring. Because of small gene pool, many individuals inherited the recessi ...
Garland E. Allen, Washington University, St. Louis: "Mechanistic
... century. It provided a highly quantitative way to understand hereditary transmission between generations and evolution in populations, even as it excluded embryonic development from its concerns. It also fit well with a variety of social and political trends such as the professionalization of biolog ...
... century. It provided a highly quantitative way to understand hereditary transmission between generations and evolution in populations, even as it excluded embryonic development from its concerns. It also fit well with a variety of social and political trends such as the professionalization of biolog ...
B1 - Genetic Variation and Evolution Quiz
... 1. Why are some people against using GM foods? We are uncertain about their health effects. 2. How many chromosomes are there in sperm and egg cells? ...
... 1. Why are some people against using GM foods? We are uncertain about their health effects. 2. How many chromosomes are there in sperm and egg cells? ...
Name: ____________ Pd.: ______ Date: What is the advantage of
... 24. Describe two problems that can be caused by genetic drift. ________population loses genetic variation; alleles that are lethal in homozygous individuals may be carried by heterozygous individuals become more common in the gene pool by chance_______________________________________________________ ...
... 24. Describe two problems that can be caused by genetic drift. ________population loses genetic variation; alleles that are lethal in homozygous individuals may be carried by heterozygous individuals become more common in the gene pool by chance_______________________________________________________ ...
PROS AND CONS OF GENETIC ENGINEERING
... • Changing the traits of one organism by inserting genetic material (DNA / genes) from a different organism into its genetic material (genome). ...
... • Changing the traits of one organism by inserting genetic material (DNA / genes) from a different organism into its genetic material (genome). ...
14. Synthetic theory of evolution
... evolutionary change Population - elementary unit of evolution (Population – any group of individuals, usually of a single species, occupying a particular area at the same time The elementary factors of evolution that changes genetic structure of a population are: mutation, isolation, genetic drift, ...
... evolutionary change Population - elementary unit of evolution (Population – any group of individuals, usually of a single species, occupying a particular area at the same time The elementary factors of evolution that changes genetic structure of a population are: mutation, isolation, genetic drift, ...
Molecular Genetics
... - Normal errors in DNA replication and repair and external factors, including radiation and reactive chemicals can cause random changes, mutations in the DNA. - Errors in mitosis or meiosis can result in changes in phenotype. - DNA mutations can be positive, negative, or neutral based on the effect ...
... - Normal errors in DNA replication and repair and external factors, including radiation and reactive chemicals can cause random changes, mutations in the DNA. - Errors in mitosis or meiosis can result in changes in phenotype. - DNA mutations can be positive, negative, or neutral based on the effect ...
cummings and clegg - nucleotide sequence diversity at the
... 4. Describe the relationship between diversity and recombination? 5. What is the relationship between selection intensity and recombination on the breadth of selection sweep? What is the relationship between background selection and reduced diversity? 6. What is alcohol dehydrogenase a good gene for ...
... 4. Describe the relationship between diversity and recombination? 5. What is the relationship between selection intensity and recombination on the breadth of selection sweep? What is the relationship between background selection and reduced diversity? 6. What is alcohol dehydrogenase a good gene for ...
Module B1a, topic 1 Food chains eg grass → rabbit → fox producer
... Darwin’s theory of evolution states that evolution happens by natural selection • Individuals in a species show a wide range of variation • Because of differences in genes • Individuals most suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce • The genes that allowed them to be suc ...
... Darwin’s theory of evolution states that evolution happens by natural selection • Individuals in a species show a wide range of variation • Because of differences in genes • Individuals most suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce • The genes that allowed them to be suc ...
Chapter 16 Evolution of Populations Reading ONLY
... Natural selection is not the only source of evolutionary change. In small populations, alleles can become more or less common simply by chance. This kind of change in allele frequency is called genetic drift. It occurs when individuals with a particular allele leave more descendants than other indiv ...
... Natural selection is not the only source of evolutionary change. In small populations, alleles can become more or less common simply by chance. This kind of change in allele frequency is called genetic drift. It occurs when individuals with a particular allele leave more descendants than other indiv ...
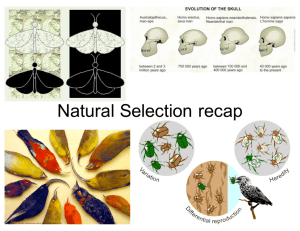
Natural Selection Intro
... new genetic variants, it just makes them more likely to survive and reproduce than others) ...
... new genetic variants, it just makes them more likely to survive and reproduce than others) ...
Evolution of populations exam answer key
... a) Allele distribution b) Allele frequency c) Relative frequency d) Relative distribution 3) A genetic mutation is a) Any change in a sequence of DNA. b) When an organism looses a limb due to a harsh environment. c) When genes are shuffled during the production of gametes. d) Any change in appearanc ...
... a) Allele distribution b) Allele frequency c) Relative frequency d) Relative distribution 3) A genetic mutation is a) Any change in a sequence of DNA. b) When an organism looses a limb due to a harsh environment. c) When genes are shuffled during the production of gametes. d) Any change in appearanc ...
Genes and Evolution - Mad River Local Schools
... 1) Genetic variety ◦ DNA mutations-adds new phenotypes to a population ◦ Genetic recombination (crossing over) allows for variety ...
... 1) Genetic variety ◦ DNA mutations-adds new phenotypes to a population ◦ Genetic recombination (crossing over) allows for variety ...
Advances in Genetics - Madison County Schools
... Cows then produce clotting protein in milk, which can then be extracted for humans. Gene Therapy • Working copies of a gene inserted directly into cells of a person with a genetic disorder • Used to correct some genetic disorders ...
... Cows then produce clotting protein in milk, which can then be extracted for humans. Gene Therapy • Working copies of a gene inserted directly into cells of a person with a genetic disorder • Used to correct some genetic disorders ...
Key ideas age 321 ivaniaa
... 2. List the kinds of mutations? mutations as change in DNA point mutation A. Insertion or deletion. B. Mutations as changes in results of gene. C. Silent mutation. D. Messene mutation. E. Frameshipft mutation. F. Nonsense mutation. G. More or fewer amino acids. H. Chromosomal mutation. ...
... 2. List the kinds of mutations? mutations as change in DNA point mutation A. Insertion or deletion. B. Mutations as changes in results of gene. C. Silent mutation. D. Messene mutation. E. Frameshipft mutation. F. Nonsense mutation. G. More or fewer amino acids. H. Chromosomal mutation. ...
Review for ch 16 and 17
... 7. A(n) ________________ is a length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay. 8. The use of half-lives to determine the age of a sample is a process called ________________ 9. Microscopic fossils may also be called _____________________ 10. Large scale evolutionary ch ...
... 7. A(n) ________________ is a length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay. 8. The use of half-lives to determine the age of a sample is a process called ________________ 9. Microscopic fossils may also be called _____________________ 10. Large scale evolutionary ch ...
Genetic Drift - stephen fleenor
... On the piece of white paper from the back, answer the following question. ...
... On the piece of white paper from the back, answer the following question. ...
handout on genetic nomenclature
... genes or alleles. Gene: single word, begins with upper case letter, at least two characters. An UPPER CASE gene name denotes the wild type form of a gene, or in the case of human, the sequence that is in the human genome database. Allele: Gene suffixed with dash and a numeral, indicating the allele. ...
... genes or alleles. Gene: single word, begins with upper case letter, at least two characters. An UPPER CASE gene name denotes the wild type form of a gene, or in the case of human, the sequence that is in the human genome database. Allele: Gene suffixed with dash and a numeral, indicating the allele. ...
genetics - Yazscience10
... • Viruses attack our cells by substituting their own genes into the cellular apparatus of human cells • Instead of making human protein, our infected cells make viral protein • Because of similarities in genetics a virus can spread from a bird to a pig to a human ...
... • Viruses attack our cells by substituting their own genes into the cellular apparatus of human cells • Instead of making human protein, our infected cells make viral protein • Because of similarities in genetics a virus can spread from a bird to a pig to a human ...