Supplementary Table 1
... growth hormone, insulin, and pest- and disease-resistant fruits and vegetables). Eugenics, a pseudo-science of selective procreation, was a movement throughout the twentieth century, worldwide as well as in Virginia, that demonstrated a misuse of the principles of heredity. The Human Genome Project ...
... growth hormone, insulin, and pest- and disease-resistant fruits and vegetables). Eugenics, a pseudo-science of selective procreation, was a movement throughout the twentieth century, worldwide as well as in Virginia, that demonstrated a misuse of the principles of heredity. The Human Genome Project ...
Propionic-Acidemia-G.. - Propionic Acidemia Foundation
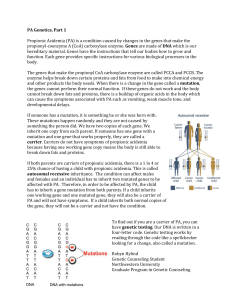
... Propionic Acidemia (PA) is a condition caused by changes in the genes that make the propionyl-coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylase enzyme. Genes are made of DNA which is our hereditary material. Genes have the instructions that tell our bodies how to grow and function. Each gene provides specific instructio ...
... Propionic Acidemia (PA) is a condition caused by changes in the genes that make the propionyl-coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylase enzyme. Genes are made of DNA which is our hereditary material. Genes have the instructions that tell our bodies how to grow and function. Each gene provides specific instructio ...
File - Biology by Napier
... 29. How can a lack of gene flow between populations lead to speciation? With no “sharing” of traits, populations may have different mutations that are successful and lead to adaptations in an environment until they are different 30. What is genetic drift? Change in allele frequency due to randomness ...
... 29. How can a lack of gene flow between populations lead to speciation? With no “sharing” of traits, populations may have different mutations that are successful and lead to adaptations in an environment until they are different 30. What is genetic drift? Change in allele frequency due to randomness ...
A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism
... 33. Gene therapy is the process of changing a gene to treat a medical disease or disorder. 34. Scientists use DNA microarray technology to study hundreds or even thousands of genes at once to understand their activity levels. 35. DNA fingerprinting analyzes sections of DNA that may have little or no ...
... 33. Gene therapy is the process of changing a gene to treat a medical disease or disorder. 34. Scientists use DNA microarray technology to study hundreds or even thousands of genes at once to understand their activity levels. 35. DNA fingerprinting analyzes sections of DNA that may have little or no ...
19-Evolution-of
... Genetic Drift - Bottle neck effect northern elephant seals of the coast of Mexico During the 1890’s, their population was reduced due to hunting to about 20 individuals. (It is also likely that one male would have fathered the offspring of the entire group.) ...
... Genetic Drift - Bottle neck effect northern elephant seals of the coast of Mexico During the 1890’s, their population was reduced due to hunting to about 20 individuals. (It is also likely that one male would have fathered the offspring of the entire group.) ...
Evolution - Cerritos College
... Darwin Proposed “The Origin Of Species By Natural Selection": OBSERVATION 1: ...
... Darwin Proposed “The Origin Of Species By Natural Selection": OBSERVATION 1: ...
Evolution
... Genetic variation is stored in a population’s gene pool Made up of all the alleles of all individuals in a population Allele frequency: a measure of how common a certain allele is in a ...
... Genetic variation is stored in a population’s gene pool Made up of all the alleles of all individuals in a population Allele frequency: a measure of how common a certain allele is in a ...
Unit 1 Rev 4 - Mr. Lesiuk
... ____4. List 5 key conditions that must be maintained in order for this gene pool to remain in this condition of no change? (see the bulleted points in the population equilibrium handout) ___ 5. List six different types of pressures or forces that can be put on a population leading to a disturbance t ...
... ____4. List 5 key conditions that must be maintained in order for this gene pool to remain in this condition of no change? (see the bulleted points in the population equilibrium handout) ___ 5. List six different types of pressures or forces that can be put on a population leading to a disturbance t ...
Mechanisms of Change
... the idea of selection to cause major changes in the features of their plants and animals over the course of decades. Farmers and breeders allowed only the plants and animals with desirable characteristics to reproduce, causing the evolution of farm stock. This process is called artificial selection ...
... the idea of selection to cause major changes in the features of their plants and animals over the course of decades. Farmers and breeders allowed only the plants and animals with desirable characteristics to reproduce, causing the evolution of farm stock. This process is called artificial selection ...
Evolution Essay Questions
... 1. Explain how the ratio of dominant to recessive alleles within a population can tell you if a population is evolving. In your explanation list the conditions that need to be in place for evolution not to happen, why we are concerned about alleles vs phenotypes, and an example of how each of the fi ...
... 1. Explain how the ratio of dominant to recessive alleles within a population can tell you if a population is evolving. In your explanation list the conditions that need to be in place for evolution not to happen, why we are concerned about alleles vs phenotypes, and an example of how each of the fi ...
Chapter 18 Worksheet
... and disruptive selection occurs when more than one extreme phenotype is favored over any intermediate ...
... and disruptive selection occurs when more than one extreme phenotype is favored over any intermediate ...
1. What is the advantage of meiosis in terms of survival
... 9. WHAT ARE THE THREE COMPONENTS OF DNA NUCLEOTIDES? ...
... 9. WHAT ARE THE THREE COMPONENTS OF DNA NUCLEOTIDES? ...
Genetic Engineering - Duplin County Schools
... • Continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics • Useful in retaining a certain set of characteristics • Can produce some serious genetic defects ...
... • Continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics • Useful in retaining a certain set of characteristics • Can produce some serious genetic defects ...
All life is based on the same genetic code
... Like its parents, the offspring will have 2 of every gene. One is from its father (blue) and one is from its mother (pink). The different combinations of genes will produce unique offspring. ...
... Like its parents, the offspring will have 2 of every gene. One is from its father (blue) and one is from its mother (pink). The different combinations of genes will produce unique offspring. ...
Outcomes of Natural Selection (Chapter 19)
... foods. After many generations, the flies were tested to see which flies they preferred to mate with. Dodd found that some reproductive isolation had occurred as a result of the geographic isolation and selection in the different environments: "maltose flies" preferred other "maltose flies," and "sta ...
... foods. After many generations, the flies were tested to see which flies they preferred to mate with. Dodd found that some reproductive isolation had occurred as a result of the geographic isolation and selection in the different environments: "maltose flies" preferred other "maltose flies," and "sta ...
Clone
... (Bacillus thuringiensis) has been transferred to maize. The gene codes for a bacterial protein called Bt toxin that kills corn borers feeding on the maize ...
... (Bacillus thuringiensis) has been transferred to maize. The gene codes for a bacterial protein called Bt toxin that kills corn borers feeding on the maize ...
Crossbreeding terminology
... Allele One of two or more forms of a gene at a particular location on a chromosome. For example, blue and brown eyes are determined by different alleles of the gene for eye colour. Chromosomes rod-like structures that are found in the nucleus of all cells. These structures contain genetic informatio ...
... Allele One of two or more forms of a gene at a particular location on a chromosome. For example, blue and brown eyes are determined by different alleles of the gene for eye colour. Chromosomes rod-like structures that are found in the nucleus of all cells. These structures contain genetic informatio ...
Genes and genomes
... of A, T, C, and G. These unique combinations code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
... of A, T, C, and G. These unique combinations code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
Selection Drift Isolating mechanisms
... industrial melanism in insects (monogenic, dominant allele codes for melanism) For one of these examples, explain how directional selection operates. ...
... industrial melanism in insects (monogenic, dominant allele codes for melanism) For one of these examples, explain how directional selection operates. ...
Concept 14.1 - Hatboro
... chart stretches of the South American coast. Darwin’s job was to document the plants, animals and geology encountered during the voyage, but more came from ...
... chart stretches of the South American coast. Darwin’s job was to document the plants, animals and geology encountered during the voyage, but more came from ...
Chapter 4
... Referring to traits that are influenced by genes at two or more loci. Examples: stature, skin color, and eye color. Many polygenic traits are also influenced by environmental factors. ...
... Referring to traits that are influenced by genes at two or more loci. Examples: stature, skin color, and eye color. Many polygenic traits are also influenced by environmental factors. ...