* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 19-Evolution-of
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Viral phylodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
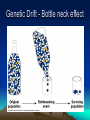
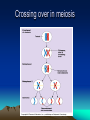
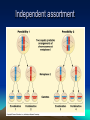
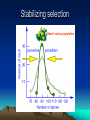
Evolution of Populations Marie Černá Microevolution • • • • • Genetic drift in small population Gene flow by migration Mutation Nonrandom mating Natural selection Genetic Drift Genetic Drift - small populations Genetic Drift - large populations Genetic Drift - Bottle neck effect Genetic Drift - Bottle neck effect northern elephant seals of the coast of Mexico During the 1890’s, their population was reduced due to hunting to about 20 individuals. (It is also likely that one male would have fathered the offspring of the entire group.) Genetic Drift - Founder principle Drosophila subobscura (fruit fly) European → American Genetic Drift - Founder principle Gene flow - migration Mutation Nonrandom mating • inbreeding • assortative mating Natural selection • the differential ability to survive and produce viable, fertile offspring • is likely to adapt a population to its environment (accumulates and maintains favorable genotypes) Genetic variation: the substrate for natural selection • within populations (polymorphism) • between populations (geographical variation) Polymorphism Geographic variation Geographic variation - Cline Sources of Genetic variation • Mutation (affection of function) • Sexual recombination Crossing over in meiosis Independent assortment Preservation of Genetic variation • Diploidy (heterozygote protection) • Balanced polymorphism Heterozygote advantage Frequency-dependent selection Modes of natural selection Directional selection is most common - during periods of environmental change - when members of a population migrate to some new habitat with different environmental conditions Directional selection Desert cactus population peccaries Diversifying selection Diversifying selection a species of finch lives in Cameroon, West Africa small-billed birds (soft seeds) large-billed birds (hard seeds) Stabilizing selection This mode of selection reduces variation and maintains the status quo for a particular phenotypic character. It keeps the majority of human birth weights In the 3 – 4 kg range. For babies much smaller or larger than this, infant mortality is greater. Stabilizing selection Desert cactus population Literature Biology, eighth edition, Campbell, Reece Unit four: Mechanisms of Evolution Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations Pages 468 – 486