* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Drift - stephen fleenor
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Viral phylodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic studies on Bulgarians wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
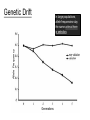
Warm-Up (2/8) On the piece of white paper from the back, answer the following question. How does artificial selection promote faster evolution than natural selection? Name Date Period 1A.1f In addition to natural selection, chance and random events can influence the evolutionary process, especially for small populations. 1A.3 Evolutionary change is also driven by random processes. 1A.3a: Genetic drift is a nonselective process occurring in small populations. 1A.3b: Reduction of genetic variation within a given population can increase the difference between populations of the same species. Genetic Drift The Fleenzaurs in China are the same species, but a different population. A population is a group which interbreeds. ff ff Ff Ff Ff FF FF ff ff Ff FF Genetic Drift Allele Frequency In large populations, allele frequencies stay the same unless there is selection. Generations Genetic Drift In small populations, allele frequency can change randomly, very quickly. = “genetic drift” Genetic Drift Populations dramatically reduced in size (such as during a natural disaster) are subject to genetic drift. = “bottleneck effect” 48% blue 52% yellow 78% blue 87% blue 22% yellow 13% yellow Critical Thinking Question #1 Two varieties of Fleenzaurs are present in a population: those with furry heads, encoded by the fh+ allele; and those with bald heads, encoded by the fh– allele. Predict how the balance of fh alleles in the Fleenzaur population might change if only a small number of individual Fleenzaurs are present. Critical Thinking Question #2 A population of tropical birds, H. tropicalis, live on an island in the Pacific Ocean. They are unable to fly to the closest island, which is 50 miles away. State one factor limiting their genetic variation, and predict how the genetic variation would change of a subset of the population which were able to migrate to the closet island. Closure On the piece of white paper from the back, answer the following question: Predict how genetic drift would be affected by a reduced population size. Name Date Period Scale 1 – 10