Modern Genetics - Hicksville Public Schools
... • Galapagos Organisms- He observed that organisms in the Galapagos resembled those from mainland, but there were significant differences. ...
... • Galapagos Organisms- He observed that organisms in the Galapagos resembled those from mainland, but there were significant differences. ...
Evolution of Populations
... reproduction Rearranges alleles into new combinations in every generation 3 mechanisms for this shuffling: ...
... reproduction Rearranges alleles into new combinations in every generation 3 mechanisms for this shuffling: ...
Let’s further study how allele frequencies can change in
... 4. Repeat this in as many generations as possible ...
... 4. Repeat this in as many generations as possible ...
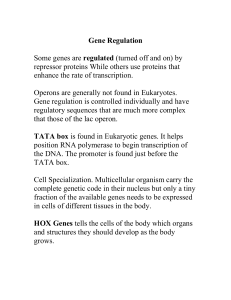
Gene Regulation
... Some genes are regulated (turned off and on) by repressor proteins While others use proteins that enhance the rate of transcription. Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the la ...
... Some genes are regulated (turned off and on) by repressor proteins While others use proteins that enhance the rate of transcription. Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the la ...
HARDY-WEINBERG and GENETIC EQUILIBRIUM
... 1. Mutations- Random change in DNA passed to offspring 2. Recombination- reshuffling of genes during Meiosis a) Independent assortment b) crossing over ...
... 1. Mutations- Random change in DNA passed to offspring 2. Recombination- reshuffling of genes during Meiosis a) Independent assortment b) crossing over ...
Genetics Mark Schedule 2010
... unlikely to become established as it will be selected against due to the individual’s chances of survival and successful reproduction being reduced. • An allele / phenotype / trait / characteristic that is favourable will be selected for and become established in the gene pool as the individual’s ch ...
... unlikely to become established as it will be selected against due to the individual’s chances of survival and successful reproduction being reduced. • An allele / phenotype / trait / characteristic that is favourable will be selected for and become established in the gene pool as the individual’s ch ...
Evolution of Populations Summary of Natural Selection
... Remember when Darwin came up with his theory, we did not yet know what the chemical factors of inheritance was We now know that it is ______ Variation can also be “carried” by individuals but not expressed (heterozygous) ...
... Remember when Darwin came up with his theory, we did not yet know what the chemical factors of inheritance was We now know that it is ______ Variation can also be “carried” by individuals but not expressed (heterozygous) ...
Notes: Microevolution Part 1 (Evolution of Populations)
... –No Natural Selection (no differences in survival or reproductive success) –Extremely Large Population (no chance for genetic drift) –Random Mating (no one is more/less attractive) ...
... –No Natural Selection (no differences in survival or reproductive success) –Extremely Large Population (no chance for genetic drift) –Random Mating (no one is more/less attractive) ...
Evolution II Task Review Answers
... 1. Adaptive radiation: a type of divergent evolution that occurs very quickly in a given area, the ancestral finches came from South America and spread to the different islands and adapted to their new environments 2. Double bubble gradualism and punctuated equilibrium Similarity: used to describe t ...
... 1. Adaptive radiation: a type of divergent evolution that occurs very quickly in a given area, the ancestral finches came from South America and spread to the different islands and adapted to their new environments 2. Double bubble gradualism and punctuated equilibrium Similarity: used to describe t ...
The Process of Microevolution
... The environment selects the best traits in the form of alleles that are advantageous for the given conditions i.e. the ability to digest a new food, or a new skin pigment may allow an organism to blend in with its environment Genotype = genetic make-up, what alleles an organism has Phenotype = appea ...
... The environment selects the best traits in the form of alleles that are advantageous for the given conditions i.e. the ability to digest a new food, or a new skin pigment may allow an organism to blend in with its environment Genotype = genetic make-up, what alleles an organism has Phenotype = appea ...
Genetic Engineering
... Finding the location of certain genes on chromosomes The arrangement of the nitrogen base pairs (A,T,C and G) determines what an organism looks like Human Genome Project ...
... Finding the location of certain genes on chromosomes The arrangement of the nitrogen base pairs (A,T,C and G) determines what an organism looks like Human Genome Project ...
Genetic Evolution Lecture
... percentage of one allele in a gene pool. For example, 50% of the alleles might have been B’s, but after the change, it might have dropped to 10%. Recall that only GROUPS can evolve, not individuals. If this is true, then genetic evolution can only occur if there is a change in the allele frequency o ...
... percentage of one allele in a gene pool. For example, 50% of the alleles might have been B’s, but after the change, it might have dropped to 10%. Recall that only GROUPS can evolve, not individuals. If this is true, then genetic evolution can only occur if there is a change in the allele frequency o ...
ACROSS 2 ______ evolution is the independent evolution of similar
... population by a small number of individuals, carrying only a small fraction of the original population's genetic variation. ________ Speciation is the genetic divergence of multiple populations inhabiting the same geographic region from a single parent species, such that those populations become dif ...
... population by a small number of individuals, carrying only a small fraction of the original population's genetic variation. ________ Speciation is the genetic divergence of multiple populations inhabiting the same geographic region from a single parent species, such that those populations become dif ...
“Evolution Practice Test” Vocabulary: Define the following
... 3. Give an example of natural selection. 4. Compare and contrast natural selection and artificial selection. 5. Describe how new traits and genetic variation come about in a population. 6. Describe how homologous structures found in skeletons can be used as evidence for evolution. Give an example of ...
... 3. Give an example of natural selection. 4. Compare and contrast natural selection and artificial selection. 5. Describe how new traits and genetic variation come about in a population. 6. Describe how homologous structures found in skeletons can be used as evidence for evolution. Give an example of ...
Genetic Mutation - Raymond Williams Foundation
... 2. Certainly there were big general themes referred to: ‘genetics – the science of difference…’; ‘ mutation – the raw material of evolution… fuel for the Darwinian factory’; ‘What is Life? – unlike, say a pebble, living beings store information and also develop it over time…’; attempted explanations ...
... 2. Certainly there were big general themes referred to: ‘genetics – the science of difference…’; ‘ mutation – the raw material of evolution… fuel for the Darwinian factory’; ‘What is Life? – unlike, say a pebble, living beings store information and also develop it over time…’; attempted explanations ...
Forces of Evolutionary Change
... Forces of Evolutionary Change What are allele frequencies?? 1. A frequency is how often something occurs 2. Written as a percent (e.g. 50%) or proportion (e.g. 0.5) 3. Allele frequencies show how genetically diverse a population is. More alleles More diverse! More even percentages of those allele ...
... Forces of Evolutionary Change What are allele frequencies?? 1. A frequency is how often something occurs 2. Written as a percent (e.g. 50%) or proportion (e.g. 0.5) 3. Allele frequencies show how genetically diverse a population is. More alleles More diverse! More even percentages of those allele ...
Plant Breeding is the actual application of the genetics research
... strategy of self-pollination followed by cross-pollination to produce vigorous hybrid plants. ...
... strategy of self-pollination followed by cross-pollination to produce vigorous hybrid plants. ...
Ch 17 Evolution of Populations
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
17.4_Molecular_Evolution
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
Genetics Vocabulary Allele: One of the variant forms of a gene at a
... recessive: A gene that produces little or no phenotypic effect when occurring in heterozygous condition with a contrasting allele and is expressed only when the determining gene is in the homozygous condition. (With a recessive gene, a disease can be “hidden” for several generations, until two reces ...
... recessive: A gene that produces little or no phenotypic effect when occurring in heterozygous condition with a contrasting allele and is expressed only when the determining gene is in the homozygous condition. (With a recessive gene, a disease can be “hidden” for several generations, until two reces ...
Solution
... 1 Formed when organic components of a bone are replaced with minerals and stone. 2 Natural ____ is the process by which organisms with advantageous heritable traits survive and reproduce to pass those traits onto more offspring than other organisms of the same species. 3 The site where “Lucy” was fo ...
... 1 Formed when organic components of a bone are replaced with minerals and stone. 2 Natural ____ is the process by which organisms with advantageous heritable traits survive and reproduce to pass those traits onto more offspring than other organisms of the same species. 3 The site where “Lucy” was fo ...
Section 16-2
... 1. Any violation of the conditions necessary for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium can result in a. independent assortment. b. disorganizing selection. ...
... 1. Any violation of the conditions necessary for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium can result in a. independent assortment. b. disorganizing selection. ...