genetic continuity
... ALTER THE GENETIC INSTRUCTIONS OF AN ORGANISM BY SUBSTITUTING DNA MOLECULES ...
... ALTER THE GENETIC INSTRUCTIONS OF AN ORGANISM BY SUBSTITUTING DNA MOLECULES ...
Population Genetics
... Natural Selection: Differential reproductive success. Two main mechanisms that cause genetic drift. ...
... Natural Selection: Differential reproductive success. Two main mechanisms that cause genetic drift. ...
A population
... phenotypes are more likely to survive and produce more offspring. Thus, passing traits to subsequent generations. Darwin’s idea was that resources are limited and that there is competition for those resources. Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. Population is the smallest unit in ...
... phenotypes are more likely to survive and produce more offspring. Thus, passing traits to subsequent generations. Darwin’s idea was that resources are limited and that there is competition for those resources. Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. Population is the smallest unit in ...
Mathematical Tools for Understanding Genome Rearrangements
... The diversity of life is a direct result of inaccuracy in DNA replication. At some point in the past, humans and mice had a common ancestor, and many "mistakes" later, we have two apparently very different species. At the level of DNA, the evolutionary distance between organisms can be estimated by ...
... The diversity of life is a direct result of inaccuracy in DNA replication. At some point in the past, humans and mice had a common ancestor, and many "mistakes" later, we have two apparently very different species. At the level of DNA, the evolutionary distance between organisms can be estimated by ...
Chapter 16
... • Toes are short, which make humans great long distance runners • Short toes are great for push off during running (toes are for balance too) • The pinky toes – are not used for running…so it may be possible that people may start being born without them… ...
... • Toes are short, which make humans great long distance runners • Short toes are great for push off during running (toes are for balance too) • The pinky toes – are not used for running…so it may be possible that people may start being born without them… ...
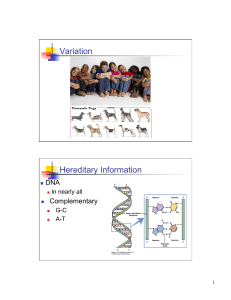
Variation Hereditary Information
... mutations (and orthodox evolution theories) fail completely. As a source of "negative variability," however, mutations serve only too well. Basing their thinking on what we observe of mutations and their net effect (genetic burden), creationists use mutations to help explain the existence of disease ...
... mutations (and orthodox evolution theories) fail completely. As a source of "negative variability," however, mutations serve only too well. Basing their thinking on what we observe of mutations and their net effect (genetic burden), creationists use mutations to help explain the existence of disease ...
Document
... Heritable differences result from differences in the genetic material of an organism Could be inherited from parent or the result of a mutation ...
... Heritable differences result from differences in the genetic material of an organism Could be inherited from parent or the result of a mutation ...
Genetics Practice MC
... DO NOT write on this sheet. Copy the problems in your notebook and answer them. This will help you study for your test on Wednesday. 1. Hereditary information is contained in the a. cell membrane b. cytoplasm ...
... DO NOT write on this sheet. Copy the problems in your notebook and answer them. This will help you study for your test on Wednesday. 1. Hereditary information is contained in the a. cell membrane b. cytoplasm ...
File
... Bottleneck effect Population has experienced a “bottleneck” and certain alleles may be over-represented ...
... Bottleneck effect Population has experienced a “bottleneck” and certain alleles may be over-represented ...
Changes Over Time - Effingham County Schools
... • The central ideas of evolution are that life has a history. It has changed over time and that different species share common ancestors. ...
... • The central ideas of evolution are that life has a history. It has changed over time and that different species share common ancestors. ...
Chapter 21 The human genome appears to have only about as
... 1. The human genome appears to have only about as many genes as the simple nematode worm, C. elegans. Which of the following best explains how the more complex humans can have relatively few genes? a. Human genes have unusually long introns involved in the regulation of gene expression. b. More than ...
... 1. The human genome appears to have only about as many genes as the simple nematode worm, C. elegans. Which of the following best explains how the more complex humans can have relatively few genes? a. Human genes have unusually long introns involved in the regulation of gene expression. b. More than ...
Document
... •The DNA Detectives (Newsweek) •Science on Trial in The Courtroom - Chapter 11 Introduction to Forensic DNA Analysis •Population & Evolutionary Genetics - Chapter 29 Introduction to Genetics •American Society of Law, Medicine, & Ethics DNA Forensics and Civil Liberties Workshop Summary •Perspective ...
... •The DNA Detectives (Newsweek) •Science on Trial in The Courtroom - Chapter 11 Introduction to Forensic DNA Analysis •Population & Evolutionary Genetics - Chapter 29 Introduction to Genetics •American Society of Law, Medicine, & Ethics DNA Forensics and Civil Liberties Workshop Summary •Perspective ...
What do I need to know for the test?
... What is a gene pool? What is relative frequency? In genetic terms, a change in the relative frequency of alleles in population = ? What are the sources of genetic variation in populations? What causes these? What is a single-gene trait? What is a polygenic trait? How is the number of phenotypes rela ...
... What is a gene pool? What is relative frequency? In genetic terms, a change in the relative frequency of alleles in population = ? What are the sources of genetic variation in populations? What causes these? What is a single-gene trait? What is a polygenic trait? How is the number of phenotypes rela ...
Unit 3 Outline - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... Mutations are genetic changes that provide the raw material for evolutionary change. Genetic Drift Genetic drift refers to changes in the allele frequencies of gene pool due to chance. The founder effect and the bottleneck effect are both examples of genetic drift. Gene Flow Gene flow is the movemen ...
... Mutations are genetic changes that provide the raw material for evolutionary change. Genetic Drift Genetic drift refers to changes in the allele frequencies of gene pool due to chance. The founder effect and the bottleneck effect are both examples of genetic drift. Gene Flow Gene flow is the movemen ...
Heredity
... Inherited traits-traits that are passed on from parents to offsprings. Genes-tiny message units Learned trait-a trait that is not passed on in DNA Dominant trait-a trait that will be expressed if it is inherited. Recessive trait-a trait that is not expressed if paired with a dominant trait Incomplet ...
... Inherited traits-traits that are passed on from parents to offsprings. Genes-tiny message units Learned trait-a trait that is not passed on in DNA Dominant trait-a trait that will be expressed if it is inherited. Recessive trait-a trait that is not expressed if paired with a dominant trait Incomplet ...
Power Point 2 - G. Holmes Braddock
... A mutation may result in a phenotypic change if the mutation occurs at a point on the gene that determines the phenotype. Mutations don’t always result in phenotypic change. Phenotypic change is mostly seen when looking into evolution Evolution is the change of a species over time ...
... A mutation may result in a phenotypic change if the mutation occurs at a point on the gene that determines the phenotype. Mutations don’t always result in phenotypic change. Phenotypic change is mostly seen when looking into evolution Evolution is the change of a species over time ...
Genetics
... Trait that may not be expressed Lowercase letter t= short, b=white Only expressed when there is no dominant trait present ...
... Trait that may not be expressed Lowercase letter t= short, b=white Only expressed when there is no dominant trait present ...
Population Change
... • Speciation is a splitting event that creates two or more distinct species from a single ancestral group. ...
... • Speciation is a splitting event that creates two or more distinct species from a single ancestral group. ...