* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Charles Darwin
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
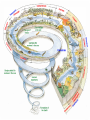
EVOLUTION STANDARD • SB5. Students will evaluate the role of natural selection in the development of the theory of evolution. • A. Trace the history of the theory of evolution ESSENTIAL QUESTION • Unit: • How is life organized at all levels from cells to the biosphere? • Today: • Where does the theory of evolution come from? SOME IMPORTANT SCIENTISTS • Francesco Redi (1626-1697) • Proved Aristotle’s idea of spontaneous generation incorrect • This introduced the idea that living things come from living things • Carolus Linneaus (1707-1778) • Wrote “Systema Naturae” • Basis of the modern classification system • Came up with the way organisms are named • Binomial nomenclature MORE SCIENTISTS • Jean Baptiste Lemarck (1744-1829) • Known for his early ideas of evolution • Charles Darwin (18091882) • Wrote “On the origin of the species” • Theory of evolution based on natural selection MORE SCIENTISTS • Gregor Mendel (18221884) • Father of genetics • Introduced the idea that traits were inherited • Watson and Crick • Pieced together the model of DNA • DNA can now be mapped • It is used as strong evidence for evolution CHECKING FOR UNDERSTANDING # 3 •Directions: Label the top of your paper as ‘Checking for Understanding’. Put today’s date as indicated below. Write the questions and the answer to the following questions: •8/26`/15 1. How did Carolus Linnaeus contribute to the theory of evolution? 2. How did Watson and crick contribute to our understanding of evolution? 3. What scientist is credited for the modern theory of evolution •Keep this paper in your notes until the next ‘Check for Understanding’. This is for a grade! WHAT IS EVOLUTION? • Evolution • Change in inherited characteristics over successive generations • Theory explains the history of life • 2 types: • Microevolution • Macroevolution MICROEVOLUTION • The accumulation of small changes in the gene pool over a short period of 2 or more generations • Outcome: change in phenotype (visible traits) frequency • Causes: • • • • • Genetic Mutations Gene flow Non Random Mating Genetic Drift Natural Selection • Only natural selection results in adaptation to the environment CAUSES OF MICROEVOLUTION • Genetic Mutation • Accidental changes in the DNA • Creates variation in a population • Gene Flow • Movement of alleles between populations by breeding individuals • Makes organisms in different populations similar. • migration • Genetic drift • Changes in allele frequencies of a gene pool due to chance • reduces variation CAUSES OF MICROEVOLUTION • Genetic Drift continued • Two types • Founder Effect • a small sample of a population settles in a location separated from the rest of the population • Genes that were uncommon in the original population might be common in the new population • Bottleneck • a population declines to a very low number and then grows CAUSES OF MICROEVOLUTION • Nonrandom Mating • Certain traits selected for • Ex: Pedigree of dogs • Two Types: • Assortative mating • Mate with individuals with a certain similar trait • Sexual selection • Males compete for female • Female chooses certain traits CHECKING FOR UNDERSTANDING # 3 •Directions: Label the top of your paper as ‘Checking for Understanding’. Put today’s date as indicated below. Write the questions and the answer to the following questions: •8/25/15 1. Explain gene flow. How does this relate to microevolution 2. How does genetic drift contribute to microevolution? 3. Define Evolution. •Keep this paper in your notes until the next ‘Check for Understanding’. This is for a grade! CAUSES OF MACROEVOLUTION • Macroevolution • Evolution above the level of individual species and populations • Adaptive Radiation • One species gives rise to 2 or more species • Response to an ecological opportunity like new habitat • Coevolution • The relationship between two species might be so close that the evolution of one species affects the evolution of the other species CAUSES OF MACROEVOLUTION • Convergent Evolution • Unrelated species evolve similar traits due to similar environments even though they live in different parts of the world • Extinction • A lineage dies off • Makes room for another species to thrive • Punctuated Equilibrium • Some biologists argue that species just appear after a period of long environmental change. CAUSES OF MACROEVOLUTION • Gradualism • Small changes (i.e. microevolution) build up over time. • Result of Macroevolution • Speciation • Formation of a new species • Link between microevolution and macroevolution • Species • Group of closely related organisms that can produce fertile offspring CHECKING FOR UNDERSTANDING # 4 •Directions: Label the top of your paper as ‘Checking for Understanding’. Put today’s date as indicated below. Write the questions and the answer to the following questions: •8/25/15 1. Connect Speciation to microevolution and macroevolution 2. Give an example of convergent evolution. 3. Define Evolution. •Keep this paper in your notes until the next ‘Check for Understanding’. This is for a grade!