* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOLOGY- Mechanisms of Evolution Unit Outline I. MICRO
Survey
Document related concepts
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Sympatric speciation wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
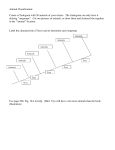
BIOLOGY- Mechanisms of Evolution Unit Outline I. MICRO EVOLUTION (Chapter 16) A. What is microevolution? How do we know a population is evolving? B. Mechanisms of Evolution (Genetic Change) 1. Natural Selection (definitions, graphs, and examples) a. Disrup tive: b. Directional: c. Stabilizing: d. Sexual Selection: 2. Mechanisms based on Chance (definitions and examples) a. Mutations: b. Genetic Drift: c. Gene Flow (migration): 3. Speciation (The Mechanism of Macroevolution) a. What is the biological species concept? Describe how a single population can evolve into two populations that no longer interbreed. b. Reproductive Isolation (Behavioral, Temporal, Geographic) C. Genetic Equilibrium (Hardy-Weinberg Principle) 1. Alllele frequencies will remain constant in a population if these FIVE conditions are met: II. MACROEVOLUTION (17.4 and Chapter 18) A. B. Patterns of Macroevolution (definitions and examples) 1. Mass Extinction: 2. Adaptive Radiation: 3. Convergent Evolution: 4. Coevolution: 5. Punctuated Equilibrium: Evolutionary Classification 1. (Linnaeus’s) Classification System a. List the 8 Taxons in order from largest to smallest: b. Name the 6 kingdoms and place them into the appropriate domains: c. Explain how this system is used to show phylogenies and common ancestry 2. Understanding and Constructing Cladograms & Phylogenetic Trees a. Can you successfully discuss the relationships represented in this cladogram? Which species are the most closely related? The most distantly related? b. Construct a cladogram with this data: Caterpillar Moth Tuna Lizard Bird Dog Cells X X X X X X Backbone Legs Wings Feathers Hair X X X X X X X X X X X