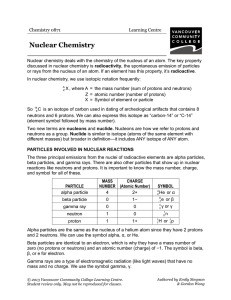
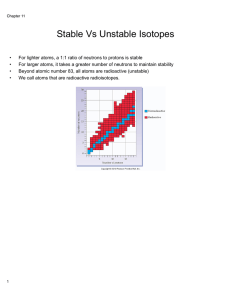
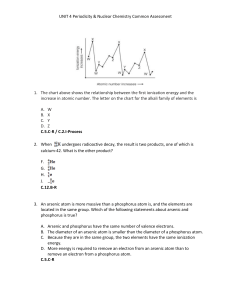
Nuclear Reactions - Kelso High School
... The explanations suggested a nuclear atom. • The fact that most of the particles passed straight through the foil, which was at least 100 atoms thick, implied that the atom must be mostly empty space. • In order to produce the large deflections at C and D, the alpha particles must be colliding with ...
... The explanations suggested a nuclear atom. • The fact that most of the particles passed straight through the foil, which was at least 100 atoms thick, implied that the atom must be mostly empty space. • In order to produce the large deflections at C and D, the alpha particles must be colliding with ...
Chem 1721 Brief Notes: Chapter 20 Chapter 20: Nuclear Chemistry
... heavy nuclei gain stability when they fragment into midweight elements and release energy; FISSION ...
... heavy nuclei gain stability when they fragment into midweight elements and release energy; FISSION ...
Unit IV Review Guide: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Reactions
... 13. The half-life of tritium H-3 is 12.3 years. If 48.0 mg is released from a nuclear power plant during the course of a mishap, what mass will be left after a. 5 half lives ...
... 13. The half-life of tritium H-3 is 12.3 years. If 48.0 mg is released from a nuclear power plant during the course of a mishap, what mass will be left after a. 5 half lives ...
Nuclear Radiation1516
... about equal to half the original mass. Two or three neutrons are also emitted. The sum of the masses of these fragments is less than the original mass. This 'missing' mass (about 0.1 percent of the original mass) has been converted into energy according to Einstein's equation. Fission can occur when ...
... about equal to half the original mass. Two or three neutrons are also emitted. The sum of the masses of these fragments is less than the original mass. This 'missing' mass (about 0.1 percent of the original mass) has been converted into energy according to Einstein's equation. Fission can occur when ...
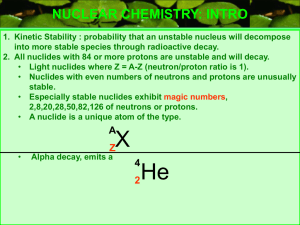
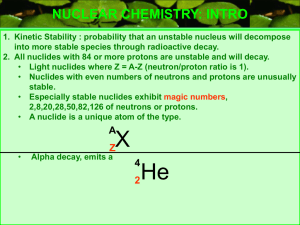
(neutron/proton ratio is 1).
... NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY: INTRO 1. Kinetic Stability : probability that an unstable nucleus will decompose into more stable species through radioactive decay. 2. All nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable and will decay. • Light nuclides where Z = A-Z (neutron/proton ratio is 1). • Nuclides with eve ...
... NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY: INTRO 1. Kinetic Stability : probability that an unstable nucleus will decompose into more stable species through radioactive decay. 2. All nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable and will decay. • Light nuclides where Z = A-Z (neutron/proton ratio is 1). • Nuclides with eve ...