Chemistry (B) HW Chapter 25
... a. Products that start a new reaction are released. b. Reactants that have two parts split. c. Products that are radioactive are lost. d. Radioactive reactants are deposited on control rods. ____ 38. Controlled nuclear chain reactions ____. a. take place in nuclear reactors b. are always fusion reac ...
... a. Products that start a new reaction are released. b. Reactants that have two parts split. c. Products that are radioactive are lost. d. Radioactive reactants are deposited on control rods. ____ 38. Controlled nuclear chain reactions ____. a. take place in nuclear reactors b. are always fusion reac ...
Problem Set 7 Solutions
... Can increase fuel utilization, because the lower absorption of sodium compared to water means fewer neutrons are absorbed in the coolant. May decrease fuel utilization, as more of the absorption events happen in the resonance regions of other materials (structural, cladding, etc.) because the neutro ...
... Can increase fuel utilization, because the lower absorption of sodium compared to water means fewer neutrons are absorbed in the coolant. May decrease fuel utilization, as more of the absorption events happen in the resonance regions of other materials (structural, cladding, etc.) because the neutro ...
Nuclear Chem Notes - Warren County Schools
... neutron, it eventually forms the fissionable nuclide of plutonium, Pu-239, which can support a chain reaction. Plutonium is a transuranium element, meaning that it has an atomic number greater than the 92 of uranium. The fissionable plutonium produced in a uranium-fueled reactor can be used as a fue ...
... neutron, it eventually forms the fissionable nuclide of plutonium, Pu-239, which can support a chain reaction. Plutonium is a transuranium element, meaning that it has an atomic number greater than the 92 of uranium. The fissionable plutonium produced in a uranium-fueled reactor can be used as a fue ...
ppt-nuclear - SandersScienceStuff
... left, divide the time passed from the half life and that will give you the amount of half lives your sample has had. You can then divide your original mass of sample by 2 as many times as you have half lives. • If you are trying to solve for the half life of your sample, take the remaining mass and ...
... left, divide the time passed from the half life and that will give you the amount of half lives your sample has had. You can then divide your original mass of sample by 2 as many times as you have half lives. • If you are trying to solve for the half life of your sample, take the remaining mass and ...
30.1 Radioactivity The atom is the smallest unit of achemical
... a proton decays into a neutron it has the same charge as electron but negative charge • it has the same mass as electron • it can penetrate with few meters in air. 2 or 3 cm of wood are enough to protect oneself. 3- Gamma decay (γ) ...
... a proton decays into a neutron it has the same charge as electron but negative charge • it has the same mass as electron • it can penetrate with few meters in air. 2 or 3 cm of wood are enough to protect oneself. 3- Gamma decay (γ) ...
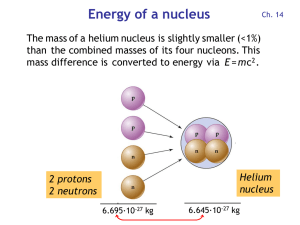
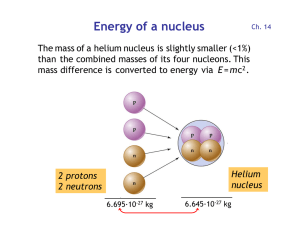
Energy per nucleon
... and 2 neutrons are combined to form the helium nucleus: E = m c2 = (5·10-29 kg) · (3·108 m/s)2 = 4.5 ·10-12 J = 28 MeV Each of the four nucleons releases 28 MeV / 4 = 7 MeV ...
... and 2 neutrons are combined to form the helium nucleus: E = m c2 = (5·10-29 kg) · (3·108 m/s)2 = 4.5 ·10-12 J = 28 MeV Each of the four nucleons releases 28 MeV / 4 = 7 MeV ...
Energy of a nucleus
... Fusion in stars • Stars convert hydrogen to helium and heavier elements. When Fe and Ni are reached, fusion stops. The star has burnt its nuclear fuel and collapses under its own gravity. • In massive stars, this collapse releases a huge amount of gravitational energy that leads to a supernova.The ...
... Fusion in stars • Stars convert hydrogen to helium and heavier elements. When Fe and Ni are reached, fusion stops. The star has burnt its nuclear fuel and collapses under its own gravity. • In massive stars, this collapse releases a huge amount of gravitational energy that leads to a supernova.The ...
Fusion or Fission
... plants use fission to produce energy, producing a lot of radioactive byproducts as a result. 4 Conversely, in fusion reactions, the nuclei from atoms with low atomic weights combine to create heavier nuclei. This reaction does not require neutrons in order to occur. Two light nuclei must collide wit ...
... plants use fission to produce energy, producing a lot of radioactive byproducts as a result. 4 Conversely, in fusion reactions, the nuclei from atoms with low atomic weights combine to create heavier nuclei. This reaction does not require neutrons in order to occur. Two light nuclei must collide wit ...