Chapter 16 – Nuclear Energy
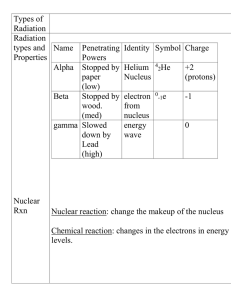
... • Radioactive atoms: Atoms that decay and emit particles and energy from their nuclei. • Radiation: alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays given off in the decaying of unstable nuclei. ...
... • Radioactive atoms: Atoms that decay and emit particles and energy from their nuclei. • Radiation: alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays given off in the decaying of unstable nuclei. ...
Radioactive Decay Laws
... A gram of isotope with mass number A contains NA isotopes 235 g ( 235U ) 6.023 1023 235U isotopes ...
... A gram of isotope with mass number A contains NA isotopes 235 g ( 235U ) 6.023 1023 235U isotopes ...
Concept Lecture Outline – Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
... b. Either 2 or 3 neutrons are also produced with the products. c. These neutrons act as "bullets" to ram into other unstable nuclei and split them, resulting in a chain reaction. d. All nuclear reactors in the world are fission reactors. 1) They cannot "blow up" like an atom bomb. 2) They produce ra ...
... b. Either 2 or 3 neutrons are also produced with the products. c. These neutrons act as "bullets" to ram into other unstable nuclei and split them, resulting in a chain reaction. d. All nuclear reactors in the world are fission reactors. 1) They cannot "blow up" like an atom bomb. 2) They produce ra ...
Nuclear Energy
... Nuclear Fusion is the combining of 2 atomic nuclei to produce a single larger nucleus. Advantages: 1. It produces more energy per atom than nuclear fission. 2. It is readily available. 3. It is safer 4. Less polluting than nuclear fission. ...
... Nuclear Fusion is the combining of 2 atomic nuclei to produce a single larger nucleus. Advantages: 1. It produces more energy per atom than nuclear fission. 2. It is readily available. 3. It is safer 4. Less polluting than nuclear fission. ...