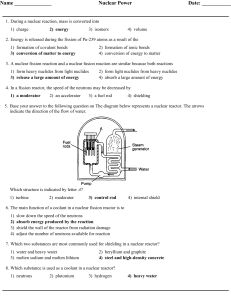
Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
... • When an unstable nucleus decays, particles and energy are emitted from the decaying nucleus. • These particles and energy are called nuclear radiation. • The three types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. ...
... • When an unstable nucleus decays, particles and energy are emitted from the decaying nucleus. • These particles and energy are called nuclear radiation. • The three types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. ...
Mass-Energy Equivalence - Dr. Haleys Physics Class
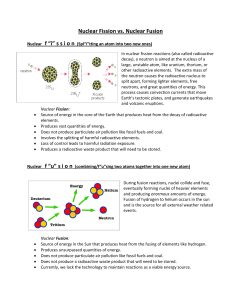
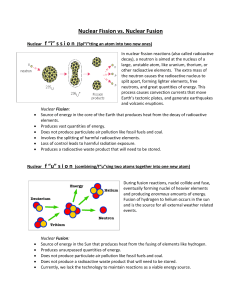
... Fission breaks the nucleus into two smaller pieces and often releases one or more extra neutrons. Some of the energy released by the reaction appears as gamma rays and some as kinetic energy of the smaller nuclei and the extra neutrons. ...
... Fission breaks the nucleus into two smaller pieces and often releases one or more extra neutrons. Some of the energy released by the reaction appears as gamma rays and some as kinetic energy of the smaller nuclei and the extra neutrons. ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Xavier High School
... Fission chain has three general steps: 1. Initiation. Reaction of a single atom starts the chain (e.g., 235U + neutron) 2. Propagation. ...
... Fission chain has three general steps: 1. Initiation. Reaction of a single atom starts the chain (e.g., 235U + neutron) 2. Propagation. ...
Unit 2 – The Atom
... • Large amount of energy generated – 1 million times more than chemical reactions – Nuclear fusion on the sun – Nuclear fission for reactors ...
... • Large amount of energy generated – 1 million times more than chemical reactions – Nuclear fusion on the sun – Nuclear fission for reactors ...
Isotope Half-Life Radiation Emitted
... • How many grams are left after one half-life? • How many grams are left after two half-lives? ...
... • How many grams are left after one half-life? • How many grams are left after two half-lives? ...
PreAP Chemistry Radioactivity WS Name Period ____ Match the
... ---------- 5. The weighted average mass of an element’s isotopes. ...
... ---------- 5. The weighted average mass of an element’s isotopes. ...
Nuclear Fission
... Radioactivity • Radioactive atoms: unstable atoms that decay and emit particles and energy from their nuclei – Not all elements are radioactive • Most cases it is only certain isotopes that are radioactive – Example: »H – 1 = »H – 2 = »H – 3 = ...
... Radioactivity • Radioactive atoms: unstable atoms that decay and emit particles and energy from their nuclei – Not all elements are radioactive • Most cases it is only certain isotopes that are radioactive – Example: »H – 1 = »H – 2 = »H – 3 = ...