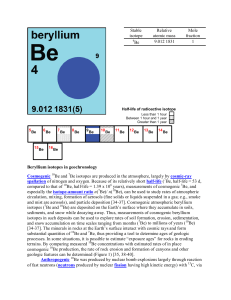
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... •Any element with more than one proton (i.e., anything but hydrogen) will have repulsions between the protons in the nucleus. •A strong nuclear force helps keep the nucleus from flying apart. •Neutrons play a key role stabilizing the nucleus. •Therefore, the ratio of neutrons to protons is an import ...
... •Any element with more than one proton (i.e., anything but hydrogen) will have repulsions between the protons in the nucleus. •A strong nuclear force helps keep the nucleus from flying apart. •Neutrons play a key role stabilizing the nucleus. •Therefore, the ratio of neutrons to protons is an import ...
Lesson 13: Nuclear Propulsion Basics
... microscopic distance, so their energy becomes converted into heat. • The balance of the energy comes from gamma rays emitted during or immediately following the fission process and from the kinetic energy of the neutrons. – Some of the latter are immediate (so-called prompt neutrons), but a small pr ...
... microscopic distance, so their energy becomes converted into heat. • The balance of the energy comes from gamma rays emitted during or immediately following the fission process and from the kinetic energy of the neutrons. – Some of the latter are immediate (so-called prompt neutrons), but a small pr ...
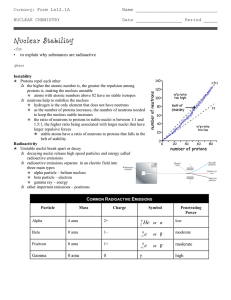
Structure of the nucleus • It is now known that the nucleus consists of
... Teams of physicists have come close to achieving ignition and a self-sustaining fusion reactor. o ...
... Teams of physicists have come close to achieving ignition and a self-sustaining fusion reactor. o ...
1 The Nucleus Total number of nucleons: mass number Number of
... becquerel – one nuclear disintegration/s curie (Ci) – number of disintegration/s from 1 g of Ra = 3.7 × 1010 disintegration/s ...
... becquerel – one nuclear disintegration/s curie (Ci) – number of disintegration/s from 1 g of Ra = 3.7 × 1010 disintegration/s ...
Radioactive Decay Series
... Nuclear Chain Reaction A chain reaction is a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction. A critical mass is the minimum amount of nuclides that provide the number of neutrons needed to maintain a chain reaction ...
... Nuclear Chain Reaction A chain reaction is a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction. A critical mass is the minimum amount of nuclides that provide the number of neutrons needed to maintain a chain reaction ...
Nuclear - chemmybear.com
... and write the balanced nuclear reaction for that less. decay process. (c) The neutron/proton ratio in Sr-90 and Cs-137 is (c) Gamma rays are observed during the radioactive too large and they emit beta particles (converting decay of carbon-11. Why is it unnecessary to inneutrons into protons) to low ...
... and write the balanced nuclear reaction for that less. decay process. (c) The neutron/proton ratio in Sr-90 and Cs-137 is (c) Gamma rays are observed during the radioactive too large and they emit beta particles (converting decay of carbon-11. Why is it unnecessary to inneutrons into protons) to low ...