Terms to Know
... Positrons : The positron is the antiparticle of the electron. It has the same mass and the same quantity of electric charge as does the electron, but its electric charge is positive rather than negative. Radioactivity : Radioactivity is the emission of radiation by unstable nuclei. That radiation ma ...
... Positrons : The positron is the antiparticle of the electron. It has the same mass and the same quantity of electric charge as does the electron, but its electric charge is positive rather than negative. Radioactivity : Radioactivity is the emission of radiation by unstable nuclei. That radiation ma ...
Fission and Fusion
... It absorbs the neutron and becomes an unstable atom of U-236. It then undergoes fission. Notice that more neutrons are released in the reaction. These neutrons can strike other U-235 atoms to initiate their fission. ...
... It absorbs the neutron and becomes an unstable atom of U-236. It then undergoes fission. Notice that more neutrons are released in the reaction. These neutrons can strike other U-235 atoms to initiate their fission. ...
13.4 The nucleus 3 - Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion
... Nuclear power stations, heat from the same chain reaction is used to make steam to generate electricity. The chain reaction is controlled by using uranium that has not been enriched so much, and by using control rods of materials that absorb neutrons. The atomic bomb exploding over Nagasaki In nucle ...
... Nuclear power stations, heat from the same chain reaction is used to make steam to generate electricity. The chain reaction is controlled by using uranium that has not been enriched so much, and by using control rods of materials that absorb neutrons. The atomic bomb exploding over Nagasaki In nucle ...
Nuclear Fission & Fusion
... •Stable Nuclei = strong nuclear force is ________ than repulsion force •Unstable Nuclei = strong nuclear force is less ________ than repulsion force ...
... •Stable Nuclei = strong nuclear force is ________ than repulsion force •Unstable Nuclei = strong nuclear force is less ________ than repulsion force ...
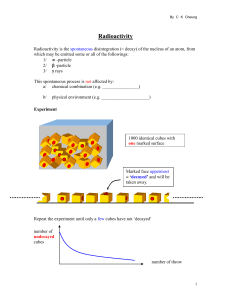
Nuclear Chemistry
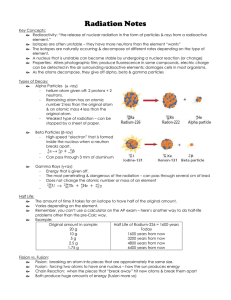
... Consists of 2 protons, 2 neutrons emitted during decay Helium nucleus ( 24He )—how particle represented Can be stopped by paper, low energy Atomic number goes down 2, atomic mass goes down 4. ...
... Consists of 2 protons, 2 neutrons emitted during decay Helium nucleus ( 24He )—how particle represented Can be stopped by paper, low energy Atomic number goes down 2, atomic mass goes down 4. ...