* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 25.3 section summary
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Inertial confinement fusion wikipedia , lookup
Muon-catalyzed fusion wikipedia , lookup
Inertial electrostatic confinement wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
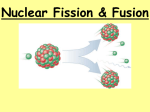
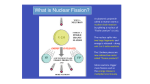
SECTION SUMMARY 25.3 Fission and fusion of atomic nuclei Summary: Nuclear fission occurs when fissionable isotopes are bombarded with neutrons. The fissionable atom breaks into two fragments of about the same size, and in the process they release more neutrons and energy. Neutron moderation is the process that reduces the speed of neutrons. Sometimes water is used as a moderator in nuclear reactors. Neutron absorption is the process that decreases the number of slow-moving neutrons. In nuclear fusion, nuclei combine to make nuclei of greater mass. The sun’s energy is produced when hydrogen nuclei fuse to make helium nuclei. Fusion releases even more energy than fission. Fusion only occurs at very high temperature- in the excess of 40, 000oC, and it is not easy produced under laboratory conditions. 25.3 Fission and fusion of atomic nuclei Vocabulary Terms: fission: the splitting of a nucleus into smaller fragments, accompanied by the release of neutrons and a large amount of energy neutron moderation: a process used in nuclear reactors to slow down neutrons so the reactor fuel captures them to continue the chain reaction neutron absorption: a process that decreases the number of slow-moving neutrons in a nuclear reactor; this is accomplished by using control rods made of a material such as cadmium, which absorbs neutrons fusion: the process of combining nuclei to produce a nucleus of greater mass uranium-253: isotope capable of fission The End of the Summary