* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit_Phys_2_nuclear_fusion__fission
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
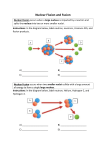
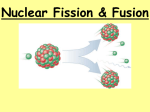
Unit Physics 2 Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding of how science works: GCSE Text Book Revision Guide Nuclear fission a) There are two fissionable substances in common use in nuclear reactors: uranium-235 and plutonium239. b) Nuclear fission is the splitting of an atomic nucleus. c) For fission to occur, the uranium-235 or plutonium239 nucleus must first absorb a neutron. Additional guidance: Candidates should be able to explain why the early Universe contained only hydrogen but now contains a large variety of different elements. The term ‘radiation pressure’ will not be required. Candidates should be familiar with the chart on the next page that shows the life cycles of stars. Additional guidance: Candidates should be able to sketch or complete a labelled diagram to illustrate how a chain reaction may occur. d) The nucleus undergoing fission splits into two smaller nuclei and two or three neutrons and energy is released. e) The neutrons may go on to start a chain reaction. Nuclear fusion a) Nuclear fusion is the joining of two atomic nuclei to form a larger one. b) Nuclear fusion is the process by which energy is released in stars. c) Stars form when enough dust and gas from space is pulled together by gravitational attraction. Smaller masses may also form and be attracted by a larger mass to become planets. d) During the ‘main sequence’ period of its life cycle a star is stable because the forces within it are balanced. e) A star goes through a life cycle. This life cycle is determined by the size of the star. f) Fusion processes in stars produce all of the naturally occurring elements. These elements may be distributed throughout the Universe by the explosion of a massive star (supernova) at the end of its life. Strengths: Weaknesses: ……………………………………………. …………………………………. ……………………………………………. …………………………………. ……………………………………………. …………………………………. To Improve I need to: …………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………