Chapter 4 Section 1-‐ Egypt Under the Pharaohs Titles Notes QCIPL
... -‐Amon-‐Re! sun god-‐ one of most important (myth of his journey across the sky-‐! symbolism of birth in east and death in west ...
... -‐Amon-‐Re! sun god-‐ one of most important (myth of his journey across the sky-‐! symbolism of birth in east and death in west ...
Egyptians Crossword Name
... 5. One who learned the art of writing in Ancient Egypt were called this.52 7. This yearly event is considered to be the "Miracle of the Nile".46 8. During the Middle Kingdom, the pharaoh directed the draining of the Nile Delta to create more of this.49 11. These people conquered Egypt by using their ...
... 5. One who learned the art of writing in Ancient Egypt were called this.52 7. This yearly event is considered to be the "Miracle of the Nile".46 8. During the Middle Kingdom, the pharaoh directed the draining of the Nile Delta to create more of this.49 11. These people conquered Egypt by using their ...
Jeopardy
... She tried to unite Rome and Egypt, ruled as Queen and used her feminine power to get what she wants -affairs with Julius Caesar and Marc Anthony to secure Egypt’s place / security in the Roman World -killed herself and Egypt became part of the Roman Empire, ending over 3000 years of dynastic rule ...
... She tried to unite Rome and Egypt, ruled as Queen and used her feminine power to get what she wants -affairs with Julius Caesar and Marc Anthony to secure Egypt’s place / security in the Roman World -killed herself and Egypt became part of the Roman Empire, ending over 3000 years of dynastic rule ...
Class Session 4
... • No natural borders • Natural borders of against enemies sea & desert • Rulers of different nationalities • Pessimistic ...
... • No natural borders • Natural borders of against enemies sea & desert • Rulers of different nationalities • Pessimistic ...
The Bronze Age - Ms. Mac`s Class
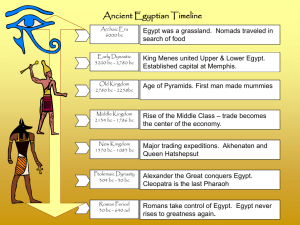
... Period of Egypt immediately follows the unification of Lower and Upper Egypt c. 3100 BC. It is generally taken to include the First and Second Dynasties, Lasting from the Proto-Dynastic Period of Egypt until about 2686 BC, or the beginning of the Old Kingdom. ...
... Period of Egypt immediately follows the unification of Lower and Upper Egypt c. 3100 BC. It is generally taken to include the First and Second Dynasties, Lasting from the Proto-Dynastic Period of Egypt until about 2686 BC, or the beginning of the Old Kingdom. ...
Worksheet - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 10. The most famous of all ancient Egyptian scripts is ______________. However, throughout three thousand years of ancient Egyptian civilization, at least three other scripts were used for different purposes. Using these scripts, scribes were able to do what? 11. The Rosetta Stone is a stone with wr ...
... 10. The most famous of all ancient Egyptian scripts is ______________. However, throughout three thousand years of ancient Egyptian civilization, at least three other scripts were used for different purposes. Using these scripts, scribes were able to do what? 11. The Rosetta Stone is a stone with wr ...
gift of the Nile
... Menes (king of Upper Egypt) conquered Lower Egypt and established his capital at Memphis He united the two crowns of Egypt into one “double crown” (pictured at left) and started the first dynasty in Egyptian history Menes is also considered the first pharaoh (god-king) of Egypt, considered all-power ...
... Menes (king of Upper Egypt) conquered Lower Egypt and established his capital at Memphis He united the two crowns of Egypt into one “double crown” (pictured at left) and started the first dynasty in Egyptian history Menes is also considered the first pharaoh (god-king) of Egypt, considered all-power ...
HIS 101 03 - Shelton State
... Which statement about daily life in ancient Egypt is NOT ACCURATE? A. Marriages were arranged by parents, and the chief purpose was to produce children. B. The property of a woman was transferred to husband upon marriage. C. The earliest known board games in the world have been found in Egyptian tom ...
... Which statement about daily life in ancient Egypt is NOT ACCURATE? A. Marriages were arranged by parents, and the chief purpose was to produce children. B. The property of a woman was transferred to husband upon marriage. C. The earliest known board games in the world have been found in Egyptian tom ...
3 Early Civilizations of Africa (textbook pages 71–76) SECTION 3 QUIZ
... 8. What evidence shows that the Egyptians believed their pharaohs were gods? a. They built vast pyramids for their tombs and buried them with many valuable things. b. Written records survive in their churches. c. They invented a 365-day calendar. d. The ruins of Meroë show evidence the Egyptians’ be ...
... 8. What evidence shows that the Egyptians believed their pharaohs were gods? a. They built vast pyramids for their tombs and buried them with many valuable things. b. Written records survive in their churches. c. They invented a 365-day calendar. d. The ruins of Meroë show evidence the Egyptians’ be ...
Western Asia and Egypt
... sister/wife Isis [the fertile soil of Egypt, the star Sirius 2. Seth [Disorder, the God of Foreign Places] and his ...
... sister/wife Isis [the fertile soil of Egypt, the star Sirius 2. Seth [Disorder, the God of Foreign Places] and his ...
Chapter 4 - Groupfusion.net
... Chaos disrupted life in Egypt Invaders, called the Hyksos, conquered lower Egypt Eventually, Ahmose, defeated the Hyksos and re-established the rule of the pharaohs ...
... Chaos disrupted life in Egypt Invaders, called the Hyksos, conquered lower Egypt Eventually, Ahmose, defeated the Hyksos and re-established the rule of the pharaohs ...
Chapter 1 - Leleua Loupe
... Developed for record keeping Scribal education established to produce professionally trained elite scribes ...
... Developed for record keeping Scribal education established to produce professionally trained elite scribes ...
Name
... 1. Why was Egypt called “the Gift of the Nile?” Because is provided Egypt with life. If the Nile didn’t flow through Egypt, there would be no fresh water in the desert. Also, the river flooded every year and helped them grow crops because the floods left behind a fresh layer of silt to fertilize the ...
... 1. Why was Egypt called “the Gift of the Nile?” Because is provided Egypt with life. If the Nile didn’t flow through Egypt, there would be no fresh water in the desert. Also, the river flooded every year and helped them grow crops because the floods left behind a fresh layer of silt to fertilize the ...
The Pyramid Builders
... • It combined the red Crown of Lower Egypt w/ the white Crown of Upper Egypt ...
... • It combined the red Crown of Lower Egypt w/ the white Crown of Upper Egypt ...
Ancient Egypt and Kush
... LESSON 2: THE OLD KINGDOM • The Old Kingdom existed from 2700 BC to 2200 BC. • It was under the rule of the Pharaoh who was seen as a king and a god and had complete control over the land. • Pharaoh Kufu is a well known ruler from this time period. • HS: Kufu built the Great Pyramid at Giza. ...
... LESSON 2: THE OLD KINGDOM • The Old Kingdom existed from 2700 BC to 2200 BC. • It was under the rule of the Pharaoh who was seen as a king and a god and had complete control over the land. • Pharaoh Kufu is a well known ruler from this time period. • HS: Kufu built the Great Pyramid at Giza. ...
Old Kingdom - Mr. Liotta
... himself king of Egypt in 1550 BC, he ushered in Egypt’s eighteenth dynasty and the start of the New Kingdom. Responding to invasions, Egypt took control of possible invasion routes by taking over areas such as Syria and Kush, and quickly became the leading military power in the region, with an empir ...
... himself king of Egypt in 1550 BC, he ushered in Egypt’s eighteenth dynasty and the start of the New Kingdom. Responding to invasions, Egypt took control of possible invasion routes by taking over areas such as Syria and Kush, and quickly became the leading military power in the region, with an empir ...
chapter 2 section 3
... Thutmose conquered more lands, and Egypt grew richer from tributes. Slavery became common in Thutmose’s reign. Slaves had some rights. They could own land, marry, and eventually obtain freedom. ...
... Thutmose conquered more lands, and Egypt grew richer from tributes. Slavery became common in Thutmose’s reign. Slaves had some rights. They could own land, marry, and eventually obtain freedom. ...
Chapter 3 - Ancient Egypt and Nubia MP
... “Hymn to the Nile” Lord of the fish, during the inundation, no bird alights on the crops. You create the grain, you bring forth the barley, assuring perpetuity to the temples. If you cease your toil and your work, then all that exists is in anguish. If the gods suffer in heaven, then the faces of m ...
... “Hymn to the Nile” Lord of the fish, during the inundation, no bird alights on the crops. You create the grain, you bring forth the barley, assuring perpetuity to the temples. If you cease your toil and your work, then all that exists is in anguish. If the gods suffer in heaven, then the faces of m ...
Class Notes: Chapter 3, Lesson 1
... Upper and Lower Egypt were two different kingdoms, each ruled by a different crown: Upper Egypt white crown, Lower Egypt - red crown. In 3100BC Menes, the Upper Egyptian King, swept into Lower Egypt and changed the course of Egyptian history. He united the two kingdoms. From then on, the kings of an ...
... Upper and Lower Egypt were two different kingdoms, each ruled by a different crown: Upper Egypt white crown, Lower Egypt - red crown. In 3100BC Menes, the Upper Egyptian King, swept into Lower Egypt and changed the course of Egyptian history. He united the two kingdoms. From then on, the kings of an ...
Chapter 4
... Merenptah was probably the last great king of the 19th Dynasty. His reign was followed by dynastic upheaval that led to the decline of the dynasty. ...
... Merenptah was probably the last great king of the 19th Dynasty. His reign was followed by dynastic upheaval that led to the decline of the dynasty. ...
Ancient Egypt - Harrisburg Academy
... • It is called this because the light of learning had gone out. ...
... • It is called this because the light of learning had gone out. ...
Ancient Egypt Study Guide
... 1. The Egyptian civilization lasted from __________ B.C.E to __________ C.E. 2. People settled in Egypt in particular locations due to ____________________________________. 3. Physical features are part of an area’s _______________________________. 4. Physical features include things such as ...
... 1. The Egyptian civilization lasted from __________ B.C.E to __________ C.E. 2. People settled in Egypt in particular locations due to ____________________________________. 3. Physical features are part of an area’s _______________________________. 4. Physical features include things such as ...
Trousdale County Schools Focused Lesson Plan 201516
... characteristics of Ancient Nubia ( the Kingdom of Kush) and their relationship to the social and economic characteristics of Ancient Egypt. ● 6.17 Develop a visual representation of the structure of Egyptian society including the role of the pharaoh as god/king, the concept of dynasties, the im ...
... characteristics of Ancient Nubia ( the Kingdom of Kush) and their relationship to the social and economic characteristics of Ancient Egypt. ● 6.17 Develop a visual representation of the structure of Egyptian society including the role of the pharaoh as god/king, the concept of dynasties, the im ...
Directions - Circle USD 375
... Kingdom. Write the letter of the sentence after the correct name at the bottom of the page. a) This ruler committed suicide to avoid surrendering to the Romans. b) She was the first woman pharaoh. c) This pharaoh believed the sun-god was the only god. d) This pharaoh built temples that were open to ...
... Kingdom. Write the letter of the sentence after the correct name at the bottom of the page. a) This ruler committed suicide to avoid surrendering to the Romans. b) She was the first woman pharaoh. c) This pharaoh believed the sun-god was the only god. d) This pharaoh built temples that were open to ...