Egyptians
... Removed the name of Amon-Re from all public inscriptions Said he was the only god Conflict over religion became struggle for power Priest of Amon-Re won the power struggle Contributed to the decline of Egyptian power ...
... Removed the name of Amon-Re from all public inscriptions Said he was the only god Conflict over religion became struggle for power Priest of Amon-Re won the power struggle Contributed to the decline of Egyptian power ...
Egypt: The Middle Kingdom
... gold and quarries that were dug for building projects. During the entire Middle Kingdom many building projects were conducted. Mentuhotep I built his mortuary temple at Deir el-Bahari. The 12th Dynasty re-established the pyramid building and every Pharaoh of that dynasty was buried in their own pyra ...
... gold and quarries that were dug for building projects. During the entire Middle Kingdom many building projects were conducted. Mentuhotep I built his mortuary temple at Deir el-Bahari. The 12th Dynasty re-established the pyramid building and every Pharaoh of that dynasty was buried in their own pyra ...
The Ancient Civilization of Egypt
... Egypt is located in North Africa The longest river in Africa goes through Egypt Egypt is hot , dry, arid most of the time It rains as little as two inches or less The ancient pyramids are located in Giza , Egypt The Great Sphinx are located in Giza, Egypt on the west ...
... Egypt is located in North Africa The longest river in Africa goes through Egypt Egypt is hot , dry, arid most of the time It rains as little as two inches or less The ancient pyramids are located in Giza , Egypt The Great Sphinx are located in Giza, Egypt on the west ...
6-2 Notes - WordPress.com
... (white crown) and Lower Egypt (red crown) • 3100 B.C.E. – Menes, king of Upper Egypt, overthrew the king of Lower Egypt • To show his victory, he wore a double crown (combining the red and white crowns) • Menes became the first pharaoh, or ruler of Egypt (the word actually means “great palace”) • Th ...
... (white crown) and Lower Egypt (red crown) • 3100 B.C.E. – Menes, king of Upper Egypt, overthrew the king of Lower Egypt • To show his victory, he wore a double crown (combining the red and white crowns) • Menes became the first pharaoh, or ruler of Egypt (the word actually means “great palace”) • Th ...
Egypt Review Key
... including the idea of a external straight ramp, an external spiral ramp, machines that could lift blocks up a layer at a time, and then the internal ramp idea. No one knows for sure how it was done. They were built mainly by peasant farmers during the times they could not work on their fields. Event ...
... including the idea of a external straight ramp, an external spiral ramp, machines that could lift blocks up a layer at a time, and then the internal ramp idea. No one knows for sure how it was done. They were built mainly by peasant farmers during the times they could not work on their fields. Event ...
File
... 7. How old was Tutankhamen when he died? 8. Who discovered Tutankhamen’s tomb? 9. What caused the Egyptian Empire to fall? 10. Who was the last pharaoh to rule Egypt? 11. Which empire took control of Egypt after Cleopatra’s rule? ...
... 7. How old was Tutankhamen when he died? 8. Who discovered Tutankhamen’s tomb? 9. What caused the Egyptian Empire to fall? 10. Who was the last pharaoh to rule Egypt? 11. Which empire took control of Egypt after Cleopatra’s rule? ...
The Egyptian Civilization
... – Invaded Nubia and SyriaPalestine. • Begins trading with… – Greece – Mesopotamia! • Invaded by Hyksos people in 1650 B.C. – They rule Egypt for 100 years. ...
... – Invaded Nubia and SyriaPalestine. • Begins trading with… – Greece – Mesopotamia! • Invaded by Hyksos people in 1650 B.C. – They rule Egypt for 100 years. ...
Ancient Egypt: The Rule of The God King
... Crops that grew in Mesopotamia arrive in the Nile Valley Nile River over floods its banks on a yearly basis depositing a rich silt Silt is the fertile topsoil carried by rivers and deposited on fields Nile River used as a transportation system because river flowed north and winds blew north to south ...
... Crops that grew in Mesopotamia arrive in the Nile Valley Nile River over floods its banks on a yearly basis depositing a rich silt Silt is the fertile topsoil carried by rivers and deposited on fields Nile River used as a transportation system because river flowed north and winds blew north to south ...
Unit 2a: Ancient Egypt - Pleasantville High School
... Natural barriers: Mediterranean Sea, Sahara Desert, Red Sea ...
... Natural barriers: Mediterranean Sea, Sahara Desert, Red Sea ...
classroom tutorials
... narrow there, only four miles across at its widest point. This area was known as Upper Egypt in ancient times. The area north of Cairo is much flatter and is almost at sea level. Here the river fans out and spreads over a maximum width of approximately 150 miles as it spills into the Mediterrenean S ...
... narrow there, only four miles across at its widest point. This area was known as Upper Egypt in ancient times. The area north of Cairo is much flatter and is almost at sea level. Here the river fans out and spreads over a maximum width of approximately 150 miles as it spills into the Mediterrenean S ...
Ancient Egypt - A Cultural Approach
... • directed productive efforts • maintained good relations with gods to assure prosperity and prevent natural disasters ...
... • directed productive efforts • maintained good relations with gods to assure prosperity and prevent natural disasters ...
Section Summary Key Terms and People Academic Vocabulary
... Much of Egyptian religion focused on the afterlife. Each person’s ka (KAH), or life force, existed after death but remained linked to the body. To keep the ka from suffering, the Egyptians developed a method called embalming to preserve bodies. The bodies were preserved as mummies, specially treated ...
... Much of Egyptian religion focused on the afterlife. Each person’s ka (KAH), or life force, existed after death but remained linked to the body. To keep the ka from suffering, the Egyptians developed a method called embalming to preserve bodies. The bodies were preserved as mummies, specially treated ...
Ancient Egypt
... fertile land located on either side of the Nile River. • The land was inundated (overwhelmed) with water during the annual floods. • When the inundation subsided, it left the earth soaked and overlaid with a fresh layer of black silt, which is why the area is referred to as “Black Land.” • This is w ...
... fertile land located on either side of the Nile River. • The land was inundated (overwhelmed) with water during the annual floods. • When the inundation subsided, it left the earth soaked and overlaid with a fresh layer of black silt, which is why the area is referred to as “Black Land.” • This is w ...
Slide 1 - Crest Ridge R-VII
... Thutmose III 4. Thutmose III became pharaoh after Hatshepsut’s death. He conquered more lands, and Egypt grew richer from tributes. ...
... Thutmose III 4. Thutmose III became pharaoh after Hatshepsut’s death. He conquered more lands, and Egypt grew richer from tributes. ...
Chapter 2, Section 2 Egypt`s Old Kingdom Vocabulary
... • Pyramids also contained items that pharaohs might need in afterlife. • Took thousands of people and years of labor to build. • Used astronomy and mathematics to create pyramids. ...
... • Pyramids also contained items that pharaohs might need in afterlife. • Took thousands of people and years of labor to build. • Used astronomy and mathematics to create pyramids. ...
Egypt PowerPoint
... Egyptian Symbolic Colors to Represent People Gender was represented by color as well as costume. It was a convention to portray men with reddish-brown skin and Women with yellow-tan color. Nubians and people from Africa were often colored darker than Egyptians. People from other nations might be sh ...
... Egyptian Symbolic Colors to Represent People Gender was represented by color as well as costume. It was a convention to portray men with reddish-brown skin and Women with yellow-tan color. Nubians and people from Africa were often colored darker than Egyptians. People from other nations might be sh ...
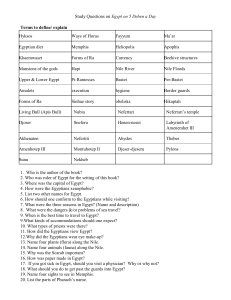
Study Questions on Egypt on 5 Deben a Day Terms to define
... 48. Name 10 Egyptian gods and what they were god/ goddess of. 49. Why is Aketaten a ghost town and abandoned? 50. What was different about Aten? 51. How did Akhenaten attempt to change Egypt? How long did it last? 52. What happened toTutankhamun’s tomb? 53. Why was Abydos so sacred to the Egyptians? ...
... 48. Name 10 Egyptian gods and what they were god/ goddess of. 49. Why is Aketaten a ghost town and abandoned? 50. What was different about Aten? 51. How did Akhenaten attempt to change Egypt? How long did it last? 52. What happened toTutankhamun’s tomb? 53. Why was Abydos so sacred to the Egyptians? ...
egyptian civilization
... Some ideas of Mesopotamia in the early development of cities were borrowed by the Egyptians. System of writing is an example. (Sumer: Cuneiform) However, Mesopotamian influence over the Egyptians didn’t last long. ...
... Some ideas of Mesopotamia in the early development of cities were borrowed by the Egyptians. System of writing is an example. (Sumer: Cuneiform) However, Mesopotamian influence over the Egyptians didn’t last long. ...
IV. Egyptian Mathematics
... Aha. He united the two kingdoms in about 3100 B.C.E. This military victory is documented for us in the Narmer palette. The early pharaohs were buried in the ancient city of Abydos, in upper Egypt. There are inscriptions on ivory and wood in these pre-pyramidal tombs known as mastabas, which contain ...
... Aha. He united the two kingdoms in about 3100 B.C.E. This military victory is documented for us in the Narmer palette. The early pharaohs were buried in the ancient city of Abydos, in upper Egypt. There are inscriptions on ivory and wood in these pre-pyramidal tombs known as mastabas, which contain ...
Egypt Notes
... Ramp theory – gradually sloping ramps Stones pulled up ramps by laborers Blocks made of limestone and granite ...
... Ramp theory – gradually sloping ramps Stones pulled up ramps by laborers Blocks made of limestone and granite ...
First Age of Empires - Elizabeth School District C-1
... Had a genuine respect for other cultures and practiced tolerance of local customs ...
... Had a genuine respect for other cultures and practiced tolerance of local customs ...
The Ancient Egyptians
... which flows through North Africa. Water form the Nile and a warm climate aided the development of agriculture. The surrounding deserts kept most attackers away. Because the people along the river did not have to worry about getting food or fighting enemies, they had the time and energy to develop on ...
... which flows through North Africa. Water form the Nile and a warm climate aided the development of agriculture. The surrounding deserts kept most attackers away. Because the people along the river did not have to worry about getting food or fighting enemies, they had the time and energy to develop on ...
Answer Key - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... - Collected taxes, but pyramids were still too costly - Pharaoh began to lose authority to nobles, who gained more authority over nomes (provinces) - Crops failed and people suffered. II.Middle Kingdom (Age of the Nobles) • 2100-1788 B.C. • A noble named Amenemhet I became pharaoh • He gave power ba ...
... - Collected taxes, but pyramids were still too costly - Pharaoh began to lose authority to nobles, who gained more authority over nomes (provinces) - Crops failed and people suffered. II.Middle Kingdom (Age of the Nobles) • 2100-1788 B.C. • A noble named Amenemhet I became pharaoh • He gave power ba ...
Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs
... – Egypt’s Golden Age; increased trade during this time of peace and stability ...
... – Egypt’s Golden Age; increased trade during this time of peace and stability ...